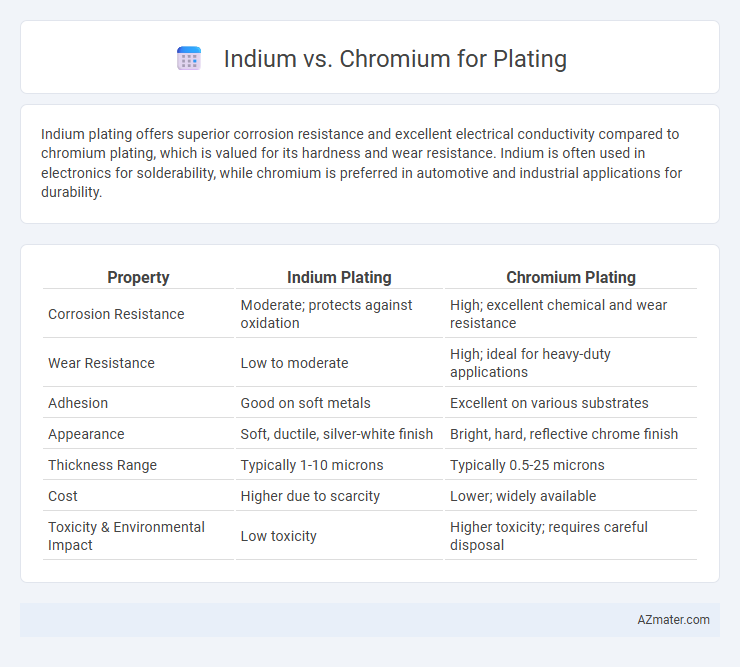
Indium plating offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity compared to chromium plating, which is valued for its hardness and wear resistance. Indium is often used in electronics for solderability, while chromium is preferred in automotive and industrial applications for durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Indium Plating | Chromium Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate; protects against oxidation | High; excellent chemical and wear resistance |
| Wear Resistance | Low to moderate | High; ideal for heavy-duty applications |
| Adhesion | Good on soft metals | Excellent on various substrates |
| Appearance | Soft, ductile, silver-white finish | Bright, hard, reflective chrome finish |
| Thickness Range | Typically 1-10 microns | Typically 0.5-25 microns |
| Cost | Higher due to scarcity | Lower; widely available |
| Toxicity & Environmental Impact | Low toxicity | Higher toxicity; requires careful disposal |
Introduction to Indium and Chromium Plating
Indium plating provides excellent corrosion resistance and superior solderability, making it ideal for electronic and aerospace applications. Chromium plating is widely recognized for its hardness, wear resistance, and attractive, mirror-like finish, commonly used in automotive and decorative industries. Both metals enhance surface properties but serve distinct functional purposes based on their unique physical and chemical characteristics.
Chemical Properties: Indium vs Chromium
Indium exhibits a lower melting point (156.6degC) and higher malleability compared to chromium, which has a melting point of 1907degC and exceptional hardness, making chromium ideal for durable plating. Chemically, indium resists corrosion in mild acids and alkalis but oxidizes easily, whereas chromium forms a stable, inert oxide layer that enhances corrosion resistance and wear durability. The distinct chemical stability and mechanical properties of chromium make it preferable for plating applications requiring hardness and longevity, while indium's softness suits specialized uses needing malleability.
Plating Process Differences
Indium plating involves a low-temperature process typically performed through electroplating or electroless methods, providing excellent corrosion resistance and softness ideal for solderability and electrical contacts. Chromium plating requires higher temperature and voltage settings, often using hexavalent or trivalent chromium baths, resulting in a hard, wear-resistant, and decorative finish. The plating thickness and adhesion properties differ significantly, with indium forming a thin, ductile layer and chromium offering a thicker, rigid coating suited for heavy-duty applications.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Indium plating provides excellent corrosion resistance by forming a stable, protective oxide layer that prevents oxidation in harsh environments, especially against acidic and saline conditions. Chromium plating offers superior hardness and durability, with a high resistance to wear and corrosion, particularly effective in automotive and industrial applications exposed to moisture and chemicals. Indium excels in specialized electronic and medical uses due to its corrosion resistance combined with conductivity, while chromium is preferred for heavy-duty coatings demanding robust protection against rust and corrosion.
Wear and Durability Factors
Indium plating offers superior wear resistance due to its softness and ability to form a self-healing oxide layer, reducing friction and surface degradation in low-load applications. Chromium plating provides exceptional hardness and durability, making it ideal for high-wear environments requiring robust abrasion and corrosion resistance. Both metals serve distinct roles in plating, with indium excelling in electrical contacts and chromium preferred for heavy-duty mechanical parts.
Surface Finish and Aesthetics
Indium plating offers a bright, silver-white surface finish with excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for decorative and electronic applications requiring a smooth, reflective appearance. Chromium plating provides a highly durable, mirror-like finish with superior hardness and wear resistance, often used in automotive and industrial parts for both aesthetic appeal and protective surface properties. While indium excels in softness and conductivity, chromium is preferred for its long-lasting luster and robustness in harsh environments.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Indium plating typically incurs higher material costs due to the metal's rarity and lower availability compared to chromium, making it less economically viable for large-scale applications. Chromium plating offers a cost-effective solution with abundant supply and well-established industrial processes, resulting in lower overall production expenses. The economic viability of indium plating is generally justified only in niche applications requiring its unique properties, whereas chromium remains the preferred choice for budget-sensitive, high-volume plating projects.
Environmental and Safety Impacts
Indium plating generally presents lower environmental and safety concerns than chromium plating, as indium is less toxic and poses minimal risk of harmful airborne emissions. Chromium plating, especially hexavalent chromium, is highly toxic, carcinogenic, and requires stringent handling protocols and waste treatment to prevent environmental contamination. Regulatory agencies often impose strict limits on chromium plating processes to mitigate health hazards and reduce ecological damage, making indium a safer alternative for environmentally conscious applications.
Common Applications for Indium and Chromium Plating
Indium plating is commonly used in electronics for its excellent solderability, corrosion resistance, and conductivity, making it ideal for semiconductor components and connectors. Chromium plating is widely applied in automotive, industrial machinery, and decorative applications due to its hardness, wear resistance, and bright, reflective finish. Indium suits specialized electronics applications, while chromium excels in high-wear and aesthetic surfaces requiring durability and corrosion protection.
Choosing the Right Plating Material
Indium provides excellent corrosion resistance and superior ductility, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility and durability in harsh environments. Chromium offers outstanding hardness and wear resistance, commonly used for decorative finishes and industrial tooling that demands a tough surface. Selecting between indium and chromium plating depends on the specific performance requirements, including conductivity, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength of the final product.
Infographic: Indium vs Chromium for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com