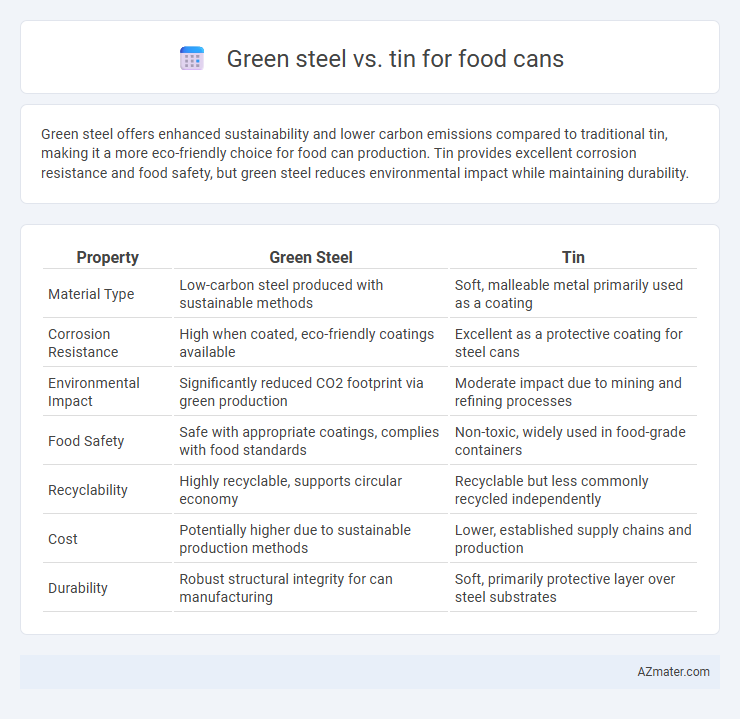
Green steel offers enhanced sustainability and lower carbon emissions compared to traditional tin, making it a more eco-friendly choice for food can production. Tin provides excellent corrosion resistance and food safety, but green steel reduces environmental impact while maintaining durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Green Steel | Tin |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Low-carbon steel produced with sustainable methods | Soft, malleable metal primarily used as a coating |
| Corrosion Resistance | High when coated, eco-friendly coatings available | Excellent as a protective coating for steel cans |
| Environmental Impact | Significantly reduced CO2 footprint via green production | Moderate impact due to mining and refining processes |
| Food Safety | Safe with appropriate coatings, complies with food standards | Non-toxic, widely used in food-grade containers |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable, supports circular economy | Recyclable but less commonly recycled independently |
| Cost | Potentially higher due to sustainable production methods | Lower, established supply chains and production |
| Durability | Robust structural integrity for can manufacturing | Soft, primarily protective layer over steel substrates |
Introduction to Green Steel and Tin in Food Canning
Green steel, produced through low-carbon methods using hydrogen or electric arc furnaces, offers an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional steel in food canning. Tin, a traditional coating applied to steel cans, provides corrosion resistance and preserves the taste and quality of canned food. Combining green steel with tin coatings supports sustainable packaging while maintaining the protective qualities essential for food safety.
Environmental Impact: Green Steel vs Tin
Green steel significantly reduces carbon emissions compared to traditional steel and tin used in food cans, leveraging hydrogen-based production instead of coal. Tin, although recyclable, involves energy-intensive mining and smelting processes that contribute to pollution and habitat disruption. The shift to green steel in food can manufacturing offers a lower environmental footprint by minimizing greenhouse gases and promoting sustainable resource use.
Material Composition and Production Processes
Green steel, produced using hydrogen-based direct reduction or electric arc furnaces powered by renewable energy, contains primarily iron with minimal carbon emissions during production. Tin, a naturally occurring metal, is primarily extracted and refined through smelting processes involving tin ore concentration and roasting, followed by electrolysis or chemical reduction to achieve high purity. The material composition of green steel offers superior structural strength and recyclability, while tin provides excellent corrosion resistance and food safety as a coating for steel cans.
Sustainability and Carbon Footprint Comparison
Green steel, produced using hydrogen reduction or electric arc furnace methods, significantly lowers carbon emissions compared to traditional steel, making it a more sustainable choice for food cans. Tin, primarily used as a coating for steel cans, has a lower environmental impact during processing but does not reduce the steel's inherent carbon footprint. Using green steel as the base material combined with tin coating optimizes both durability and sustainability by minimizing overall greenhouse gas emissions in the lifecycle of food packaging.
Food Safety and Preservation Qualities
Green steel offers superior food safety and preservation qualities compared to tin, as it is often coated with food-grade coatings that resist corrosion and prevent metal leaching into food. Tin cans, while historically popular, may react with acidic foods, potentially compromising taste and safety over time. Advances in green steel technology ensure longer shelf life and enhanced protection against contamination, making it a preferred choice for sustainable and safe food packaging.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Green steel offers significant cost efficiency in food cans due to its lower production energy requirements and reduced carbon taxes compared to traditional tin, making it an economically attractive alternative. While tin remains widely available with a well-established supply chain ensuring consistency, green steel's market availability is rapidly increasing as more manufacturers adopt environmentally friendly materials. The balance between green steel's sustainable cost benefits and tin's entrenched market presence is driving innovation in food can production and supplier strategies.
Recycling and End-of-Life Scenarios
Green steel offers superior recyclability compared to tin in food cans, as it can be recycled repeatedly without losing quality, reducing the need for virgin raw materials and lowering carbon emissions. Tin-plated steel cans, while recyclable, require complex processes to separate the tin coating, which can hinder recycling efficiency and increase contamination risks. End-of-life scenarios favor green steel due to its alignment with circular economy principles, promoting sustainable resource use and minimizing landfill waste in food packaging.
Technological Innovations in Green Steel and Tin
Technological innovations in green steel focus on hydrogen-based direct reduction processes, which significantly lower carbon emissions compared to traditional blast furnace methods, making steel more sustainable for food can production. Tin, traditionally used as a protective coating in food cans, has seen advancements in nano-coating technologies that enhance corrosion resistance and food safety without relying on toxic additives. These innovations provide environmentally friendly solutions that maintain packaging integrity and extend shelf life, addressing both ecological and health concerns in the food industry.
Industry Adoption and Consumer Perception
Green steel adoption in the food can industry is rapidly increasing due to its lower carbon footprint and enhanced sustainability credentials compared to traditional tin-plated steel. Major manufacturers are integrating green steel into their supply chains to meet regulatory standards and appeal to eco-conscious consumers demanding environmentally responsible packaging. Consumer perception favors green steel cans as they symbolize innovation and commitment to reducing environmental impact, driving market differentiation and brand loyalty.
Future Prospects: The Evolution of Food Can Materials
Green steel, produced with reduced carbon emissions, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional tin for food can manufacturing, promising significant environmental benefits. Future prospects highlight advances in eco-friendly steelmaking processes that enhance recyclability and durability while maintaining food safety standards. Ongoing innovation in green steel technology is expected to revolutionize packaging by reducing the carbon footprint and supporting circular economy practices.
Infographic: Green steel vs Tin for Food can
 azmater.com
azmater.com