Copper plumbing pipes offer superior corrosion resistance, antimicrobial properties, and excellent thermal conductivity compared to steel pipes, which are more prone to rust and scale buildup. Steel pipes provide higher strength and durability for high-pressure applications but require protective coatings to prevent corrosion.
Table of Comparison
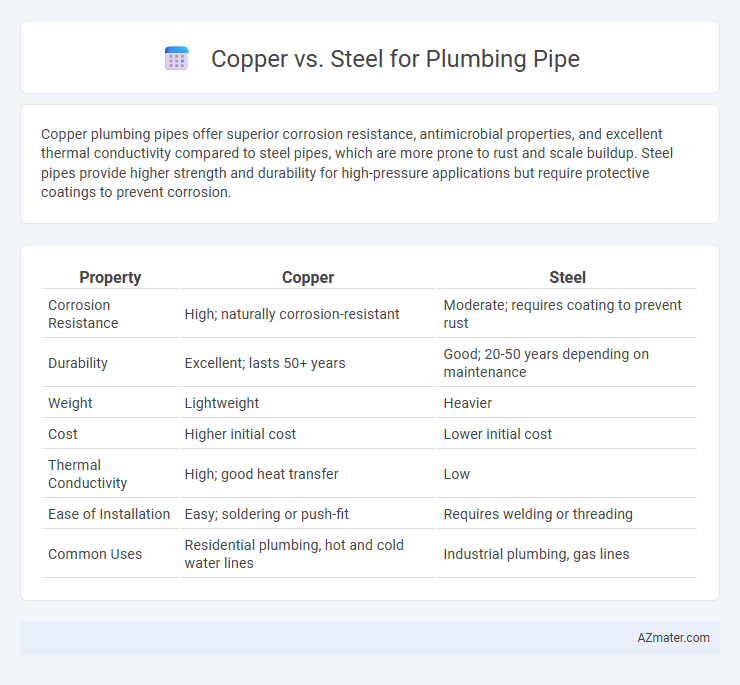
| Property | Copper | Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High; naturally corrosion-resistant | Moderate; requires coating to prevent rust |
| Durability | Excellent; lasts 50+ years | Good; 20-50 years depending on maintenance |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Thermal Conductivity | High; good heat transfer | Low |
| Ease of Installation | Easy; soldering or push-fit | Requires welding or threading |
| Common Uses | Residential plumbing, hot and cold water lines | Industrial plumbing, gas lines |
Introduction to Copper and Steel Plumbing Pipes
Copper plumbing pipes offer excellent corrosion resistance, durability, and natural antimicrobial properties, making them a popular choice for residential water supply systems. Steel pipes, available as galvanized or stainless steel, provide superior strength and are often used in high-pressure or industrial applications but may require protective coatings to prevent rust. Both materials have distinct advantages depending on factors such as water quality, installation environment, and budget constraints.
Material Composition and Properties
Copper plumbing pipes are composed primarily of copper, a metal known for its high thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and natural antimicrobial properties, making it ideal for potable water systems. Steel pipes, typically made from carbon steel or galvanized steel, offer superior tensile strength and durability but are prone to corrosion without proper coatings or treatments. The material composition of copper provides excellent resistance to scale buildup and biological growth, whereas steel pipes require additional maintenance to prevent rust and degradation over time.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Copper pipes offer superior durability with a typical lifespan of 50 to 70 years due to their resistance to corrosion and high temperatures. Steel pipes, particularly galvanized steel, generally last 20 to 50 years but are prone to rust and corrosion over time, which can compromise water quality and pipe integrity. The greater corrosion resistance and longevity of copper make it a preferred choice for long-term plumbing infrastructure.
Cost Analysis: Copper vs Steel Pipes
Copper pipes generally have a higher upfront cost compared to steel pipes, with prices influenced by fluctuating metal markets and manufacturing expenses. Steel pipes, specifically galvanized steel, tend to be more affordable but may incur higher maintenance costs over time due to corrosion and potential leak repairs. When evaluating long-term expenses, copper offers greater durability and lower maintenance, often resulting in better overall cost efficiency despite the initial investment.
Corrosion Resistance and Maintenance
Copper plumbing pipes exhibit superior corrosion resistance due to their natural ability to form a protective oxide layer that prevents rust, ensuring longevity and minimal maintenance. Steel pipes, particularly galvanized varieties, are prone to rust and corrosion over time, necessitating frequent inspections and potential replacements. Low maintenance requirements and resistance to chemical reactions make copper the preferred choice for plumbing systems in environments with varying water pH levels.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Copper plumbing pipes require soldering or compression fittings during installation, demanding skilled labor and specialized equipment, which can increase installation time and costs. Steel pipes, especially galvanized steel, often require threading or welding, making the process more labor-intensive and less adaptable for quick modifications. Copper's inherent flexibility allows easier bending and fitting in tight spaces, reducing the need for additional joints, whereas steel pipes are rigid and necessitate multiple fittings to navigate corners or obstacles.
Water Quality Impact and Safety
Copper pipes offer superior antimicrobial properties that inhibit bacterial growth, enhancing water quality by maintaining purity and reducing the risk of contamination. Steel pipes, particularly galvanized steel, are prone to corrosion and rust, which can leach iron and other metals into water, negatively affecting taste, color, and safety. Copper's durability and resistance to biofilm formation contribute to safer, cleaner plumbing systems, making it a preferred choice for potable water applications.
Applications: Residential vs Commercial Use
Copper pipes excel in residential plumbing due to their corrosion resistance, durability, and ability to withstand high temperatures, making them ideal for water supply lines and heating systems. Steel pipes, especially galvanized or stainless steel, are favored in commercial plumbing for their superior strength and pressure tolerance, suitable for large-scale water distribution and industrial applications. While copper provides better longevity in typical home environments, steel's robustness supports heavy-duty commercial infrastructure requiring high mechanical performance.
Environmental Considerations and Recyclability
Copper plumbing pipes offer superior recyclability with a recovery rate of nearly 90%, significantly reducing mining waste and energy consumption associated with raw material extraction. Steel pipes, while also recyclable, typically have a lower recycling rate and require more energy-intensive processing, contributing to higher carbon emissions. Choosing copper over steel can lead to a smaller environmental footprint due to copper's natural antimicrobial properties, durability, and efficient recyclability in plumbing applications.
Choosing the Right Pipe: Key Factors to Consider
Copper pipes offer excellent corrosion resistance and durability, making them ideal for potable water systems and longevity in plumbing installations. Steel pipes, particularly galvanized steel, provide superior strength and pressure tolerance, suited for industrial applications or exterior plumbing exposed to mechanical stress. Consider factors such as water quality, installation environment, cost, and maintenance requirements when choosing between copper and steel plumbing pipes to ensure optimal performance and lifespan.
Infographic: Copper vs Steel for Plumbing Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com