Steel offers superior durability and corrosion resistance for musical instruments, making it ideal for strings and structural components. Brass provides warm tonal qualities and excellent malleability, commonly used in wind instruments and decorative elements.
Table of Comparison
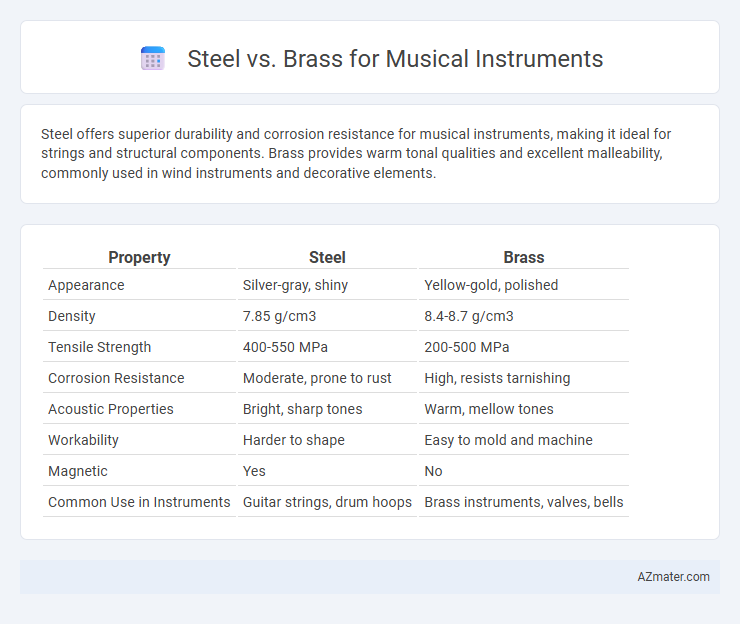
| Property | Steel | Brass |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Silver-gray, shiny | Yellow-gold, polished |
| Density | 7.85 g/cm3 | 8.4-8.7 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 400-550 MPa | 200-500 MPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, prone to rust | High, resists tarnishing |
| Acoustic Properties | Bright, sharp tones | Warm, mellow tones |
| Workability | Harder to shape | Easy to mold and machine |
| Magnetic | Yes | No |
| Common Use in Instruments | Guitar strings, drum hoops | Brass instruments, valves, bells |
Introduction: Comparing Steel and Brass in Musical Instruments
Steel and brass are fundamental materials in musical instrument construction, each impacting sound quality and durability. Steel offers high tensile strength and resistance to wear, producing a bright, resonant tone favored in strings and percussion. Brass, known for its malleability and warm, rich timbre, is commonly used in wind instruments like trumpets and saxophones.
Sound Characteristics: Tone and Resonance Differences
Steel produces a bright, clear tone with strong projection and sharp attack, making it ideal for instruments requiring vibrant sound clarity such as guitars and pianos. Brass offers a warmer, richer resonance with a mellower timbre, enhancing instruments like trumpets and saxophones by providing smooth, rounded sound qualities. The distinct density and elasticity of steel versus brass directly influence vibration patterns, resulting in their characteristic tonal differences and resonance behaviors.
Durability and Longevity of Steel vs Brass
Steel offers superior durability and resistance to corrosion compared to brass, making it ideal for musical instruments exposed to frequent handling and varying environmental conditions. Brass, while softer and more prone to denting and tarnishing, provides a warmer tonal quality but requires regular maintenance to preserve its longevity. Instruments crafted with stainless steel components tend to maintain structural integrity longer, reducing the need for repairs and replacements over time.
Weight and Handling: Player Comfort
Steel musical instruments typically weigh more than brass counterparts, which can impact player comfort during extended performances. Brass instruments offer a lighter feel and greater ease of handling, reducing fatigue and allowing for better agility. The choice between steel and brass ultimately affects the musician's endurance and control, with brass favored for its ergonomic advantages.
Maintenance and Corrosion Resistance
Steel offers superior durability but requires regular maintenance to prevent rust and corrosion, especially in humid environments, making it less ideal for instruments exposed to moisture. Brass, favored for its natural corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning, develops a protective patina over time that enhances its longevity with minimal upkeep. Choosing between steel and brass depends on balancing maintenance efforts with desired sound quality, as brass also tends to resist tarnishing better in everyday use.
Cost and Availability in Instrument Manufacturing
Steel offers a lower cost and greater availability compared to brass, making it a popular choice in mass-produced musical instruments such as guitar strings and drum hardware. Brass, though more expensive due to its alloy composition of copper and zinc, is valued for its acoustic properties and is commonly used in higher-end wind instruments and decorative fittings. Manufacturers often balance budget constraints with desired tonal qualities, leading to steel's dominance in affordable, widely accessible instruments while brass remains preferred for premium craftsmanship.
Application in Different Musical Instruments
Steel is commonly used in guitar strings and piano wires due to its high tensile strength and bright tonal quality, producing clear, sustained sounds ideal for string instruments. Brass, with its malleability and warm, rich tonal properties, is preferred for wind instruments such as trumpets, trombones, and French horns, enhancing their resonant and mellow sound. The choice between steel and brass significantly influences the timbre and playability of musical instruments across diverse applications.
Influence on Playability and Technique
Steel strings offer higher tension and brightness, enhancing articulation and dynamic control for advanced techniques like fingerpicking and bending. Brass strings produce a warmer, mellower tone with moderate tension, facilitating smoother slides and easier finger vibrato, benefiting beginners and players seeking a softer touch. The choice between steel and brass influences tactile feedback and tonal clarity, directly affecting playability and technique expression.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Steel and brass differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability when used in musical instruments. Steel production typically involves higher carbon emissions due to fossil fuel-intensive processes, whereas brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, relies on metals that can be more challenging to recycle efficiently and often involves mining practices with substantial ecological footprints. Choosing sustainable brass or recycled steel materials can help reduce environmental harm, promoting eco-friendly manufacturing in the musical instrument industry.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Musical Needs
Steel offers durability and brightness, making it ideal for instruments requiring strong projection and resistance to wear. Brass provides a warmer tone and greater malleability, preferred for instruments emphasizing rich, mellow sounds and intricate craftsmanship. Selecting between steel and brass depends on desired sound quality, instrument type, and playing style for optimal musical performance.
Infographic: Steel vs Brass for Musical Instrument
 azmater.com
azmater.com