Cobalt plating offers superior hardness, corrosion resistance, and wear durability compared to zinc plating, making it ideal for high-performance industrial applications. Zinc plating provides effective corrosion protection at a lower cost, commonly used for automotive and construction parts requiring moderate durability.
Table of Comparison
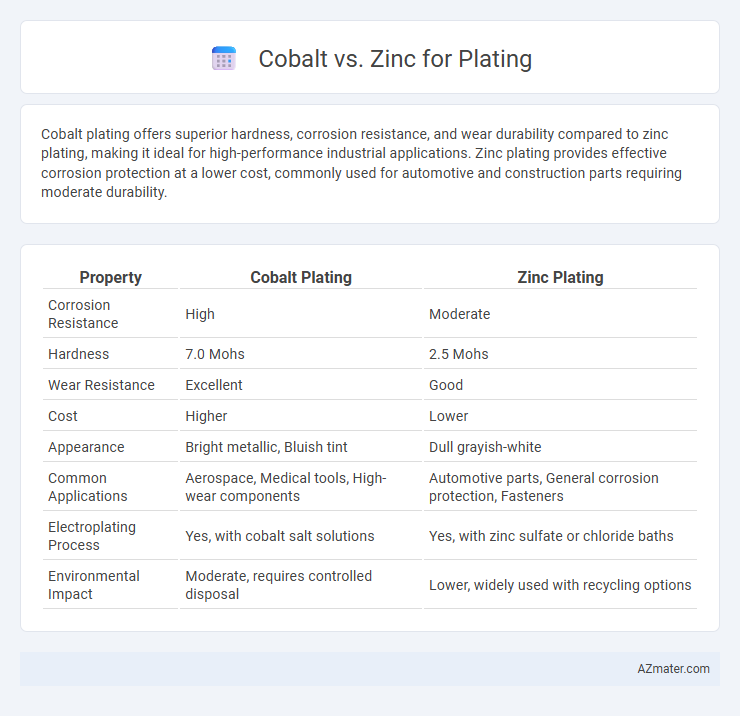
| Property | Cobalt Plating | Zinc Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Hardness | 7.0 Mohs | 2.5 Mohs |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Appearance | Bright metallic, Bluish tint | Dull grayish-white |
| Common Applications | Aerospace, Medical tools, High-wear components | Automotive parts, General corrosion protection, Fasteners |
| Electroplating Process | Yes, with cobalt salt solutions | Yes, with zinc sulfate or chloride baths |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate, requires controlled disposal | Lower, widely used with recycling options |
Introduction to Metal Plating: Cobalt vs Zinc
Cobalt and zinc are widely used metals in plating processes due to their distinct protective and aesthetic properties. Cobalt plating offers superior hardness, corrosion resistance, and wear durability, making it ideal for industrial tools and high-performance components. Zinc plating is favored for its excellent rust prevention and cost-effectiveness, commonly applied in automotive parts and fasteners for enhanced longevity.
Chemical Properties of Cobalt and Zinc
Cobalt, a transition metal with atomic number 27, exhibits excellent corrosion resistance and magnetic properties due to its stable +2 and +3 oxidation states, making it highly effective for protective and decorative plating. Zinc, atomic number 30, primarily forms a +2 oxidation state and provides superior sacrificial anode properties, offering robust corrosion protection by preferentially oxidizing in galvanic cells. Both metals display distinct electrochemical behaviors where cobalt's resistance to oxidation complements zinc's galvanic protection in various plating applications.
Plating Process Overview: Cobalt vs Zinc
Cobalt plating offers superior hardness, corrosion resistance, and enhanced wear properties compared to zinc plating, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Zinc plating provides effective corrosion protection through sacrificial coating, is cost-efficient, and commonly used for automotive and construction industries. Both processes involve electrochemical deposition, but cobalt requires precise current control and temperature regulation to ensure uniform coatings.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Cobalt plating offers superior corrosion resistance compared to zinc, especially in harsh environments with exposure to acids or saltwater, due to its dense and stable oxide layer. Zinc plating is effective for protecting steel by sacrificially corroding first, but it tends to degrade faster under aggressive conditions without additional coatings. For long-term durability against rust and chemical wear, cobalt plating provides enhanced protection and maintains surface integrity more effectively than zinc.
Surface Finish and Appearance Differences
Cobalt plating offers a bright, hard, and wear-resistant surface with a slightly bluish metallic sheen, enhancing corrosion resistance and providing a visually striking finish. Zinc plating provides a duller, matte silver appearance with moderate corrosion protection, often requiring additional topcoats to improve aesthetic appeal and durability. Differences in surface finish between cobalt and zinc plating are critical for applications demanding both functional protection and high-quality visual presentation.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Cobalt offers superior durability and wear resistance compared to zinc, making it ideal for high-friction and heavy-duty applications. Zinc plating provides good corrosion protection but tends to wear off faster under mechanical stress. The hardness of cobalt coatings significantly enhances surface longevity and resistance to abrasion.
Cost Analysis: Cobalt vs Zinc Plating
Cobalt plating generally incurs higher costs due to the metal's rarity and complex processing requirements, whereas zinc plating offers a more economical alternative with widespread availability and simpler application methods. The price difference significantly impacts large-scale industrial use, where zinc plating's affordability drives its preference for corrosion resistance. Cost efficiency in zinc plating is further enhanced by lower material consumption and reduced energy expenditure compared to cobalt plating.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Cobalt plating poses significant environmental concerns due to its toxicity and the challenges in waste disposal, often requiring strict regulatory controls to prevent soil and water contamination. Zinc plating generally offers a more environmentally friendly alternative, as zinc is less toxic and its coatings facilitate corrosion resistance with lower ecological risks. Safety protocols for cobalt involve handling hazardous chemicals and protective equipment, whereas zinc plating processes demand fewer precautions, making zinc a safer option in industrial applications.
Typical Applications for Cobalt and Zinc Plating
Cobalt plating is commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries due to its excellent corrosion resistance, hardness, and wear protection, especially for turbine blades, engine components, and surgical instruments. Zinc plating is widely applied in automotive, construction, and electronics sectors for corrosion protection of steel parts, including fasteners, bolts, and electrical connectors, benefiting from its cost-effectiveness and sacrificial protection properties. Both metals enhance surface durability but are selected based on specific environmental and mechanical requirements of the application.
Choosing the Right Metal: Key Considerations
Selecting between cobalt and zinc for plating involves assessing corrosion resistance, adhesion properties, and application environment. Cobalt offers superior hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for high-friction components, while zinc provides excellent corrosion protection through sacrificial coating, especially in automotive or outdoor applications. Cost-effectiveness and desired finish appearance also play crucial roles in determining the optimal metal for plating projects.
Infographic: Cobalt vs Zinc for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com