Ruthenium enhances pyrotechnic formulations by improving oxidation resistance and catalytic activity, while Strontium is primarily used for producing vivid red flames and enhancing color brightness. Ruthenium's rarity and cost limit its use compared to the more abundant and color-specific Strontium in pyrotechnic applications.
Table of Comparison
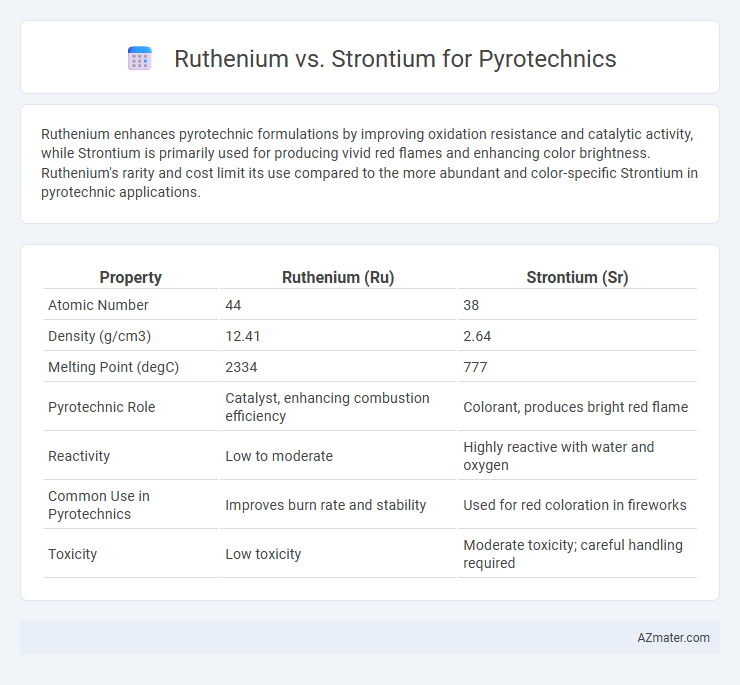
| Property | Ruthenium (Ru) | Strontium (Sr) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 44 | 38 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 12.41 | 2.64 |
| Melting Point (degC) | 2334 | 777 |
| Pyrotechnic Role | Catalyst, enhancing combustion efficiency | Colorant, produces bright red flame |
| Reactivity | Low to moderate | Highly reactive with water and oxygen |
| Common Use in Pyrotechnics | Improves burn rate and stability | Used for red coloration in fireworks |
| Toxicity | Low toxicity | Moderate toxicity; careful handling required |
Introduction to Ruthenium and Strontium in Pyrotechnics
Ruthenium is a rare transition metal known for its catalytic properties and is rarely used directly in pyrotechnics but can enhance color stability and burn rates in specialized formulations. Strontium, predominantly found in strontium nitrate and strontium carbonate, is widely utilized in pyrotechnics for producing vibrant red flames and improving combustion efficiency. The contrast lies in strontium's prominent role in coloration and ignition versus ruthenium's niche applications in enhancing reaction kinetics within pyrotechnic mixtures.
Chemical Properties Relevant to Pyrotechnics
Ruthenium exhibits exceptional catalytic properties and high thermal stability, making it valuable in pyrotechnic compositions that require controlled ignition and sustained burning rates. Strontium is renowned for its vivid red flame coloration and oxidizing ability, essential for producing bright, stable flames in fireworks and signal flares. The chemical inertness of ruthenium under pyrotechnic conditions contrasts with strontium's active role in color generation, influencing their distinct applications in enhancing pyrotechnic performance.
Color Effects: Ruthenium vs Strontium Compounds
Ruthenium compounds produce subtle, often metallic or grayish hues that enhance spark and flare effects in pyrotechnics, while strontium compounds are renowned for their vivid red color emissions, making them a staple for bright red flames. Strontium salts, like strontium nitrate or strontium carbonate, are highly efficient at producing intense, stable red colors due to their strong emission in the red spectrum around 606 nm. In contrast, ruthenium's use is more specialized for augmenting brightness and texture rather than serving as a primary colorant, resulting in limited color impact compared to the bold and vibrant effects achieved with strontium compounds.
Reaction Stability and Safety Considerations
Ruthenium compounds in pyrotechnics offer enhanced reaction stability due to their high thermal resistance and controlled oxidation states, reducing the risk of unintended ignition. Strontium-based compositions, commonly used for red coloration, are relatively stable but can pose safety concerns related to moisture sensitivity and potential toxic byproducts upon combustion. Prioritizing ruthenium in formulations improves safety by minimizing volatile reaction pathways, whereas careful handling and precise formulation adjustments are critical when using strontium to avoid hazardous decomposition.
Availability and Cost Comparison
Ruthenium is a rare platinum-group metal with limited availability, making it significantly more expensive than strontium, which is relatively abundant and readily sourced from common mineral deposits. The high cost of ruthenium restricts its widespread use in pyrotechnics, whereas strontium's affordability and abundance make it a popular choice for producing vibrant red flames. Strontium compounds, such as strontium nitrate and strontium carbonate, provide cost-effective colorants compared to the scarce and costly ruthenium-based materials.
Environmental Impact of Ruthenium and Strontium
Ruthenium in pyrotechnics offers a lower environmental impact due to its relatively inert chemical nature and reduced toxicity compared to strontium compounds, which are known for releasing strontium ions that may contribute to soil and water contamination. Strontium-based pyrotechnic formulations often produce harmful strontium salts, which pose ecological risks and potential human health hazards through bioaccumulation and groundwater pollution. Choosing ruthenium over strontium can therefore enhance environmental safety by minimizing toxic residue and reducing long-term ecological exposure.
Performance and Burn Characteristics in Fireworks
Ruthenium and Strontium differ significantly in pyrotechnic performance and burn characteristics; Ruthenium, often employed as a catalyst, enhances burn stability and ignition sensitivity, while Strontium primarily functions as a red colorant producing vibrant red flames with moderate burn rates. Ruthenium's catalytic properties contribute to more controlled and sustained combustion, optimizing reaction efficiency in complex compositions. Strontium compounds exhibit strong oxidizing behavior that influences flame temperature and duration, making them essential for coloration but less effective in modifying burn velocity compared to Ruthenium.
Compatibility with Other Pyrotechnic Materials
Ruthenium exhibits excellent compatibility with a wide range of pyrotechnic materials, including oxidizers like potassium perchlorate and reducers such as aluminum powder, ensuring stable combustion and vibrant color output. Strontium, commonly used for its intense red flame, pairs effectively with chlorates and nitrates but can be sensitive to moisture and may react adversely with strong reducers if not properly formulated. Careful consideration of these compatibility factors is crucial for optimizing performance and safety in pyrotechnic compositions.
Applications: Unique Uses in Fireworks Displays
Ruthenium is rarely used in pyrotechnics due to its high cost and rare availability, while strontium is a prominent element in fireworks displays for its ability to produce vibrant red colors. Strontium compounds, especially strontium nitrate and strontium carbonate, are crucial in creating intense red flames and spark effects, making them essential in both consumer and professional fireworks. Ruthenium's primary pyrotechnic interest lies in its catalytic properties for ignition processes rather than direct color production.
Future Trends: Innovations with Ruthenium and Strontium
Emerging trends in pyrotechnics highlight Ruthenium's potential for enhancing catalyst efficiency and flame color modulation, offering more sustainable and vibrant displays. Strontium remains the key element for producing intense red hues, with innovations focusing on combining it with rare-earth elements to improve stability and brightness. Future research is prioritizing hybrid compounds of Ruthenium and Strontium to create safer, environmentally friendly pyrotechnic formulations with enhanced performance characteristics.
Infographic: Ruthenium vs Strontium for Pyrotechnic
 azmater.com
azmater.com