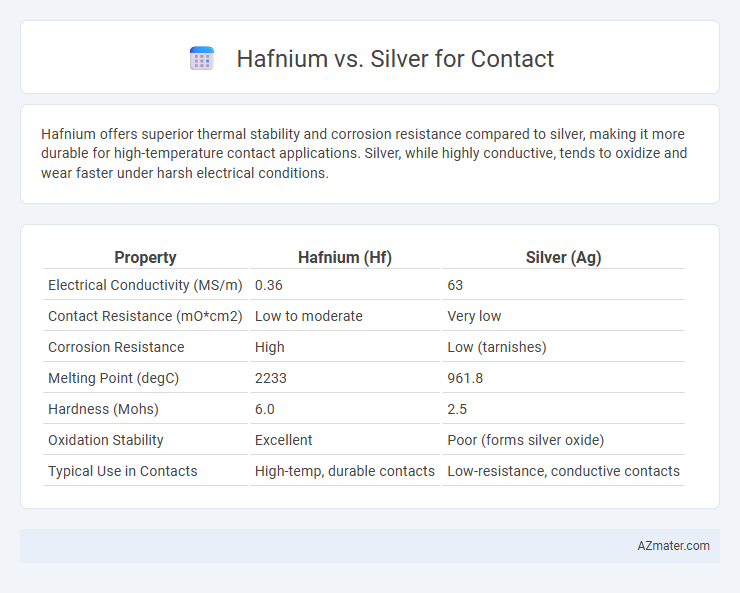
Hafnium offers superior thermal stability and corrosion resistance compared to silver, making it more durable for high-temperature contact applications. Silver, while highly conductive, tends to oxidize and wear faster under harsh electrical conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hafnium (Hf) | Silver (Ag) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity (MS/m) | 0.36 | 63 |
| Contact Resistance (mO*cm2) | Low to moderate | Very low |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Low (tarnishes) |
| Melting Point (degC) | 2233 | 961.8 |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 6.0 | 2.5 |
| Oxidation Stability | Excellent | Poor (forms silver oxide) |
| Typical Use in Contacts | High-temp, durable contacts | Low-resistance, conductive contacts |
Introduction to Hafnium and Silver as Contact Materials
Hafnium and silver are prominent contact materials utilized in electronic devices, each offering distinct electrical and physical properties. Hafnium is valued for its high melting point, excellent corrosion resistance, and strong chemical stability, making it suitable for high-temperature and harsh environment applications. Silver provides superior electrical conductivity and lower contact resistance, but its softness may lead to wear and oxidation issues in contact interfaces.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Silver exhibits the highest electrical conductivity among metals, measured at approximately 63 x 10^6 S/m, making it the preferred choice for electrical contacts requiring minimal resistive losses. Hafnium's conductivity is significantly lower, around 0.95 x 10^6 S/m, limiting its use in high-conductivity applications but offering benefits in corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability. For contact materials, silver ensures superior electrical performance, while hafnium is suitable where environmental durability and thermal resilience are prioritized.
Thermal Conductivity Properties
Hafnium exhibits significantly lower thermal conductivity compared to silver, with hafnium's thermal conductivity around 23 W/m*K versus silver's exceptional 429 W/m*K at room temperature. This substantial difference makes silver an ideal choice for electrical contacts requiring efficient heat dissipation to prevent overheating and maintain performance. Conversely, hafnium's lower thermal conductivity limits its effectiveness in thermal management but provides benefits in high-temperature and corrosion-resistant applications where conductivity is less critical.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Hafnium exhibits superior corrosion and oxidation resistance compared to silver, making it a preferred choice for contacts in harsh environments. Hafnium's native oxide layer is highly stable and forms a protective barrier that prevents further degradation under high temperatures and corrosive conditions. Silver, while an excellent conductor, tends to oxidize and tarnish more easily, leading to reduced contact reliability over time.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Hafnium shows superior mechanical strength and durability compared to silver when used in electrical contacts due to its high melting point of approximately 2,233degC and excellent resistance to mechanical wear and fatigue. Silver, while possessing excellent electrical conductivity, has a lower melting point of 961.8degC and is softer, making it more prone to deformation and reduced lifespan under high-stress conditions. Contacts made with hafnium alloys maintain structural integrity and reliable performance in harsh environments, making them ideal for high-load applications requiring enhanced mechanical durability.
Cost and Availability
Hafnium offers superior electrical properties but comes with a significantly higher cost due to limited global reserves and complex extraction processes, impacting its availability. Silver, widely available with established mining and refining infrastructure, remains the cost-effective choice for contacts in large-scale applications despite lower performance metrics compared to hafnium. Industries prioritize silver for budget-sensitive projects while reserving hafnium for high-performance needs where cost is less restrictive.
Applications in Electronics and Industry
Hafnium offers superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability compared to silver, making it ideal for harsh electronics and industrial environments. Silver excels in electrical conductivity, widely used in connectors and conductive coatings for its low resistance and excellent thermal conduction. Electronics benefiting from hafnium include high-performance integrated circuits and capacitors, while silver dominates in printed circuit boards and switches.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Hafnium offers superior corrosion resistance and stability in high-temperature environments compared to silver, reducing environmental risks related to material degradation and contamination in electrical contacts. Silver, while highly conductive, poses environmental concerns due to its potential toxicity to aquatic life and the challenges of recycling silver-containing components. Choosing hafnium contacts enhances safety by minimizing hazardous material exposure and supports sustainable practices through longer operational life and lower environmental impact.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
Hafnium contacts exhibit superior lifespan due to their excellent resistance to oxidation and wear compared to silver, which tends to tarnish and degrade faster under electrical arcing conditions. Maintenance requirements for hafnium are lower as it maintains stable electrical conductivity over prolonged use, reducing the frequency of replacements or cleaning. Silver contacts, while initially offering lower resistance, demand regular inspection and upkeep to prevent performance deterioration caused by surface corrosion and material loss.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Hafnium and Silver for Contacts
Hafnium offers superior wear resistance and excellent conductivity, making it ideal for high-performance electrical contacts exposed to harsh environments. Silver provides the highest electrical and thermal conductivity but is prone to oxidation and wear, limiting its durability in demanding applications. Selecting between hafnium and silver depends on balancing conductivity needs with reliability requirements, where hafnium excels in longevity and silver leads in pure conductivity.
Infographic: Hafnium vs Silver for Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com