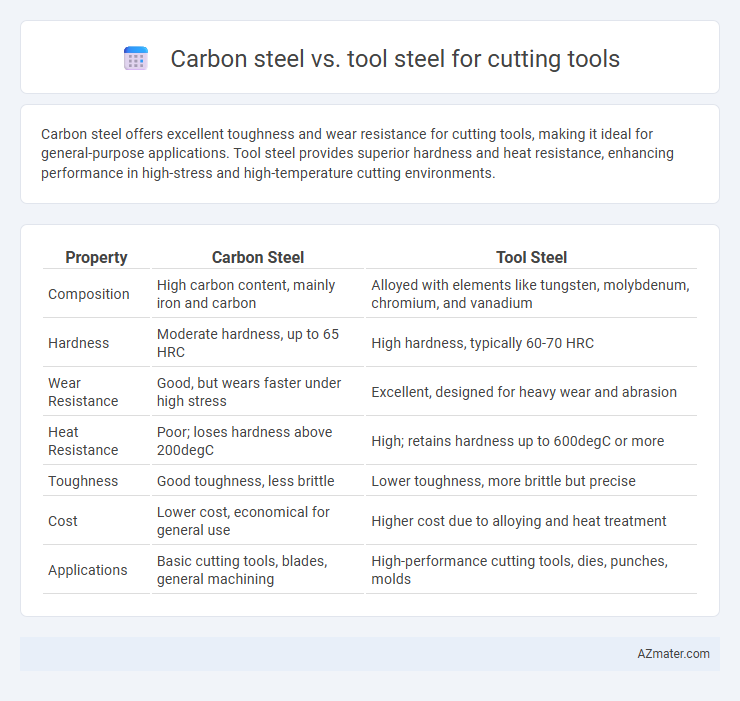
Carbon steel offers excellent toughness and wear resistance for cutting tools, making it ideal for general-purpose applications. Tool steel provides superior hardness and heat resistance, enhancing performance in high-stress and high-temperature cutting environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Steel | Tool Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High carbon content, mainly iron and carbon | Alloyed with elements like tungsten, molybdenum, chromium, and vanadium |
| Hardness | Moderate hardness, up to 65 HRC | High hardness, typically 60-70 HRC |
| Wear Resistance | Good, but wears faster under high stress | Excellent, designed for heavy wear and abrasion |
| Heat Resistance | Poor; loses hardness above 200degC | High; retains hardness up to 600degC or more |
| Toughness | Good toughness, less brittle | Lower toughness, more brittle but precise |
| Cost | Lower cost, economical for general use | Higher cost due to alloying and heat treatment |
| Applications | Basic cutting tools, blades, general machining | High-performance cutting tools, dies, punches, molds |
Introduction to Cutting Tool Materials
Carbon steel and tool steel are fundamental materials used in cutting tools, each offering distinct properties tailored to machining applications. Carbon steel provides excellent hardness and edge retention at a lower cost, making it suitable for general-purpose cutting tools and applications involving softer materials. Tool steel, enriched with alloying elements like chromium, vanadium, and molybdenum, delivers superior wear resistance, toughness, and heat resistance, ideal for high-precision, heavy-duty cutting tasks and prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
Overview of Carbon Steel
Carbon steel, composed primarily of iron and carbon with trace elements, is favored for cutting tools due to its excellent hardness and wear resistance after heat treatment. It offers a cost-effective solution with good machinability and sharpness retention but lacks the high-temperature strength and toughness found in tool steels. Carbon steel cutting tools are ideal for applications involving lower cutting speeds and softer materials.
Overview of Tool Steel
Tool steel is a specialized type of steel designed to withstand high wear, heat, and deformation, making it ideal for cutting tools. Unlike carbon steel, tool steel contains alloying elements such as tungsten, molybdenum, chromium, and vanadium, which enhance hardness, toughness, and heat resistance, ensuring superior performance in demanding machining operations. Its ability to maintain a sharp cutting edge at elevated temperatures makes tool steel the preferred choice for industrial cutting applications.
Composition Differences: Carbon vs Tool Steel
Carbon steel cutting tools primarily consist of iron with 0.5% to 1.5% carbon content, offering moderate hardness and wear resistance. Tool steel contains higher concentrations of alloying elements such as tungsten, molybdenum, chromium, and vanadium, which enhance toughness, heat resistance, and durability for cutting applications. These compositional differences result in tool steel outperforming carbon steel in high-stress and high-temperature cutting environments.
Hardness and Wear Resistance Comparison
Carbon steel cutting tools offer moderate hardness and wear resistance, making them suitable for low to medium cutting speeds and materials with less abrasive properties. Tool steel exhibits significantly higher hardness, often reaching up to 70 HRC, and superior wear resistance due to alloying elements like tungsten, molybdenum, and vanadium, enabling it to maintain sharpness under high-speed and heavy-duty cutting conditions. The enhanced carbide formation in tool steel provides exceptional durability and longevity compared to carbon steel, particularly in applications involving hard or abrasive workpieces.
Edge Retention and Sharpness
Tool steel exhibits superior edge retention and sharpness compared to carbon steel due to its higher alloy content and heat treatment capabilities, making it ideal for cutting tools requiring long-lasting precision. Carbon steel offers good initial sharpness but tends to dull faster under heavy use, limiting its performance in demanding cutting applications. The enhanced wear resistance and hardness of tool steel ensure consistent cutting efficiency and durability over time.
Machinability and Processing
Carbon steel offers superior machinability compared to tool steel due to its lower hardness and simpler alloy composition, allowing faster and easier cutting processes. Tool steel, known for its high hardness and wear resistance, requires advanced machining techniques and slower processing to avoid tool wear and maintain precision. Selecting between carbon steel and tool steel depends on the balance between ease of machining and the desired durability of the cutting tool.
Cost Considerations
Carbon steel cutting tools typically have lower initial costs due to simpler alloy composition and easier manufacturing processes, making them suitable for budget-conscious applications with less demanding cutting requirements. Tool steel, containing higher alloy elements such as tungsten, molybdenum, and vanadium, offers superior hardness and wear resistance but comes at a significantly higher price point reflective of its enhanced performance and longer tool life. When evaluating cost considerations, the total expense must factor in tool longevity, maintenance frequency, and replacement intervals, where tool steel often provides better long-term value despite the upfront investment.
Applications in Cutting Tools
Carbon steel is widely used in cutting tools for its affordability and ease of sharpening, making it ideal for woodworking and general-purpose knives. Tool steel, with higher alloy content and heat resistance, excels in industrial applications requiring durability, such as drilling, milling, and heavy-duty machining. Its superior hardness and wear resistance extend tool life in demanding cutting environments where precision and toughness are critical.
Choosing the Right Steel for Cutting Tools
Selecting the right steel for cutting tools involves comparing carbon steel and tool steel based on hardness, wear resistance, and toughness. Tool steel offers superior hardness and heat resistance, making it ideal for high-performance cutting applications, while carbon steel provides good sharpness and is more affordable for general-purpose cutting tools. Understanding the specific machining demands and operating conditions helps determine whether the enhanced durability of tool steel or the cost-effective sharpness of carbon steel best suits a cutting tool's requirements.
Infographic: Carbon steel vs Tool steel for Cutting tool
 azmater.com
azmater.com