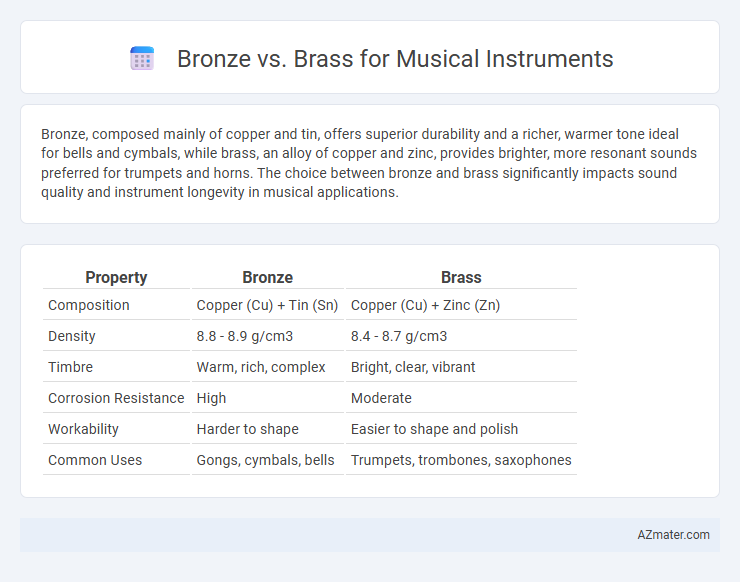
Bronze, composed mainly of copper and tin, offers superior durability and a richer, warmer tone ideal for bells and cymbals, while brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, provides brighter, more resonant sounds preferred for trumpets and horns. The choice between bronze and brass significantly impacts sound quality and instrument longevity in musical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bronze | Brass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper (Cu) + Tin (Sn) | Copper (Cu) + Zinc (Zn) |
| Density | 8.8 - 8.9 g/cm3 | 8.4 - 8.7 g/cm3 |
| Timbre | Warm, rich, complex | Bright, clear, vibrant |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Workability | Harder to shape | Easier to shape and polish |
| Common Uses | Gongs, cymbals, bells | Trumpets, trombones, saxophones |
Introduction to Bronze and Brass in Musical Instruments
Bronze, an alloy primarily of copper and tin, is prized in musical instruments like cymbals and bells for its durability and rich, resonant sound quality. Brass, composed mainly of copper and zinc, is extensively used in wind instruments such as trumpets and trombones due to its malleability and bright, vibrant tonal characteristics. Both metals offer distinct acoustic properties that influence the timbre and projection of the instruments crafted from them.
Composition and Properties of Bronze
Bronze, primarily composed of copper and tin, offers superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to brass, which is mainly copper and zinc. The tin content in bronze enhances its hardness and tonal quality, making it ideal for musical instruments like cymbals and bells that require a rich, resonant sound. Bronze's dense structure provides a unique warm timbre and long sustain, crucial for artistic acoustic performance.
Composition and Properties of Brass
Brass, an alloy primarily composed of copper and zinc, offers excellent acoustic properties and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for musical instruments like trumpets and trombones. Its density and malleability allow for precise shaping and bright, resonant tones, contrasting with bronze, which contains copper and tin and produces a warmer, darker sound. Brass's superior workability and durability contribute to its widespread use in wind instruments, enhancing both playability and sound quality.
Sound Quality: Bronze vs Brass
Bronze produces a bright, clear tone with a rich harmonic spectrum, making it ideal for percussion instruments like cymbals and bells due to its resonant and sustained sound quality. Brass offers a warmer, mellower timbre with balanced overtones, commonly preferred for wind instruments such as trumpets and trombones because of its smooth, flexible tonal response. The choice between bronze and brass significantly influences the instrument's projection, timbre complexity, and overall sound character.
Durability and Maintenance Comparison
Bronze offers superior durability for musical instruments due to its higher resistance to corrosion and wear, making it ideal for long-lasting performance. Brass, while slightly less durable, provides easier maintenance because it is more malleable and requires less frequent polishing to maintain its appearance. Both materials support distinct tonal qualities, but bronze's sturdiness ensures fewer repairs and extended instrument lifespan.
Cost and Availability for Instrument Makers
Bronze, an alloy primarily of copper and tin, is generally more expensive than brass due to tin's higher cost and limited availability, affecting its affordability for instrument makers. Brass, composed mainly of copper and zinc, is widely available and more cost-effective, making it the preferred choice for many manufacturers seeking durability and acoustic quality without high expenditure. Instrument makers often opt for brass to balance production costs and material accessibility while ensuring consistent supply for large-scale manufacturing.
Popular Brass Instruments and Their Uses
Popular brass instruments such as trumpets, trombones, and tubas are typically crafted from brass due to its excellent acoustic properties and corrosion resistance. Brass alloys provide a bright, resonant tone ideal for orchestras, marching bands, and jazz ensembles, enhancing the instrument's projection and responsiveness. Bronze, while durable and used mainly in percussion instruments like cymbals and gongs, is less common in brass instrument construction because it produces a darker timbre and is heavier.
Popular Bronze Instruments and Their Uses
Popular bronze instruments include cymbals, gongs, and certain types of bells, prized for their bright, resonant tones and durability in orchestral and marching band settings. Bronze alloys, typically a mix of copper and tin, offer superior acoustic properties and corrosion resistance, enhancing sound projection and clarity. Musicians favor bronze instruments for their ability to produce rich harmonics, making them essential in classical music, jazz percussion, and traditional ensembles worldwide.
Player Preferences and Performance Considerations
Bronze offers a brighter, more focused tone preferred by players seeking clear articulation and projection, commonly used in cymbals and certain resonant instruments. Brass provides warmer, richer sound qualities favored for versatility in wind instruments like trumpets and trombones, enhancing ease of playability and dynamic range. Performance considerations include bronze's durability and resonance, which suit aggressive playing styles, while brass allows greater flexibility in tonal color and response.
Choosing the Right Alloy for Your Musical Needs
Bronze and brass differ significantly in tone and durability, making alloy selection crucial for musical instruments. Bronze, primarily composed of copper and tin, offers a warm, rich sound ideal for cymbals and certain brass instruments, while brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, provides a brighter, more resonant tone favored in trumpets and trombones. Selecting the right alloy depends on the desired sound quality, instrument type, and playing style, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Bronze vs Brass for Musical Instrument
 azmater.com
azmater.com