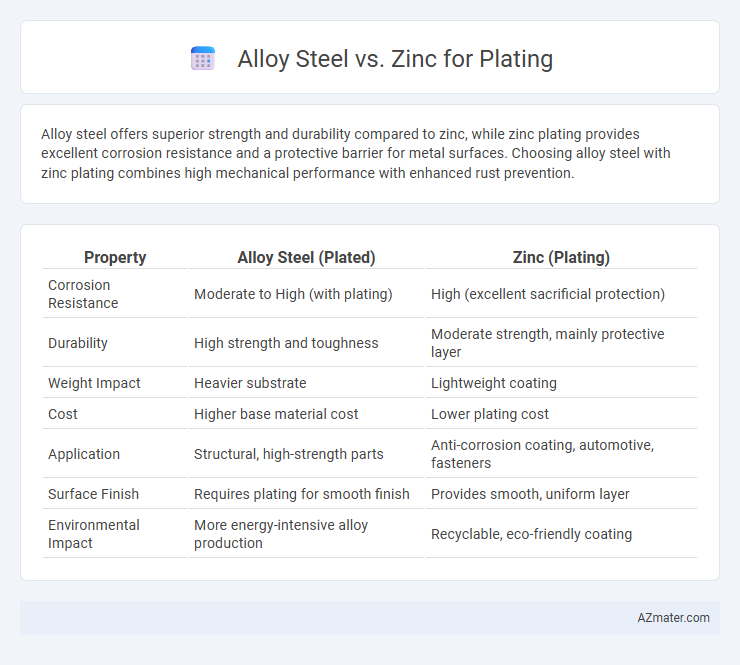
Alloy steel offers superior strength and durability compared to zinc, while zinc plating provides excellent corrosion resistance and a protective barrier for metal surfaces. Choosing alloy steel with zinc plating combines high mechanical performance with enhanced rust prevention.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alloy Steel (Plated) | Zinc (Plating) |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate to High (with plating) | High (excellent sacrificial protection) |
| Durability | High strength and toughness | Moderate strength, mainly protective layer |
| Weight Impact | Heavier substrate | Lightweight coating |
| Cost | Higher base material cost | Lower plating cost |
| Application | Structural, high-strength parts | Anti-corrosion coating, automotive, fasteners |
| Surface Finish | Requires plating for smooth finish | Provides smooth, uniform layer |
| Environmental Impact | More energy-intensive alloy production | Recyclable, eco-friendly coating |
Introduction to Alloy Steel and Zinc Plating
Alloy steel, characterized by its enhanced mechanical properties due to the addition of elements like chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, requires effective corrosion protection for durability in industrial applications. Zinc plating, a popular method for protecting alloy steel, involves depositing a thin layer of zinc to create a sacrificial barrier that prevents rust and extends the steel's lifespan. This combination leverages the strength of alloy steel with the corrosion resistance provided by zinc coating, making it ideal for automotive, construction, and heavy machinery components.
Overview of Plating Processes
Alloy steel plating typically involves processes like electroplating, where a thin layer of metal such as nickel or chromium is deposited to enhance corrosion resistance and surface hardness, often requiring pre-treatment steps to ensure adhesion. Zinc plating, commonly done through electro-galvanizing or hot-dip galvanizing, provides a sacrificial protective coating that prevents rusting by corroding preferentially to the underlying steel. Both plating methods use cleaning, rinsing, and drying stages to prepare the alloy steel substrate and ensure uniform coating thickness and durability.
Chemical Properties of Alloy Steel
Alloy steel exhibits enhanced chemical properties due to the presence of elements such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, which improve corrosion resistance and strength. Unlike zinc plating, which primarily acts as a sacrificial barrier preventing oxidation, the alloying elements in the steel itself alter its microstructure and chemical reactivity. These intrinsic chemical properties make alloy steel more resistant to chemical degradation in harsh environments compared to zinc-coated surfaces.
Corrosion Resistance of Zinc Plating
Zinc plating provides exceptional corrosion resistance by forming a protective zinc oxide layer that prevents rust and degradation of alloy steel surfaces. Unlike alloy steel alone, which can be prone to oxidation, zinc plating acts as a sacrificial anode, corroding first and thereby extending the lifespan of the underlying metal. This protective mechanism makes zinc-plated alloy steel ideal for applications exposed to moisture and harsh environments, enhancing durability and reducing maintenance costs.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Alloy steel, known for its high tensile strength and resistance to wear, offers superior durability compared to zinc plating, which primarily serves as a corrosion-resistant coating rather than a structural reinforcement. The strength of alloy steel makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications where mechanical load and impact resistance are critical, while zinc plating enhances the longevity of steel components by preventing rust and surface degradation. Combining alloy steel with zinc plating can optimize both mechanical strength and corrosion resistance for extended service life in demanding environments.
Cost Analysis: Alloy Steel vs Zinc Plating
Alloy steel typically incurs higher initial material costs compared to zinc plating, which offers an economical protective coating for steel substrates. Zinc plating provides corrosion resistance at a lower price point, reducing long-term maintenance expenses. The overall cost efficiency favors zinc plating when balancing durability and budget constraints in industrial applications.
Industrial Applications and Uses
Alloy steel offers superior strength and wear resistance in industrial applications such as automotive components, heavy machinery, and structural parts, where durability under high stress is crucial. Zinc plating provides effective corrosion protection for alloy steel and other metals, commonly used in construction, electrical equipment, and fasteners exposed to outdoor environments. Combining alloy steel with zinc plating enhances lifespan and performance in harsh industrial conditions by preventing rust while maintaining mechanical integrity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Alloy steel plating typically requires energy-intensive processes and can involve hazardous chemicals, leading to significant environmental concerns such as waste generation and pollution. Zinc plating offers enhanced corrosion resistance with less environmental toxicity, as zinc is more abundant and easier to recycle, contributing to improved sustainability. Choosing zinc over alloy steel plating helps reduce ecological footprint by minimizing hazardous waste and promoting circular metal use.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors
Alloy steel offers superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to zinc plating, which primarily serves as a sacrificial layer to protect the base metal. Maintenance of alloy steel components typically requires less frequent intervention due to their inherent mechanical strength and resistance to wear, whereas zinc-plated surfaces may need regular inspections and reapplication to prevent rust and deterioration. Longevity of alloy steel in harsh environments surpasses zinc plating, which can degrade over time, especially under abrasive or chemically aggressive conditions.
Choosing the Right Material for Plating
Alloy steel offers superior strength and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and wear resistance before plating. Zinc plating provides excellent sacrificial protection against rust, especially for steel substrates, enhancing longevity in harsh environments. Selecting between alloy steel and zinc plating depends on the specific mechanical demands and environmental exposure of the finished product.
Infographic: Alloy steel vs Zinc for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com