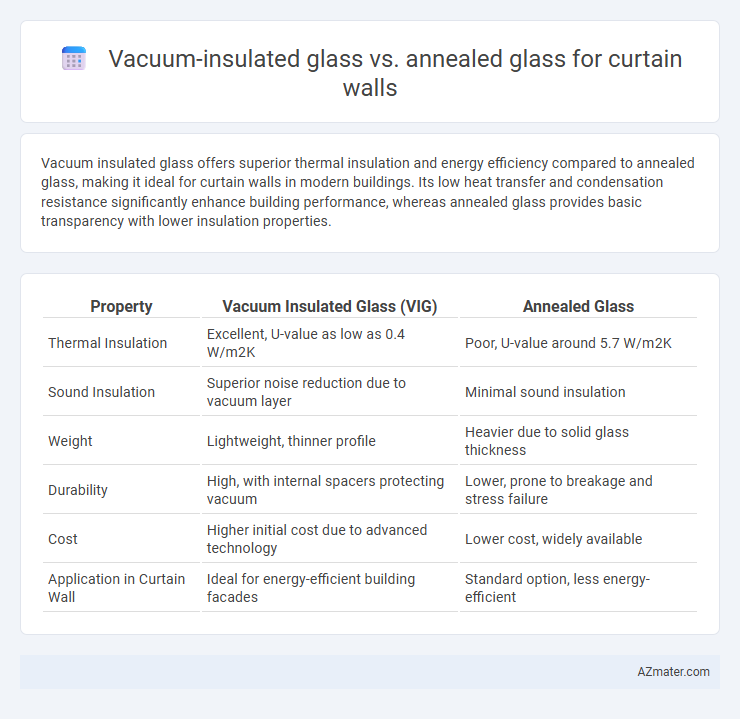
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency compared to annealed glass, making it ideal for curtain walls in modern buildings. Its low heat transfer and condensation resistance significantly enhance building performance, whereas annealed glass provides basic transparency with lower insulation properties.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG) | Annealed Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, U-value as low as 0.4 W/m2K | Poor, U-value around 5.7 W/m2K |
| Sound Insulation | Superior noise reduction due to vacuum layer | Minimal sound insulation |
| Weight | Lightweight, thinner profile | Heavier due to solid glass thickness |
| Durability | High, with internal spacers protecting vacuum | Lower, prone to breakage and stress failure |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced technology | Lower cost, widely available |
| Application in Curtain Wall | Ideal for energy-efficient building facades | Standard option, less energy-efficient |
Introduction to Curtain Wall Glazing Options
Curtain wall glazing options include vacuum insulated glass (VIG) and annealed glass, both pivotal in balancing aesthetics and energy efficiency. Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation due to its airless space, reducing heat transfer and improving building energy performance, while annealed glass provides cost-effective durability but lacks the high insulative properties of VIG. Selecting the appropriate glazing depends on factors like thermal requirements, project budget, and desired facade transparency for modern curtain wall systems.
Understanding Vacuum Insulated Glass
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal insulation for curtain walls by minimizing heat transfer through a near-vacuum space between glass panes, significantly reducing energy loss compared to traditional annealed glass. VIG enhances building energy efficiency, reduces condensation risk, and improves indoor comfort by maintaining stable interior temperatures. Unlike annealed glass, which lacks insulating gas layers, vacuum insulated glass provides advanced performance properties critical for modern, energy-efficient curtain wall systems.
Key Features of Annealed Glass
Annealed glass for curtain walls offers key features such as improved clarity, enhanced strength compared to non-treated glass, and excellent thermal stability for stable performance in various weather conditions. It provides cost-effective manufacturing and easy fabrication, including cutting and drilling, making it versatile for large glass panels. Unlike vacuum insulated glass, annealed glass lacks advanced insulation properties but excels in optical quality and mechanical reliability for architectural applications.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal performance compared to annealed glass, achieving U-values as low as 0.4 W/m2K, significantly reducing heat transfer through curtain walls. Its vacuum layer eliminates conductive and convective heat loss, enhancing energy efficiency and indoor comfort in building facades. In contrast, annealed glass typically has a U-value around 5.8 W/m2K, providing minimal insulation and higher energy consumption for heating and cooling.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal insulation compared to annealed glass, significantly reducing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency in curtain wall systems. The vacuum space between panes in VIG minimizes conductive and convective heat loss, resulting in lower U-values and enhanced thermal performance suitable for high-performance building envelopes. In contrast, annealed glass lacks this insulating capacity, leading to higher energy consumption for heating and cooling in buildings.
Sound Insulation Capabilities
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior sound insulation for curtain walls by minimizing air pressure variations between panes, resulting in significantly reduced noise transmission compared to annealed glass. Unlike annealed glass, which provides basic sound attenuation, vacuum insulated glass incorporates a vacuum layer that effectively blocks airborne sound waves and enhances acoustic performance. This advanced technology is particularly beneficial in urban environments where mitigating exterior noise is critical for indoor comfort and productivity.
Safety and Durability Factors
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers enhanced thermal insulation and superior resistance to stress-related breakage compared to annealed glass, making it safer for curtain wall applications where energy efficiency and durability are critical. Annealed glass lacks the reinforced strength and shatter resistance found in tempered or laminated options often recommended for curtain walls, increasing the risk of breakage under impact or thermal stress. VIG panels maintain structural integrity longer by reducing condensation and thermal expansion effects, thereby extending the lifespan and safety of curtain wall systems in diverse weather conditions.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior aesthetic appeal for curtain walls due to its slim profile and minimal frame depth, allowing for sleek, modern designs and expansive uninterrupted views. Annealed glass, while more cost-effective, is thicker and less adaptable in design flexibility, often requiring larger frames and limiting light transmission and transparency options. The enhanced clarity and thermal performance of vacuum insulated glass enable architects to achieve innovative, energy-efficient facades without compromising visual elegance.
Cost Analysis: Vacuum Insulated vs Annealed Glass
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) for curtain walls commands a higher initial investment compared to annealed glass due to advanced manufacturing processes and specialized materials. Despite the upfront cost, VIG offers superior thermal performance, reducing energy expenses and enhancing building efficiency over time. Annealed glass presents a more budget-friendly option but may incur higher long-term costs from increased heating and cooling demands.
Choosing the Right Glass for Curtain Walls
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency compared to annealed glass, making it ideal for curtain walls in extreme climates or buildings pursuing LEED certification. Annealed glass, while more cost-effective and easier to fabricate, lacks the insulating properties necessary for high-performance curtain wall systems. Selecting vacuum insulated glass enhances occupant comfort and reduces HVAC costs by minimizing heat transfer and condensation risks in curtain wall applications.
Infographic: Vacuum insulated glass vs Annealed glass for Curtain wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com