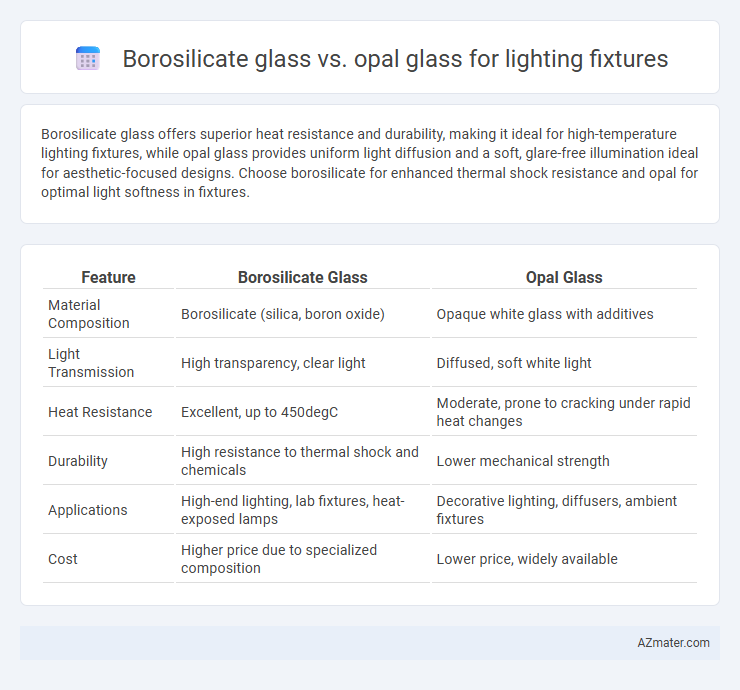
Borosilicate glass offers superior heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature lighting fixtures, while opal glass provides uniform light diffusion and a soft, glare-free illumination ideal for aesthetic-focused designs. Choose borosilicate for enhanced thermal shock resistance and opal for optimal light softness in fixtures.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Borosilicate Glass | Opal Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Borosilicate (silica, boron oxide) | Opaque white glass with additives |
| Light Transmission | High transparency, clear light | Diffused, soft white light |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent, up to 450degC | Moderate, prone to cracking under rapid heat changes |
| Durability | High resistance to thermal shock and chemicals | Lower mechanical strength |
| Applications | High-end lighting, lab fixtures, heat-exposed lamps | Decorative lighting, diffusers, ambient fixtures |
| Cost | Higher price due to specialized composition | Lower price, widely available |
Introduction to Glass Types for Lighting Fixtures
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-heat lighting fixtures such as halogen and LED lamps. Opal glass provides a diffused, soft light output with excellent glare reduction, commonly used in decorative and ambient lighting applications. Selecting between borosilicate and opal glass depends on the fixture's heat tolerance requirements and desired light diffusion properties.
What Is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass known for its exceptional thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for lighting fixtures exposed to high temperatures. It contains boron trioxide, which significantly reduces thermal expansion, thereby preventing cracks or breakage under heat stress. Compared to opal glass, borosilicate offers superior clarity and strength, making it a preferred material for industrial and high-performance lighting applications.
What Is Opal Glass?
Opal glass is a type of glass characterized by its milky, translucent appearance, often achieved by adding certain oxides or incorporating tiny air bubbles during manufacturing. Unlike borosilicate glass, which is known for its high thermal and chemical resistance, opal glass primarily enhances light diffusion and provides a soft, uniform glow, making it ideal for lighting fixtures that require glare-free illumination. Its aesthetic appeal and ability to evenly distribute light distinguish opal glass as a popular choice for decorative lamps and lighting covers.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and impact strength, making it highly durable for lighting fixtures exposed to temperature fluctuations or mechanical stress. Opal glass, while aesthetically pleasing with its diffused light quality, is less resistant to thermal shock and prone to cracking under sudden temperature changes. The enhanced durability and strength of borosilicate glass ensure longer lifespan and reliability in demanding lighting applications compared to opal glass.
Light Diffusion and Aesthetics
Borosilicate glass offers superior light diffusion with its high thermal resistance and clarity, ensuring consistent illumination without yellowing over time. Opal glass provides a softer, more diffused glow due to its milky, semi-opaque finish, enhancing ambient lighting and aesthetic appeal in decorative fixtures. Both materials balance durability and style, with borosilicate emphasizing performance and opal focusing on warmth and visual comfort in lighting design.
Heat Resistance and Performance
Borosilicate glass offers superior heat resistance up to 450degC, making it ideal for high-temperature lighting fixtures and reducing the risk of thermal shock. Opal glass provides diffused light with moderate heat resistance around 150-200degC, suitable for decorative fixtures but less effective in high-heat environments. Borosilicate's durability and thermal stability enhance performance in industrial or high-wattage applications, while opal glass prioritizes aesthetic diffusion over heat endurance.
Maintenance and Cleaning
Borosilicate glass is highly resistant to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, making it easier to clean with standard household cleaners without risking damage or clouding. Opal glass, while providing a softer, diffused light, tends to be more porous and can trap dust and grime, requiring gentler cleaning methods and regular maintenance to prevent surface dullness. Borosilicate's durability ensures longer-lasting clarity and reduced maintenance frequency compared to the more delicate surface of Opal glass in lighting fixtures.
Cost and Availability
Borosilicate glass typically costs more than opal glass due to its higher thermal resistance and durability, making it suitable for premium lighting fixtures. Opal glass is generally more affordable and widely available, preferred for diffused lighting applications where soft light distribution is desired. Availability of borosilicate glass can be limited compared to the mass-produced opal glass, impacting lead times and overall project costs.
Best Applications for Each Glass Type
Borosilicate glass is ideal for lighting fixtures requiring high thermal resistance and durability, such as laboratory lamps, outdoor lighting, and industrial applications where heat and impact resistance are critical. Opal glass excels in decorative and ambient lighting, providing uniform light diffusion and reducing glare, making it perfect for residential, commercial, and hospitality settings where aesthetic appeal and soft illumination are priorities. Choosing borosilicate glass ensures safety in high-temperature or rugged environments, while opal glass enhances visual comfort and design in controlled indoor lighting scenarios.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Lighting Needs
Borosilicate glass, known for its high thermal resistance and durability, is ideal for lighting fixtures exposed to intense heat or rapid temperature changes, ensuring long-lasting performance and safety. Opal glass offers excellent light diffusion with a soft, uniform glow, making it perfect for ambient lighting where aesthetics and glare reduction are priorities. Selecting between borosilicate and opal glass depends on the balance between thermal durability requirements and the desired lighting effect for the space.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs Opal glass for Lighting fixture
 azmater.com
azmater.com