Bulletproof glass offers enhanced security and impact resistance for curtain walls, while insulated glass provides superior thermal performance and energy efficiency. Choosing between them depends on prioritizing safety or insulation needs in building design.
Table of Comparison
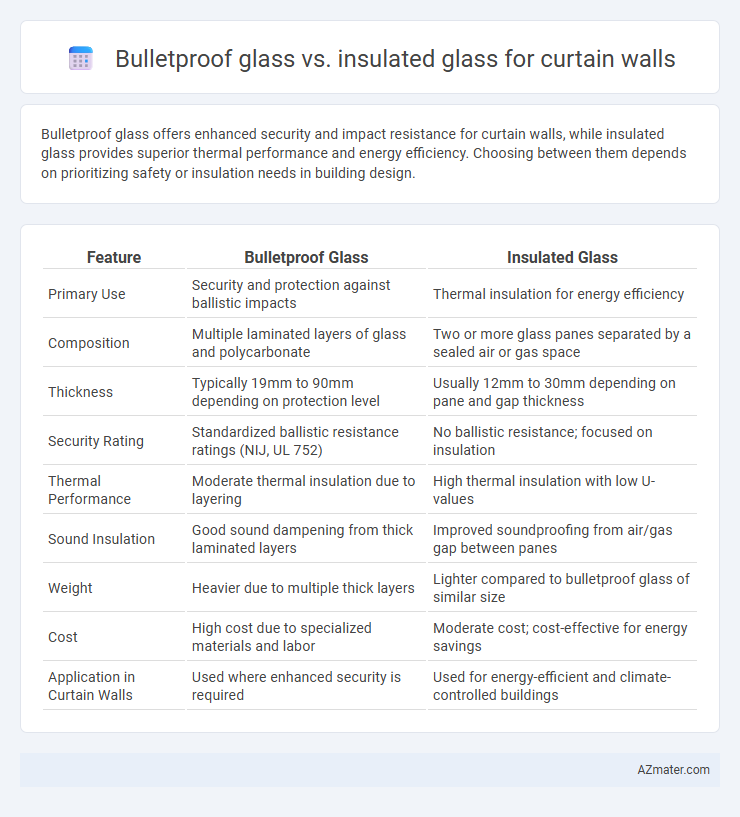
| Feature | Bulletproof Glass | Insulated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Security and protection against ballistic impacts | Thermal insulation for energy efficiency |
| Composition | Multiple laminated layers of glass and polycarbonate | Two or more glass panes separated by a sealed air or gas space |
| Thickness | Typically 19mm to 90mm depending on protection level | Usually 12mm to 30mm depending on pane and gap thickness |
| Security Rating | Standardized ballistic resistance ratings (NIJ, UL 752) | No ballistic resistance; focused on insulation |
| Thermal Performance | Moderate thermal insulation due to layering | High thermal insulation with low U-values |
| Sound Insulation | Good sound dampening from thick laminated layers | Improved soundproofing from air/gas gap between panes |
| Weight | Heavier due to multiple thick layers | Lighter compared to bulletproof glass of similar size |
| Cost | High cost due to specialized materials and labor | Moderate cost; cost-effective for energy savings |
| Application in Curtain Walls | Used where enhanced security is required | Used for energy-efficient and climate-controlled buildings |
Introduction to Curtain Wall Systems
Bulletproof glass and insulated glass are critical components in curtain wall systems, each offering distinct benefits for building facades. Bulletproof glass enhances security by providing ballistic resistance, making it ideal for high-risk environments, while insulated glass improves energy efficiency and thermal insulation, contributing to sustainable building performance. Choosing between these glass types depends on project priorities such as safety, energy savings, and environmental conditions in modern curtain wall applications.
Overview of Bulletproof Glass
Bulletproof glass, also known as ballistic glass, is a multi-layered security material designed to resist high-velocity impacts, making it ideal for curtain wall applications requiring enhanced protection against forced entry and ballistic threats. It typically consists of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, providing superior strength and durability compared to standard insulated glass. While insulated glass primarily focuses on thermal insulation and energy efficiency, bulletproof glass emphasizes safety and impact resistance without compromising structural integrity in curtain wall systems.
Overview of Insulated Glass
Insulated glass for curtain walls consists of two or more glass panes separated by a spacer filled with air or gas, enhancing thermal performance and energy efficiency. Unlike bulletproof glass, which prioritizes impact resistance and security, insulated glass focuses on reducing heat transfer and improving acoustic insulation. This type of glass is ideal for maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures and lowering energy costs in commercial and residential buildings.
Key Differences: Bulletproof vs Insulated Glass
Bulletproof glass for curtain walls offers high impact resistance and security by combining multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate materials to withstand ballistic threats. Insulated glass, on the other hand, enhances energy efficiency and thermal insulation through the use of double or triple glazing with inert gas fills and low-emissivity coatings. The primary difference lies in bulletproof glass providing protection against physical attacks, while insulated glass improves building energy performance and occupant comfort.
Security Features and Applications
Bulletproof glass offers superior security features with multi-layered, polycarbonate or laminated composites designed to resist high-velocity impacts and forced entry, making it ideal for high-risk buildings such as banks, government facilities, and embassies in curtain wall applications. Insulated glass, primarily focused on thermal performance and energy efficiency, provides basic security through tempered or laminated layers but lacks the robust impact resistance of bulletproof variants, suitable for commercial and residential curtain walls where security threats are moderate. Choosing between bulletproof and insulated glass depends on the specific security requirements and building application, balancing protection levels with energy performance needs.
Energy Efficiency and Thermal Performance
Bulletproof glass for curtain walls offers enhanced security but typically has lower energy efficiency compared to insulated glass, which is specifically designed to improve thermal performance through multiple layers and gas fills that reduce heat transfer. Insulated glass units (IGUs) significantly minimize energy loss by providing superior insulation, thereby reducing heating and cooling costs while maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures. Although bulletproof glass can be combined with insulation technologies, insulated glass remains the preferred choice for optimizing energy efficiency and thermal comfort in curtain wall applications.
Acoustic Insulation Capabilities
Bulletproof glass provides high security and impact resistance but typically offers limited acoustic insulation compared to insulated glass. Insulated glass, consisting of two or more glass panes separated by an air or gas-filled space, excels in reducing sound transmission due to its multi-layer structure and thermal break. For curtain walls, insulated glass panels are preferred when acoustic insulation is a primary concern, while bulletproof glass is chosen mainly for safety and protection.
Cost Comparison: Initial and Long-Term Expenses
Bulletproof glass for curtain walls incurs higher initial costs due to specialized manufacturing processes and materials designed for impact resistance and security. Insulated glass generally offers lower upfront expenses and contributes to energy savings by improving thermal performance, resulting in reduced heating and cooling costs over time. Long-term expenses for bulletproof glass may include maintenance and potential upgrades, while insulated glass provides ongoing energy efficiency benefits that can offset its initial investment.
Aesthetic and Design Considerations
Bulletproof glass enhances curtain wall aesthetics by offering a sleek, uninterrupted facade with high clarity and minimal distortion, ideal for modern architectural designs requiring both security and visual appeal. Insulated glass contributes to energy efficiency through thermal performance while allowing for versatile design options, such as varying thicknesses and coatings, which can influence light transmission and exterior finish. Balancing bulletproof glass's robust security with insulated glass's thermal benefits ensures curtain walls meet both safety and aesthetic demands without compromising architectural vision.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Curtain Wall
Bulletproof glass provides enhanced security and impact resistance, ideal for high-risk areas in curtain walls, while insulated glass excels in thermal performance and energy efficiency. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing safety requirements with climate control needs, considering factors like building location, occupancy, and local building codes. Prioritizing both protection and insulation ensures optimal performance and occupant comfort in curtain wall applications.
Infographic: Bulletproof glass vs Insulated glass for Curtain wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com