Tempered glass offers enhanced strength and safety for facades, resisting impacts and thermal stress, while tinted glass provides solar control by reducing glare and heat gain. Combining these materials optimizes building performance by balancing durability and energy efficiency.
Table of Comparison
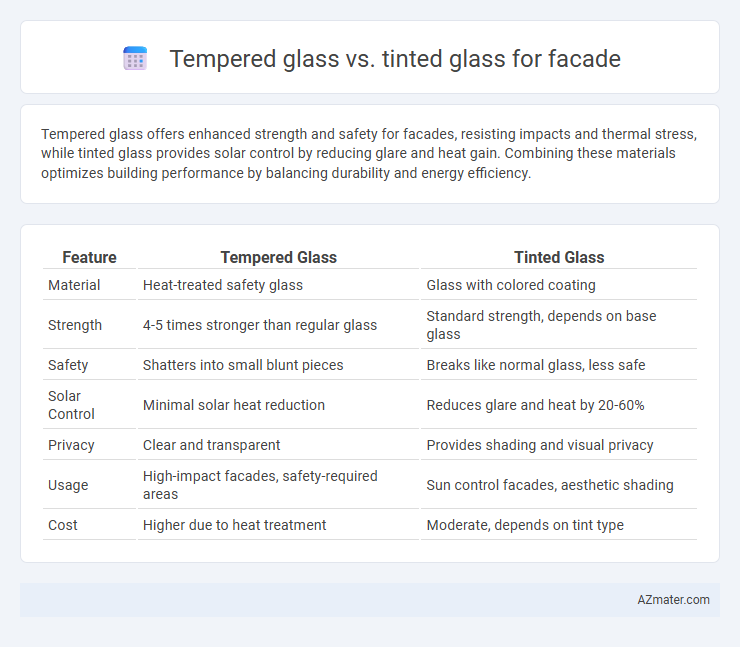
| Feature | Tempered Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Heat-treated safety glass | Glass with colored coating |
| Strength | 4-5 times stronger than regular glass | Standard strength, depends on base glass |
| Safety | Shatters into small blunt pieces | Breaks like normal glass, less safe |
| Solar Control | Minimal solar heat reduction | Reduces glare and heat by 20-60% |
| Privacy | Clear and transparent | Provides shading and visual privacy |
| Usage | High-impact facades, safety-required areas | Sun control facades, aesthetic shading |
| Cost | Higher due to heat treatment | Moderate, depends on tint type |
Introduction to Facade Glass Solutions
Tempered glass and tinted glass are essential materials in modern facade glass solutions, each offering distinct benefits for building exteriors. Tempered glass provides superior strength and safety through a heat-treated process that makes it resistant to impact and thermal stress. Tinted glass enhances energy efficiency by reducing solar heat gain and glare, contributing to improved occupant comfort and lower cooling costs.
What is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to normal glass. It is designed to shatter into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, reducing injury risk in case of breakage, making it ideal for facade applications requiring enhanced safety and durability. Unlike tinted glass, which primarily alters light transmission and aesthetic, tempered glass focuses on structural integrity and impact resistance.
What is Tinted Glass?
Tinted glass is a type of architectural glass infused with colorants during its manufacturing process to reduce solar heat gain, glare, and UV radiation, enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort in building facades. Unlike clear glass, tinted glass absorbs a portion of sunlight, diminishing brightness and providing improved privacy without compromising natural light transmission. This characteristic makes tinted glass a preferred choice for commercial and residential facades aiming to balance aesthetics, energy savings, and thermal performance.
Key Properties: Tempered vs Tinted Glass
Tempered glass offers superior strength and safety due to its heat treatment process, making it highly resistant to impact and thermal stress, which is essential for facade applications in high-wind or high-traffic areas. Tinted glass primarily provides solar control by reducing glare and heat gain through its colored coating, improving energy efficiency and occupant comfort but without significantly enhancing structural strength. Choosing between tempered and tinted glass depends on whether the priority is mechanical durability or solar heat management for building facades.
Aesthetic Differences for Modern Facades
Tempered glass for facades offers a sleek, clear aesthetic that enhances natural light penetration and provides a crisp, modern look with high transparency. Tinted glass introduces a subtle color variation or shading that reduces glare and adds a distinctive visual depth, contributing to a dynamic facade appearance. The aesthetic choice between tempered and tinted glass significantly influences the building's exterior style, balancing brightness and privacy in contemporary architecture.
Energy Efficiency and Thermal Performance
Tempered glass offers superior strength and safety but has limited impact on energy efficiency, while tinted glass significantly reduces solar heat gain, enhancing thermal performance and lowering cooling costs. Tinted glass can block up to 60% of solar radiation, decreasing reliance on air conditioning and improving energy savings in facades. Combining tempered glass with specialized tints or coatings optimizes both durability and thermal insulation for energy-efficient building envelopes.
Safety and Security Considerations
Tempered glass offers superior safety and security for facades due to its increased strength and shatter-resistant properties, breaking into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards. Tinted glass enhances privacy and reduces glare but does not provide the same level of impact resistance or safety as tempered glass. Combining tempered glass with tinting can optimize both security and visual comfort in building facades.
UV Protection and Sunlight Control
Tempered glass offers superior strength and enhanced UV protection by filtering harmful rays, reducing interior fading and damage. Tinted glass controls sunlight by absorbing and reflecting solar radiation, thereby minimizing glare and heat gain while also providing moderate UV protection. Combining tempered glass with tinting technology optimizes facade durability, energy efficiency, and occupant comfort through effective sunlight control and UV shielding.
Cost Comparison and Installation Factors
Tempered glass generally incurs higher costs due to its heat treatment process, which enhances strength and safety, making it ideal for facade applications requiring durability. Tinted glass, often less expensive, reduces solar heat gain and glare, contributing to energy efficiency without extensive processing expenses. Installation of tempered glass demands precise handling and specialized equipment to avoid damage, while tinted glass is easier to install but may require careful positioning to maximize shading benefits.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Building's Facade
Tempered glass offers superior strength and safety for facades, resisting impacts and thermal stress, while tinted glass enhances energy efficiency by reducing solar heat gain and glare. Choosing the right glass depends on balancing structural demands with aesthetic and environmental performance tailored to the building's location and usage. Combining tempered and tinted glass can optimize durability and energy savings for modern architectural designs.
Infographic: Tempered glass vs Tinted glass for Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com