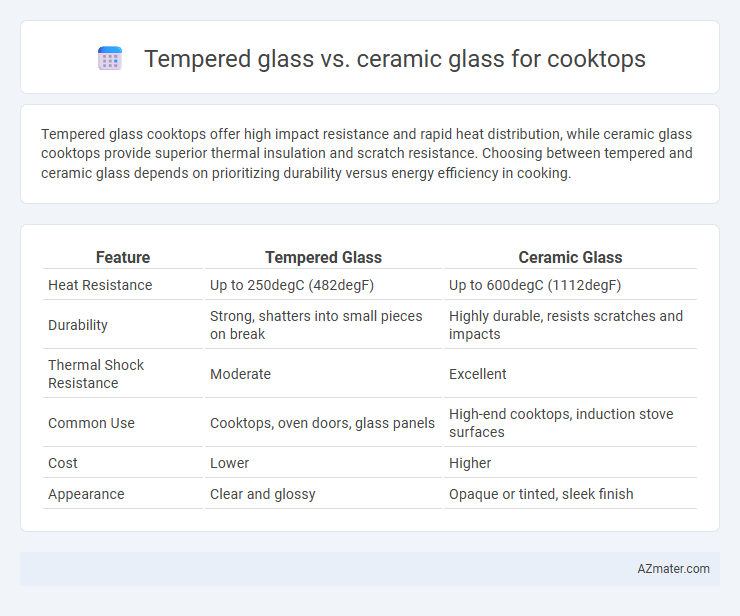
Tempered glass cooktops offer high impact resistance and rapid heat distribution, while ceramic glass cooktops provide superior thermal insulation and scratch resistance. Choosing between tempered and ceramic glass depends on prioritizing durability versus energy efficiency in cooking.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tempered Glass | Ceramic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 250degC (482degF) | Up to 600degC (1112degF) |
| Durability | Strong, shatters into small pieces on break | Highly durable, resists scratches and impacts |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Common Use | Cooktops, oven doors, glass panels | High-end cooktops, induction stove surfaces |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Appearance | Clear and glossy | Opaque or tinted, sleek finish |
Introduction to Tempered Glass and Ceramic Glass Cooktops
Tempered glass cooktops are made by heating glass to a high temperature and then rapidly cooling it to increase strength and thermal resistance, making them highly durable and resistant to heat shocks. Ceramic glass cooktops consist of a smooth, heat-resistant ceramic fused with a glass surface, providing excellent heat distribution and a sleek, modern aesthetic ideal for induction and radiant cooktops. Both materials offer benefits such as easy cleaning and improved safety, but ceramic glass typically supports more precise temperature control and energy efficiency.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Tempered glass cooktops are made from soda-lime glass that undergoes rapid heating and cooling to increase strength and thermal resistance, resulting in a durable and shatter-resistant surface. Ceramic glass cooktops consist of a glass-ceramic composite containing crystalline phases embedded in an amorphous matrix, produced through controlled crystallization that offers superior heat resistance and even heat distribution. The manufacturing process of ceramic glass involves precise thermal treatments to form a smooth, heat-conductive surface, while tempered glass relies on mechanical strengthening methods that enhance impact resistance but less thermal stability.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Shock Performance
Tempered glass cooktops offer excellent heat resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 600degF (315degC), while ceramic glass can endure even higher sustained temperatures, often exceeding 700degF (370degC), making it ideal for intensive cooking. In terms of thermal shock performance, ceramic glass excels due to its ability to rapidly and evenly distribute heat, minimizing the risk of cracking under sudden temperature changes, whereas tempered glass is more susceptible to breakage when exposed to rapid thermal shifts. Choosing ceramic glass ensures superior durability and longevity in environments with frequent and extreme heat fluctuations.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Tempered glass cooktops offer excellent durability with high resistance to thermal shocks and impacts, making them less prone to breaking under sudden temperature changes. Ceramic glass cooktops excel in scratch resistance due to their hard, smooth surface that withstands abrasive contact from pots, pans, and utensils. Both materials provide robust performance, but tempered glass emphasizes impact durability while ceramic glass prioritizes surface resilience.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Tempered glass cooktops offer a sleek, glossy finish that enhances modern kitchen aesthetics with a smooth, shiny surface available in black or white tones, creating a minimalist and elegant look. Ceramic glass cooktops provide greater versatility in design, allowing for patterns, colors, and textures that can complement various kitchen styles while maintaining heat resistance and durability. Both materials deliver a streamlined, easy-to-clean surface, but ceramic glass stands out for customization and artistic expression in cooktop design.
Cleaning and Maintenance Requirements
Tempered glass cooktops offer a smooth surface that resists stains and is easy to clean with non-abrasive scrubbers and mild detergents, reducing maintenance time. Ceramic glass cooktops, while also smooth and aesthetically sleek, require careful cleaning to avoid scratches and special ceramic cooktop cleaners to maintain their glossy finish. Both materials are durable, but tempered glass generally demands less intensive upkeep compared to ceramic glass, which is more sensitive to abrasive cleaning agents and harsh scrubbing.
Safety Features and Impact Resistance
Tempered glass cooktops offer high impact resistance due to their heat-treated manufacturing process, which enhances durability and prevents shattering into sharp pieces upon breakage. Ceramic glass cooktops, made from a special glass-ceramic composite, provide excellent thermal shock resistance and withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking but are generally less impact-resistant than tempered glass. In terms of safety features, tempered glass is designed to break safely under extreme impact, while ceramic glass prioritizes thermal stability and scratch resistance, making it essential to consider usage scenarios when selecting between the two.
Energy Efficiency and Cooking Performance
Tempered glass cooktops offer high thermal resistance and durability, ensuring efficient heat distribution and rapid temperature changes for consistent cooking performance. Ceramic glass cooktops provide excellent heat retention and an even cooking surface, minimizing energy loss and enhancing fuel efficiency. Both materials support energy-efficient cooking, but ceramic glass tends to maintain heat longer, reducing overall energy consumption during meal preparation.
Cost Comparison and Longevity
Tempered glass cooktops generally cost less initially, ranging between $150 to $500, while ceramic glass options often start at $300 and can exceed $1,000 due to advanced heat resistance and aesthetics. Tempered glass, though durable, tends to show scratches and may crack under sudden temperature changes, leading to a shorter lifespan averaging 5-7 years. Ceramic glass cooktops offer enhanced longevity, typically lasting 10-15 years, supported by higher resistance to thermal shock and easier surface maintenance despite the higher upfront investment.
Which Cooktop Glass is Right for You?
Tempered glass cooktops offer high durability and resistance to impact and thermal shock, making them ideal for vigorous cooking environments and frequent use. Ceramic glass cooktops provide a smooth, sleek surface with excellent heat distribution and aesthetic appeal, suitable for precise cooking control and modern kitchen designs. Choosing between tempered and ceramic glass depends on your cooking style, budget, and preference for durability versus design elegance.
Infographic: Tempered glass vs Ceramic glass for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com