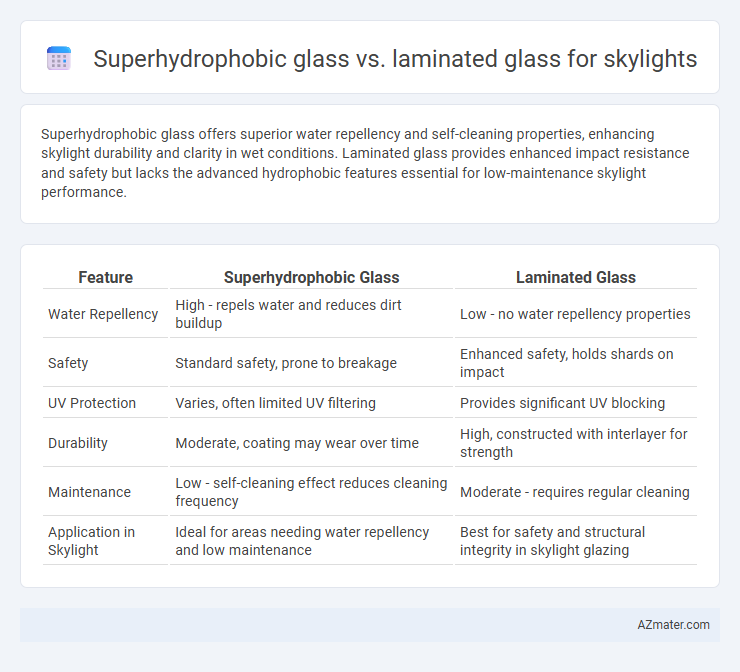
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior water repellency and self-cleaning properties, enhancing skylight durability and clarity in wet conditions. Laminated glass provides enhanced impact resistance and safety but lacks the advanced hydrophobic features essential for low-maintenance skylight performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Superhydrophobic Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Water Repellency | High - repels water and reduces dirt buildup | Low - no water repellency properties |
| Safety | Standard safety, prone to breakage | Enhanced safety, holds shards on impact |
| UV Protection | Varies, often limited UV filtering | Provides significant UV blocking |
| Durability | Moderate, coating may wear over time | High, constructed with interlayer for strength |
| Maintenance | Low - self-cleaning effect reduces cleaning frequency | Moderate - requires regular cleaning |
| Application in Skylight | Ideal for areas needing water repellency and low maintenance | Best for safety and structural integrity in skylight glazing |
Introduction to Skylight Glass Options
Skylight glass options primarily include superhydrophobic glass and laminated glass, each offering unique advantages. Superhydrophobic glass features a water-repellent coating that maintains clarity by preventing water and dirt accumulation, ideal for skylights exposed to harsh weather. Laminated glass provides enhanced safety and impact resistance through multiple bonded layers, making it suitable for skylight installations requiring durability and security.
What Is Superhydrophobic Glass?
Superhydrophobic glass features a nanoscale coating that repels water, preventing droplets from sticking and enhancing visibility and cleanliness on skylights. Laminated glass consists of multiple layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, offering enhanced safety, impact resistance, and UV protection for skylight applications. The hydrophobic properties of superhydrophobic glass reduce maintenance and improve daylight transmission, making it ideal for skylights exposed to rain and pollution.
Laminated Glass: Composition and Features
Laminated glass for skylights consists of two or more glass layers bonded together with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which enhances safety and durability by preventing shattering upon impact. This composition allows laminated glass to provide superior impact resistance, UV protection, and noise reduction compared to traditional glass types. Its structural integrity and ability to maintain transparency under pressure make it an ideal choice for skylight applications requiring enhanced security and energy efficiency.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Superhydrophobic glass for skylights offers exceptional durability due to its self-cleaning properties that repel water, dirt, and debris, reducing surface wear and maintenance frequency. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers bonded with interlayers, provides enhanced impact resistance and structural integrity, which significantly extends its lifespan under mechanical stress and weather fluctuations. While laminated glass excels in shatter resistance and safety, superhydrophobic coatings contribute to prolonged clarity and surface preservation, making them complementary in durability and longevity considerations.
Self-Cleaning Properties and Maintenance
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior self-cleaning properties for skylights due to its water-repellent surface, which minimizes dirt accumulation and reduces the need for frequent cleaning. Laminated glass, while providing enhanced safety and durability through its interlayer, lacks inherent self-cleaning capabilities and typically requires regular maintenance to remove dust and debris. Choosing superhydrophobic glass significantly lowers long-term upkeep costs by leveraging its naturally dirt-resistant and easy-to-clean surface.
Safety and Security Considerations
Superhydrophobic glass for skylights enhances safety by repelling water, reducing the risk of water damage and maintaining clear visibility, which helps prevent accidents caused by impaired vision. Laminated glass offers superior security benefits through its multi-layer composition that holds shards in place upon breakage, significantly reducing injury risks and deterring forced entry. Choosing between superhydrophobic and laminated glass depends on prioritizing weather resistance versus impact and intrusion protection for optimal skylight safety.
Light Transmission and Aesthetic Impacts
Superhydrophobic glass for skylights offers superior light transmission due to its enhanced water repellency, maintaining clarity by preventing water stains and dirt accumulation on the surface. Laminated glass provides robust safety and UV protection but can slightly reduce light transmission because of its interlayer, potentially causing minor optical distortion. From an aesthetic perspective, superhydrophobic glass preserves a pristine, clear appearance over time, while laminated glass may exhibit subtle haze from the interlayer, affecting visual clarity.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation
Superhydrophobic glass for skylights enhances energy efficiency by repelling water and dirt, maintaining optimal solar heat gain and natural light transmission without frequent cleaning, which reduces HVAC load. Laminated glass offers superior insulation due to its multi-layer structure that minimizes heat transfer and enhances thermal comfort while providing safety benefits through impact resistance. Both materials improve energy performance, but laminated glass excels in insulation, whereas superhydrophobic glass optimizes maintenance and light efficiency.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Lifetime Value
Superhydrophobic glass for skylights offers higher upfront installation costs due to advanced nanocoating technologies but reduces long-term maintenance expenses by repelling water, dirt, and contaminants more effectively than laminated glass. Laminated glass typically presents lower initial costs and provides enhanced safety and impact resistance, yet may require more frequent cleaning and replacement, increasing lifetime expenses. Evaluating lifetime value involves balancing superhydrophobic glass's durability and self-cleaning efficiency against laminated glass's cost-efficiency and structural protection benefits.
Which Glass Type Is Best for Skylights?
Superhydrophobic glass is ideal for skylights due to its self-cleaning properties and water-repellent surface, reducing maintenance and improving natural light clarity. Laminated glass offers superior safety with its shatter-resistant layers, providing enhanced protection against impact and extreme weather conditions. For skylights, selecting superhydrophobic glass ensures optimal transparency and durability, while laminated glass prioritizes safety and structural integrity.
Infographic: Superhydrophobic glass vs Laminated glass for Skylight
 azmater.com
azmater.com