Smart glass offers adaptive thermal insulation by regulating heat transfer through dynamic opacity, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. Foam glass provides stable, high-performance insulation with excellent compressive strength and moisture resistance, ideal for durable, long-lasting thermal barriers.
Table of Comparison
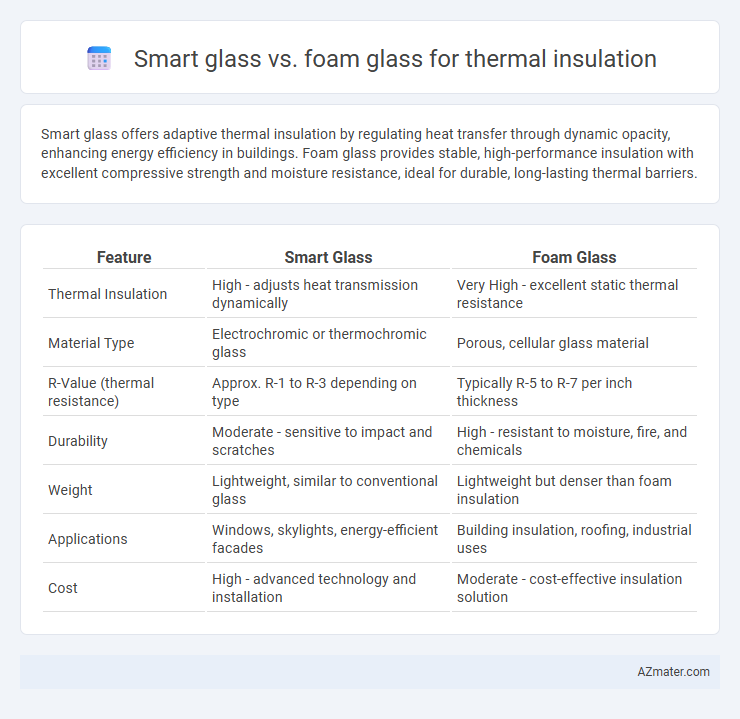
| Feature | Smart Glass | Foam Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High - adjusts heat transmission dynamically | Very High - excellent static thermal resistance |
| Material Type | Electrochromic or thermochromic glass | Porous, cellular glass material |
| R-Value (thermal resistance) | Approx. R-1 to R-3 depending on type | Typically R-5 to R-7 per inch thickness |
| Durability | Moderate - sensitive to impact and scratches | High - resistant to moisture, fire, and chemicals |
| Weight | Lightweight, similar to conventional glass | Lightweight but denser than foam insulation |
| Applications | Windows, skylights, energy-efficient facades | Building insulation, roofing, industrial uses |
| Cost | High - advanced technology and installation | Moderate - cost-effective insulation solution |
Introduction to Thermal Insulation Materials
Thermal insulation materials like smart glass and foam glass are engineered to reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency in buildings. Smart glass utilizes electrochromic or thermochromic technology to dynamically control solar heat gain and light transmission, while foam glass offers excellent thermal resistance with low thermal conductivity due to its closed-cell, porous structure. Both materials contribute to reducing energy consumption but differ in application, with smart glass ideal for adaptive environments and foam glass suited for structural insulation needs.
What is Smart Glass?
Smart glass is an advanced glazing technology that dynamically controls heat and light transmission through electrical or chemical means, enhancing thermal insulation by reducing energy loss and improving indoor comfort. Unlike foam glass, a rigid insulation material made from recycled glass with high compressive strength and low thermal conductivity, smart glass adapts to changing environmental conditions to optimize solar heat gain and natural lighting. This adaptive capability makes smart glass a versatile solution for energy-efficient building designs aiming to minimize heating and cooling demands.
What is Foam Glass?
Foam glass is a lightweight, rigid insulation material made from recycled glass combined with a foaming agent, creating a closed-cell structure that offers exceptional thermal insulation and moisture resistance. Unlike smart glass, which primarily controls light and heat transmission through electrochromic technology, foam glass excels in providing durable, non-combustible insulation for extreme temperature conditions in industrial and building applications. Its high compressive strength and resistance to chemicals make foam glass an ideal choice for long-lasting thermal insulation solutions.
How Smart Glass Provides Thermal Insulation
Smart glass enhances thermal insulation by dynamically controlling solar heat gain through electrochromic or thermochromic technologies, adjusting transparency based on external temperatures and sunlight intensity. This reduces reliance on HVAC systems by limiting heat loss in winter and minimizing heat ingress during summer, improving energy efficiency. Unlike foam glass, which provides static insulation through its porous structure, smart glass offers adaptive thermal management tailored to environmental conditions.
Thermal Properties of Foam Glass
Foam glass offers superior thermal insulation due to its closed-cell structure, delivering low thermal conductivity typically around 0.04 W/m*K, which effectively reduces heat transfer in building envelopes. Unlike smart glass, foam glass provides consistent insulating performance without requiring electrical input or adjustment, making it highly energy-efficient for permanent insulation applications. Its high compressive strength and resistance to moisture further enhance its thermal stability and durability in diverse environmental conditions.
Energy Efficiency: Smart Glass vs. Foam Glass
Smart glass enhances energy efficiency by dynamically controlling solar heat gain and natural daylight, reducing reliance on HVAC systems and lighting, which cuts electricity consumption. Foam glass offers superior thermal insulation due to its closed-cell structure, minimizing heat transfer and effectively maintaining indoor temperatures with high compressive strength and moisture resistance. Both materials improve energy efficiency, but smart glass optimizes energy use through adaptive transparency, while foam glass provides robust, passive thermal insulation.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Smart glass offers moderate durability with a typical lifespan of 10 to 20 years, influenced by coating quality and environmental exposure, whereas foam glass provides exceptional durability, often lasting over 50 years due to its resistance to moisture, fire, and chemical corrosion. The rigid structure of foam glass enhances its stability in harsh conditions, making it more reliable for long-term thermal insulation applications compared to the more fragile smart glass. Maintenance requirements for foam glass are minimal, while smart glass may require periodic replacement or repairs to maintain optimal thermal performance and functionality.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Smart glass offers straightforward installation with minimal structural modifications, as it integrates directly into window frames, reducing labor costs and installation time compared to foam glass. Foam glass requires more specialized handling and precise cutting to fit insulation cavities, often involving adhesives or mechanical fastening, which can increase installation complexity. Maintenance for smart glass is generally limited to electronic component checks and occasional cleaning, whereas foam glass demands periodic inspections for cracks or moisture ingress to maintain its insulating properties and structural integrity.
Cost Analysis: Smart Glass Versus Foam Glass
Smart glass generally commands a higher initial investment compared to foam glass due to advanced technology and manufacturing complexities, with costs ranging from $50 to $150 per square foot versus foam glass's $20 to $60 per square foot. While smart glass offers dynamic thermal regulation and energy savings over time, foam glass provides consistent insulation with minimal maintenance, often resulting in lower long-term operational expenses. Evaluating payback periods, smart glass may achieve cost-effectiveness in high-energy-cost regions through reduced HVAC loads, whereas foam glass remains a budget-friendly, durable option for static thermal insulation needs.
Choosing the Right Insulation for Your Project
Smart glass offers dynamic control of solar heat gain, reducing cooling costs and enhancing occupant comfort, making it ideal for projects focused on energy efficiency and daylight management. Foam glass provides excellent thermal insulation with superior compressive strength, moisture resistance, and fireproof properties, suitable for harsh environments and structural applications. Choosing the right insulation depends on project requirements such as climate control, durability, and installation logistics, with smart glass best for adaptive thermal regulation and foam glass ideal for static, high-performance insulation.
Infographic: Smart glass vs Foam glass for Thermal insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com