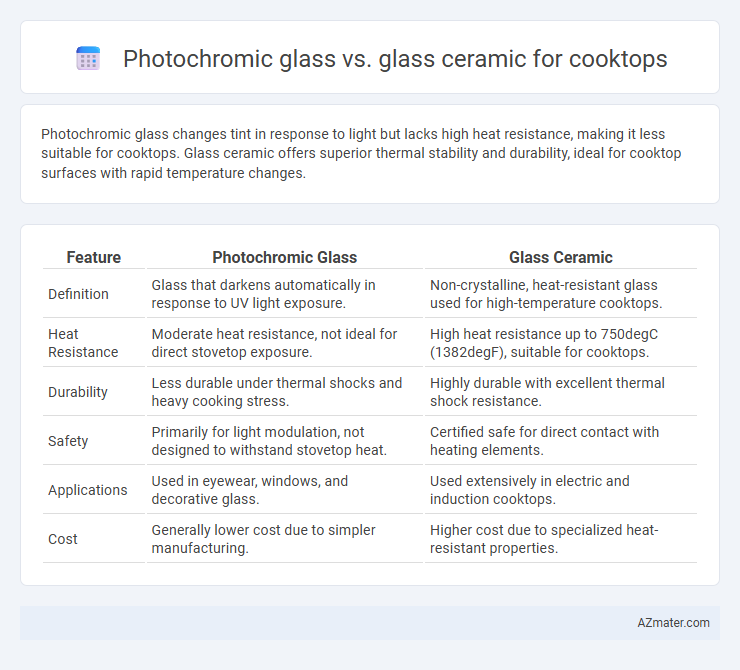
Photochromic glass changes tint in response to light but lacks high heat resistance, making it less suitable for cooktops. Glass ceramic offers superior thermal stability and durability, ideal for cooktop surfaces with rapid temperature changes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Photochromic Glass | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Glass that darkens automatically in response to UV light exposure. | Non-crystalline, heat-resistant glass used for high-temperature cooktops. |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat resistance, not ideal for direct stovetop exposure. | High heat resistance up to 750degC (1382degF), suitable for cooktops. |
| Durability | Less durable under thermal shocks and heavy cooking stress. | Highly durable with excellent thermal shock resistance. |
| Safety | Primarily for light modulation, not designed to withstand stovetop heat. | Certified safe for direct contact with heating elements. |
| Applications | Used in eyewear, windows, and decorative glass. | Used extensively in electric and induction cooktops. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to simpler manufacturing. | Higher cost due to specialized heat-resistant properties. |
Introduction to Cooktop Material Options
Photochromic glass offers dynamic light adjustment properties, enhancing visibility and aesthetic appeal in cooktops, while glass ceramic is prized for its high thermal stability and durability under intense heat. Cooktop materials must withstand rapid temperature changes, resist thermal shock, and provide a smooth surface for efficient cooking, making glass ceramic a leading choice for professional and home kitchens. Selecting between photochromic glass and glass ceramic depends on prioritizing either adaptive light control or superior heat resistance and scratch durability.
What is Photochromic Glass?
Photochromic glass is a type of material that dynamically changes its tint in response to sunlight or ultraviolet (UV) exposure, making it ideal for controlling light and heat. Unlike glass ceramic used for cooktops, which is engineered for high thermal resistance and durability under direct heat, photochromic glass focuses on adaptive transparency to enhance energy efficiency and comfort. This technology is particularly useful in automotive and architectural applications rather than high-temperature cooking surfaces.
Understanding Glass Ceramic for Cooktops
Glass ceramic for cooktops offers exceptional heat resistance and thermal shock durability, allowing rapid temperature changes without cracking. Its surface remains smooth and easy to clean, while providing excellent energy efficiency by concentrating heat directly on cookware. Unlike photochromic glass, which changes tint with light exposure, glass ceramic prioritizes functional performance and safety in high-temperature cooking environments.
Heat Resistance: Photochromic Glass vs Glass Ceramic
Photochromic glass exhibits moderate heat resistance suitable for low-temperature applications, but it rapidly darkens under intense heat, which may limit visibility and performance on cooktops. Glass ceramic demonstrates superior heat resistance, withstanding thermal shock up to 800degC and maintaining structural integrity during direct high-temperature cooking processes. This makes glass ceramic the preferred material for cooktops where consistent heat tolerance and durability are critical.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Photochromic glass offers moderate durability with the ability to change tint based on light exposure, but it may degrade faster under constant heat and frequent temperature changes typical of cooktops. Glass ceramic cooktops are engineered for high thermal resistance and mechanical strength, providing superior durability and a longer lifespan, often exceeding 10 years with proper care. The heat tolerance of glass ceramic, typically over 700degC, surpasses that of photochromic glass, making it the optimal choice for long-lasting, heat-intensive cooking surfaces.
Aesthetic and Design Possibilities
Photochromic glass offers dynamic aesthetic appeal by changing color or tint in response to light, enabling cooktops to adapt visually to ambient lighting or user preferences. Glass ceramic provides a sleek, uniform surface with superb heat resistance and durability, allowing for seamless integration of touch controls and customizable patterns without compromising functionality. Both materials enhance design flexibility, with photochromic glass emphasizing interactive visual effects and glass ceramic prioritizing minimalist, timeless elegance.
Safety Features of Each Material
Photochromic glass offers advanced UV protection by darkening in response to sunlight, reducing glare and potential burns while cooking. Glass ceramic cooktops feature high thermal shock resistance and evenly distribute heat, minimizing the risk of cracking and enhancing overall safety during temperature fluctuations. Both materials provide robust durability, but glass ceramic ensures superior heat tolerance and resistance to mechanical impact, making it ideal for high-temperature cooking surfaces.
Maintenance and Cleaning Differences
Photochromic glass requires gentle cleaning with non-abrasive, pH-neutral solutions to prevent damage to its light-reactive coatings, ensuring long-lasting performance and appearance. Glass ceramic cooktops are more durable and can tolerate stronger, specialized cooktop cleaners that effectively remove grease and burnt residues without harming the surface. Maintenance of photochromic glass demands extra caution to avoid scratching, while glass ceramic cooktops benefit from easier cleaning routines due to their heat-resistant and stain-resistant properties.
Cost Considerations: Which is More Affordable?
Photochromic glass cooktops generally come with higher upfront costs due to advanced light-sensitive technology, making them less affordable for budget-conscious consumers. Glass ceramic cooktops, widely used in kitchens, offer a more economical option with durable heat resistance and easier manufacturing processes, reducing overall expenses. For cost-effective cooking surfaces, glass ceramic provides better value without compromising functionality.
Verdict: Choosing the Right Cooktop Material
Photochromic glass offers adaptive light control and a sleek modern look but may lack the high thermal resistance required for cooktops. Glass ceramic excels with superior heat tolerance, durability, and uniform heat distribution, making it ideal for cooking surfaces. For cooktop applications, glass ceramic remains the preferred choice due to its optimal performance under intense heat and longevity.
Infographic: Photochromic glass vs Glass ceramic for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com