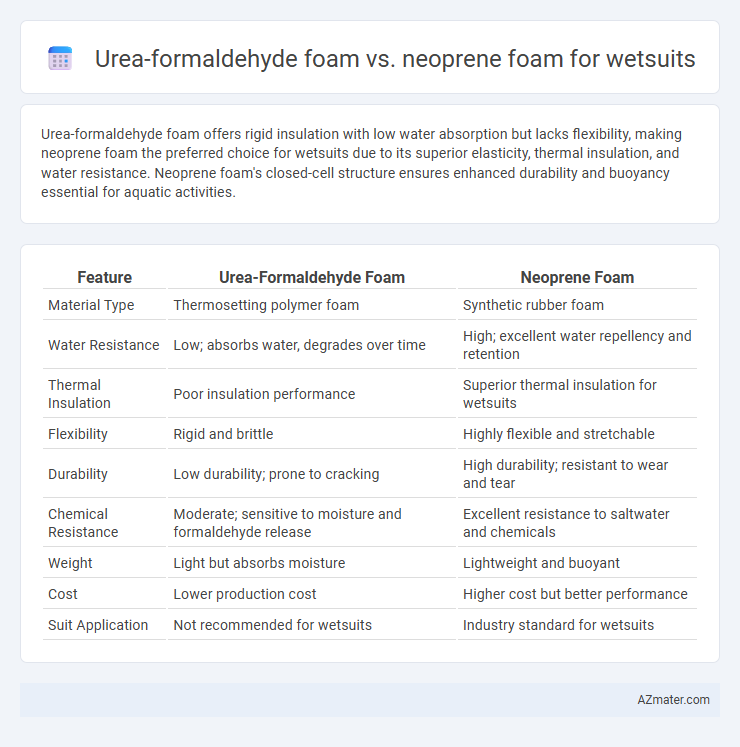
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers rigid insulation with low water absorption but lacks flexibility, making neoprene foam the preferred choice for wetsuits due to its superior elasticity, thermal insulation, and water resistance. Neoprene foam's closed-cell structure ensures enhanced durability and buoyancy essential for aquatic activities.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Urea-Formaldehyde Foam | Neoprene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermosetting polymer foam | Synthetic rubber foam |
| Water Resistance | Low; absorbs water, degrades over time | High; excellent water repellency and retention |
| Thermal Insulation | Poor insulation performance | Superior thermal insulation for wetsuits |
| Flexibility | Rigid and brittle | Highly flexible and stretchable |
| Durability | Low durability; prone to cracking | High durability; resistant to wear and tear |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate; sensitive to moisture and formaldehyde release | Excellent resistance to saltwater and chemicals |
| Weight | Light but absorbs moisture | Lightweight and buoyant |
| Cost | Lower production cost | Higher cost but better performance |
| Suit Application | Not recommended for wetsuits | Industry standard for wetsuits |
Introduction to Wet Suit Materials
Urea-formaldehyde foam and neoprene foam serve different purposes as wetsuit materials, with neoprene being the industry standard due to its superior flexibility and insulation properties. Neoprene foam is a synthetic rubber that provides excellent thermal protection by trapping heat and repelling water, making it ideal for extended underwater use. Urea-formaldehyde foam, less common in wetsuits, offers rigidity but lacks the stretch and durability required for effective cold water performance.
Overview of Urea-formaldehyde Foam
Urea-formaldehyde foam is a rigid, closed-cell foam known for its excellent thermal insulation and high compressive strength, making it a suitable material for wetsuit cores when warmth retention is critical. Compared to neoprene foam, urea-formaldehyde exhibits lower flexibility and durability under repeated flexing but offers superior moisture resistance and structural stability in wet environments. Its chemical composition provides enhanced resistance to water absorption, which contributes to improved buoyancy and insulation in aquatic activities.
Overview of Neoprene Foam
Neoprene foam, a synthetic rubber material, is widely used in wetsuit manufacturing due to its excellent thermal insulation, flexibility, and durability in aquatic environments. It features a closed-cell structure that provides superior water resistance and buoyancy compared to urea-formaldehyde foam, which is less flexible and more brittle when wet. Neoprene's resistance to chemical degradation and UV exposure makes it the preferred choice for wetsuits designed for prolonged use and harsh conditions.
Thermal Insulation Properties Comparison
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers excellent thermal insulation due to its closed-cell structure, which minimizes heat transfer and enhances buoyancy in wetsuits. Neoprene foam, widely used for wetsuits, provides superior flexibility and retains heat effectively through its nitrogen gas-filled cells, ensuring comfort in cold water. While both foams provide insulation, neoprene's balance of thermal retention and elasticity makes it the preferred choice for wetsuit applications.
Flexibility and Comfort Differences
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers moderate flexibility but tends to be stiffer and less compressible compared to neoprene foam, which is widely used in wetsuits for its superior elasticity and ability to conform closely to the body. Neoprene foam provides enhanced comfort due to its lightweight, cushioning properties, and excellent water resistance, maintaining insulation even when wet. The flexibility of neoprene significantly improves range of motion and reduces fatigue during aquatic activities, making it the preferred material for wetsuit construction over the more rigid urea-formaldehyde foam.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Urea-formaldehyde foam exhibits higher rigidity but lower flexibility compared to neoprene foam, resulting in reduced durability under repeated bending and flexing typical in wetsuit use. Neoprene foam offers superior elasticity and resistance to water absorption, significantly extending wetsuit lifespan by maintaining structural integrity and thermal insulation over time. Studies indicate neoprene wetsuits can last up to 3-5 years with regular use, whereas urea-formaldehyde foam degrades faster due to brittleness and moisture susceptibility.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Urea-formaldehyde foam, commonly used as insulation, releases formaldehyde gas during production and decomposition, posing significant environmental and health risks, and it is not biodegradable, leading to long-term waste issues. Neoprene foam, widely used in wetsuits, traditionally relies on petroleum-based processes but newer formulations incorporating limestone and recycled materials have improved its sustainability profile by reducing carbon footprint and enhancing recyclability. Choosing neoprene over urea-formaldehyde foam for wetsuits significantly lowers environmental impact due to better chemical stability, reduced toxic emissions, and advancements in eco-friendly manufacturing technologies.
Water Resistance and Performance
Urea-formaldehyde foam lacks water resistance, absorbing moisture and degrading quickly in wet suit applications, which reduces thermal insulation and longevity. Neoprene foam offers superior water resistance with closed-cell structure that minimizes water absorption, maintaining insulation and flexibility during prolonged exposure. High-performance wet suits prioritize neoprene foam for durability, buoyancy, and thermal efficiency in aquatic environments.
Cost-Effectiveness Assessment
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers a lower initial cost compared to neoprene foam, making it a budget-friendly option for wetsuit insulation. However, its lower durability and water resistance can lead to higher replacement expenses over time. Neoprene foam provides superior thermal insulation and longevity, resulting in better long-term cost-effectiveness despite a higher upfront investment.
Final Verdict: Which Foam is Better for Wet Suits?
Neoprene foam is superior to urea-formaldehyde foam for wetsuits due to its exceptional flexibility, durability, and superior thermal insulation properties. Urea-formaldehyde foam lacks the flexibility and water resistance necessary for prolonged use in wetsuits, leading to faster degradation and reduced comfort. Choosing neoprene ensures enhanced performance, longevity, and comfort in aquatic environments.
Infographic: Urea-formaldehyde foam vs Neoprene foam for Wet suit
 azmater.com
azmater.com