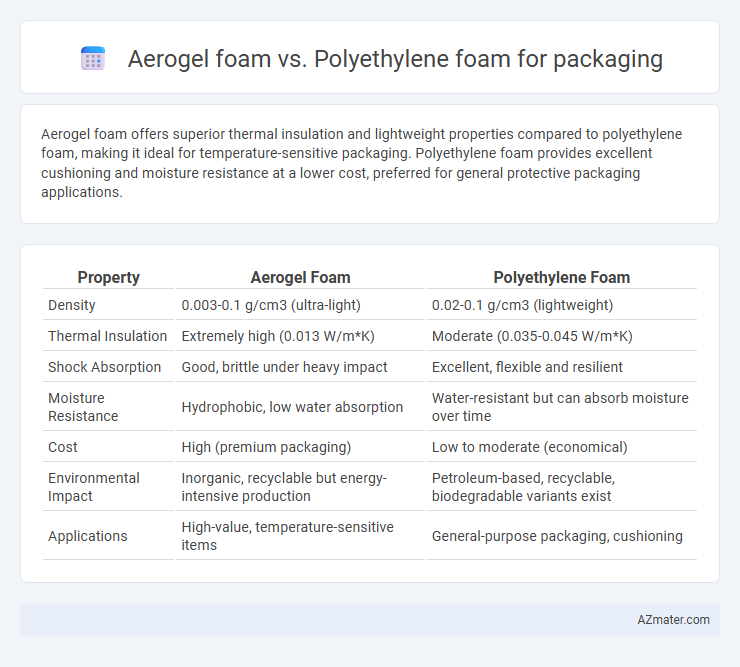
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for temperature-sensitive packaging. Polyethylene foam provides excellent cushioning and moisture resistance at a lower cost, preferred for general protective packaging applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aerogel Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.003-0.1 g/cm3 (ultra-light) | 0.02-0.1 g/cm3 (lightweight) |
| Thermal Insulation | Extremely high (0.013 W/m*K) | Moderate (0.035-0.045 W/m*K) |
| Shock Absorption | Good, brittle under heavy impact | Excellent, flexible and resilient |
| Moisture Resistance | Hydrophobic, low water absorption | Water-resistant but can absorb moisture over time |
| Cost | High (premium packaging) | Low to moderate (economical) |
| Environmental Impact | Inorganic, recyclable but energy-intensive production | Petroleum-based, recyclable, biodegradable variants exist |
| Applications | High-value, temperature-sensitive items | General-purpose packaging, cushioning |
Introduction to Aerogel and Polyethylene Foams
Aerogel foam, known for its ultra-low density and excellent thermal insulation, is composed of a nanoporous silica structure that offers superior protection against temperature fluctuations and mechanical shocks. Polyethylene foam, a closed-cell polymer material, provides lightweight cushioning, moisture resistance, and impact absorption suitable for a wide range of packaging applications. The distinct physical properties of aerogel foam, including high porosity and thermal barrier capabilities, contrast with the flexible, durable, and economical nature of polyethylene foam, influencing material selection based on packaging requirements.
Material Composition and Properties
Aerogel foam, composed primarily of silica or other nanoporous materials, offers exceptional thermal insulation and lightweight properties with a density as low as 0.003 g/cm3, making it ideal for protecting sensitive items against extreme temperature fluctuations. In contrast, polyethylene foam is made from polymerized ethylene, characterized by its flexibility, impact resistance, and moisture resistance, with a typical density range of 20-60 kg/m3 suitable for cushioning and shock absorption in packaging. The superior compressive strength and low thermal conductivity of aerogel foam provide advantages in high-performance packaging, whereas polyethylene foam excels in cost-effectiveness and versatility for general protective applications.
Weight and Density Comparison
Aerogel foam exhibits an ultra-low density typically ranging from 0.003 to 0.1 g/cm3, significantly lighter than polyethylene foam, which usually has a density between 0.02 and 0.05 g/cm3. The lightweight nature of aerogel foam enhances its suitability for high-performance packaging applications requiring minimal added weight without sacrificing protection. Polyethylene foam, while denser and heavier, offers reliable cushioning at a lower cost but may increase overall shipping weight compared to aerogel-based solutions.
Thermal Insulation Capabilities
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation capabilities compared to polyethylene foam due to its ultra-low thermal conductivity and porous nanostructure, effectively minimizing heat transfer. Polyethylene foam provides moderate insulation, primarily relying on trapped air pockets, but its thermal resistance is significantly lower than that of aerogel foam. For packaging applications requiring high-temperature stability and protection against extreme thermal fluctuations, aerogel foam is the optimal choice.
Shock Absorption and Cushioning Performance
Aerogel foam offers superior shock absorption and cushioning performance compared to polyethylene foam due to its ultra-lightweight, high porosity, and exceptional resilience under impact. Its nanostructured matrix efficiently dissipates kinetic energy, reducing the risk of damage to fragile items during transit. Polyethylene foam provides adequate cushioning but falls short in energy absorption and weight efficiency, making aerogel foam a preferred choice for high-performance packaging applications.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Aerogel foam offers superior moisture resistance due to its hydrophobic properties and extremely low permeability, making it highly effective in preventing water absorption and chemical infiltration. Polyethylene foam resists moisture but is more susceptible to chemical degradation, especially when exposed to solvents and oils over time. For packaging applications requiring robust protection against humid or chemically aggressive environments, aerogel foam outperforms polyethylene foam by maintaining integrity and preventing contamination.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aerogel foam outperforms polyethylene foam in environmental impact due to its superior thermal insulation and biodegradability, reducing energy consumption and landfill waste. Polyethylene foam, derived from non-renewable petroleum and resistant to decomposition, contributes significantly to plastic pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Choosing aerogel foam enhances sustainability by promoting eco-friendly disposal and lowering carbon footprint during packaging and transportation processes.
Cost Analysis for Packaging Applications
Aerogel foam typically incurs higher initial costs compared to polyethylene foam due to its advanced manufacturing processes and superior thermal insulation properties. Polyethylene foam remains a cost-effective choice for packaging applications, offering excellent cushioning at a fraction of aerogel's price, making it preferable for large-scale or budget-sensitive projects. Evaluating total cost of ownership involves balancing aerogel's premium benefits against polyethylene foam's affordability and widespread availability in packaging solutions.
Use Cases in Various Industries
Aerogel foam excels in thermal insulation and lightweight protection, making it ideal for aerospace, electronics, and pharmaceutical packaging where temperature sensitivity and shock absorption are critical. Polyethylene foam is widely used in automotive, consumer goods, and food industries due to its durability, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness for cushioning and impact protection. Both materials serve distinct use cases: aerogel foam for high-performance insulation and delicate items, polyethylene foam for affordable, versatile packaging solutions.
Choosing the Right Foam for Packaging Needs
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation and cushioning properties, making it ideal for packaging sensitive electronics or temperature-sensitive goods. Polyethylene foam provides excellent shock absorption, durability, and moisture resistance at a lower cost, suitable for general packaging and shipping applications. Selecting the right foam depends on prioritizing insulation performance versus cost-efficiency and protection level for the packaged items.
Infographic: Aerogel foam vs Polyethylene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com