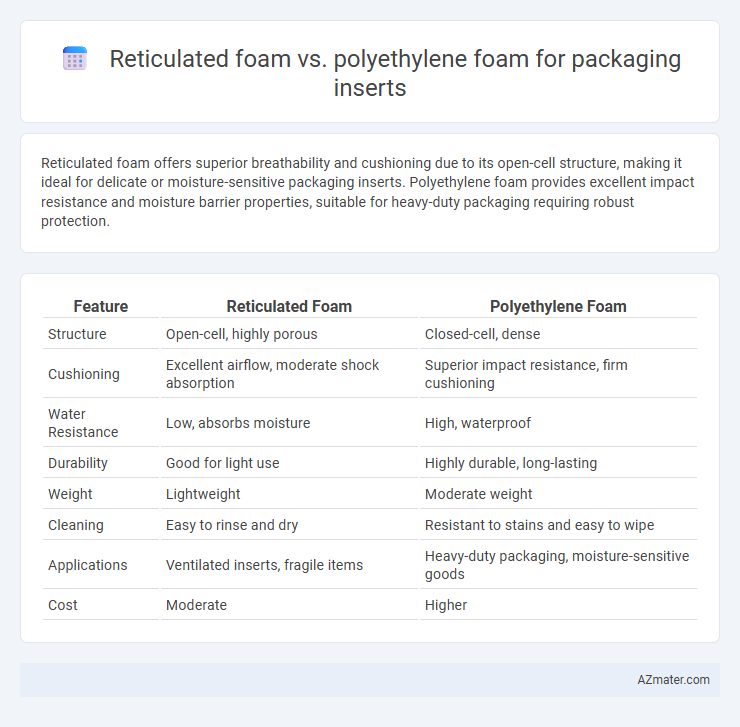
Reticulated foam offers superior breathability and cushioning due to its open-cell structure, making it ideal for delicate or moisture-sensitive packaging inserts. Polyethylene foam provides excellent impact resistance and moisture barrier properties, suitable for heavy-duty packaging requiring robust protection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Reticulated Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Open-cell, highly porous | Closed-cell, dense |
| Cushioning | Excellent airflow, moderate shock absorption | Superior impact resistance, firm cushioning |
| Water Resistance | Low, absorbs moisture | High, waterproof |
| Durability | Good for light use | Highly durable, long-lasting |
| Weight | Lightweight | Moderate weight |
| Cleaning | Easy to rinse and dry | Resistant to stains and easy to wipe |
| Applications | Ventilated inserts, fragile items | Heavy-duty packaging, moisture-sensitive goods |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to Packaging Foam Materials
Reticulated foam and polyethylene foam serve distinct roles in packaging inserts due to their structural and material properties. Reticulated foam, characterized by its open-cell, highly porous structure, allows excellent airflow and cushioning, making it ideal for protective packaging of delicate items that require shock absorption and ventilation. Polyethylene foam, a closed-cell, dense material, excels in providing superior impact resistance and moisture barrier, widely used in packaging applications where durability and protection against environmental factors are critical.
What is Reticulated Foam?
Reticulated foam is an open-cell foam characterized by its high permeability, allowing air and liquids to pass freely through its interconnected pore structure, making it ideal for cushioning and protective packaging inserts. Unlike polyethylene foam, which is closed-cell and denser, reticulated foam provides superior breathability and impact absorption, safeguarding delicate items during transportation. Its lightweight and durable nature ensures enhanced shock resistance while minimizing material bulk in packaging applications.
What is Polyethylene Foam?
Polyethylene foam is a durable, closed-cell foam known for its excellent shock absorption, moisture resistance, and lightweight properties, making it ideal for protective packaging inserts. Its versatility and ability to provide cushioning for sensitive items protect products from impact damage during shipping and handling. Compared to reticulated foam, polyethylene foam offers superior resistance to water, chemicals, and compression, enhancing the longevity and reliability of packaging solutions.
Key Differences: Structure and Composition
Reticulated foam features an open-cell structure with interconnected pores, providing high breathability and impact absorption, whereas polyethylene foam has a closed-cell structure offering superior resistance to moisture and compression. The composition of reticulated foam typically involves polyurethane, making it lightweight and flexible, while polyethylene foam consists of polymerized ethylene, resulting in a denser and more resilient material. These structural and compositional differences influence their suitability for packaging inserts, with reticulated foam excelling in cushioning delicate items and polyethylene foam offering robust protection against moisture and vibration.
Cushioning Performance Comparison
Reticulated foam exhibits superior air flow and compression resilience due to its open-cell structure, making it highly effective for cushioning fragile items in packaging inserts. Polyethylene foam, with its closed-cell structure, offers excellent impact absorption and moisture resistance but tends to be denser and less breathable than reticulated foam. For applications requiring lightweight cushioning with enhanced breathability, reticulated foam outperforms polyethylene foam, while polyethylene foam excels in providing robust, moisture-resistant protection.
Durability and Longevity
Reticulated foam offers superior durability with its open-cell structure that resists compression and maintains shape over extended use, making it ideal for delicate or repeatedly handled packaging inserts. Polyethylene foam provides excellent longevity due to its closed-cell composition, which enhances moisture resistance and prevents degradation from environmental stressors. Both materials ensure protection, but reticulated foam excels in impact absorption, while polyethylene foam outperforms in water and chemical resistance.
Customization and Design Flexibility
Reticulated foam offers superior customization and design flexibility for packaging inserts due to its open-cell structure, allowing precise cutting and shaping to fit complex product contours. Polyethylene foam, while durable and impact-resistant, provides less intricate design options as its closed-cell composition limits detailed modifications. Choosing reticulated foam enhances tailored protection and aesthetic presentation in packaging applications requiring detailed inserts.
Cost Implications: Reticulated vs Polyethylene Foam
Reticulated foam typically offers lower material costs due to its open-cell structure, making it less dense and requiring less raw material than polyethylene foam, which is denser and more expensive. However, polyethylene foam provides superior cushioning and impact resistance, potentially reducing product damage and associated replacement costs, which can offset its higher initial price. Selecting the appropriate foam involves balancing upfront expense with long-term protection benefits, influencing overall packaging cost efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Reticulated foam, characterized by its open-cell structure, is highly recyclable and often made from thermoplastic materials like polyurethane, enabling efficient recovery and reuse in packaging inserts. Polyethylene foam, a closed-cell polymer, offers excellent cushioning but poses recycling challenges due to its chemical stability and limited acceptance in curbside programs, thereby increasing its environmental footprint. Choosing reticulated foam typically supports sustainable packaging goals by reducing landfill waste and facilitating circular economy practices compared to polyethylene foam.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Packaging Inserts
Reticulated foam offers excellent airflow and drainage due to its open-cell structure, making it ideal for packaging inserts that require breathability and cushioning for delicate items. Polyethylene foam provides superior impact resistance and moisture resistance with its closed-cell construction, suitable for heavy-duty protection and long-term storage. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing protection needs, weight considerations, and environmental factors specific to the packaged product.
Infographic: Reticulated foam vs Polyethylene foam for Packaging insert
 azmater.com
azmater.com