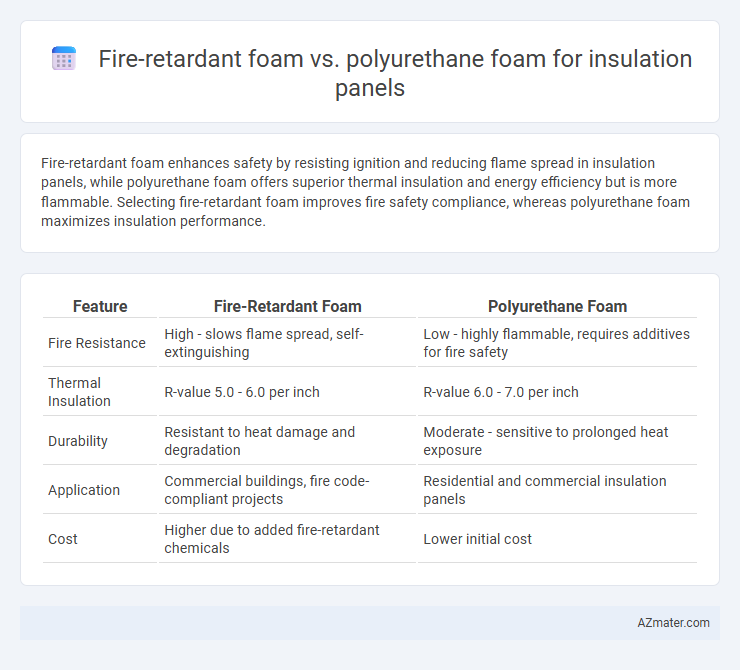
Fire-retardant foam enhances safety by resisting ignition and reducing flame spread in insulation panels, while polyurethane foam offers superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency but is more flammable. Selecting fire-retardant foam improves fire safety compliance, whereas polyurethane foam maximizes insulation performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire-Retardant Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | High - slows flame spread, self-extinguishing | Low - highly flammable, requires additives for fire safety |
| Thermal Insulation | R-value 5.0 - 6.0 per inch | R-value 6.0 - 7.0 per inch |
| Durability | Resistant to heat damage and degradation | Moderate - sensitive to prolonged heat exposure |
| Application | Commercial buildings, fire code-compliant projects | Residential and commercial insulation panels |
| Cost | Higher due to added fire-retardant chemicals | Lower initial cost |
Introduction to Insulation Panel Materials
Fire-retardant foam and polyurethane foam are two primary materials used in insulation panels, each offering distinct thermal resistance and safety properties. Fire-retardant foam is engineered with chemical additives that inhibit combustion, making it ideal for enhancing building fire safety standards. Polyurethane foam provides superior thermal insulation due to its closed-cell structure, resulting in high R-values and energy efficiency for residential and commercial applications.
Understanding Fire-Retardant Foam
Fire-retardant foam for insulation panels is specifically engineered to resist ignition and slow the spread of flames, enhancing building safety compared to standard polyurethane foam. This foam typically contains chemical additives that form a protective char layer when exposed to heat, reducing flammability and toxic smoke emissions. Its use in insulation panels is common in commercial and residential buildings requiring higher fire safety standards and compliance with strict building codes.
What is Polyurethane Foam?
Polyurethane foam is a versatile insulation material composed of polymer chains formed by the reaction of polyols and isocyanates, offering high thermal resistance and lightweight properties. This closed-cell foam provides excellent moisture resistance and soundproofing, making it widely used in building panels for energy efficiency. Compared to fire-retardant foam, polyurethane foam requires additional treatments or additives to enhance its fire resistance and meet safety regulations in insulation applications.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Fire-retardant foam offers enhanced thermal stability and maintains insulating properties at elevated temperatures, reducing heat transfer more effectively than standard polyurethane foam. Polyurethane foam provides superior initial thermal resistance due to its low thermal conductivity but may degrade faster under fire exposure, leading to increased thermal conductivity over time. Choosing fire-retardant foam enhances long-term thermal performance and safety in insulation panels exposed to high heat conditions.
Fire Resistance and Safety Standards
Fire-retardant foam used in insulation panels is specially formulated to inhibit ignition, slow flame spread, and reduce smoke production, meeting rigorous fire safety standards such as ASTM E84 Class A and UL 94 V-0 ratings. Polyurethane foam, while offering excellent thermal insulation with R-values typically ranging from 6 to 7 per inch, is inherently more flammable and often requires additional fire retardant additives or protective coverings to comply with fire resistance regulations. Choosing fire-retardant foam ensures enhanced safety in residential and commercial buildings by minimizing fire hazards and improving compliance with building codes that prioritize occupant protection.
Durability and Longevity
Fire-retardant foam offers enhanced durability due to its resistance to combustion and reduced degradation under high temperatures, making it suitable for long-term insulation panel applications. Polyurethane foam, while providing excellent thermal insulation, tends to degrade faster when exposed to heat and sunlight, potentially reducing its lifespan in demanding conditions. Choosing fire-retardant foam improves fire safety and ensures prolonged structural integrity and performance of insulation panels.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fire-retardant foam insulation panels typically contain halogenated flame retardants, which can release toxic chemicals during manufacturing and disposal, posing significant environmental hazards. Polyurethane foam, while offering excellent insulation properties and energy efficiency, relies on petrochemical-based components and often involves blowing agents with high global warming potential, impacting sustainability negatively. Choosing bio-based or non-toxic alternatives within both categories enhances environmental performance and aligns better with sustainable building practices.
Cost Analysis: Fire-Retardant vs Polyurethane Foam
Fire-retardant foam insulation panels typically incur higher initial costs compared to standard polyurethane foam due to added chemical treatments enhancing fire resistance. Despite the increased upfront investment, fire-retardant foam can reduce long-term expenses by minimizing fire damage risks and potentially lowering insurance premiums. Polyurethane foam panels offer lower installation costs but may require additional fire safety measures, impacting overall budget considerations.
Best Applications for Each Foam Type
Fire-retardant foam excels in applications requiring enhanced fire safety, such as commercial buildings, schools, and hospitals, due to its ability to resist ignition and slow flame spread. Polyurethane foam is ideal for residential insulation and cold storage facilities, offering superior thermal resistance and moisture control. Selecting between these foams depends on prioritizing fire protection or energy efficiency based on the insulation panel's specific use case.
Which Foam is Right for Your Insulation Needs?
Fire-retardant foam offers enhanced safety with flame-resistant properties suitable for areas with strict fire codes, while polyurethane foam provides superior thermal insulation and cost-efficiency. Choosing between the two depends on balancing fire safety requirements with the desired R-value and budget constraints for your insulation project. For environments demanding stringent fire protection, fire-retardant foam is ideal, whereas polyurethane foam excels in general applications prioritizing thermal performance.
Infographic: Fire-retardant foam vs Polyurethane foam for Insulation panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com