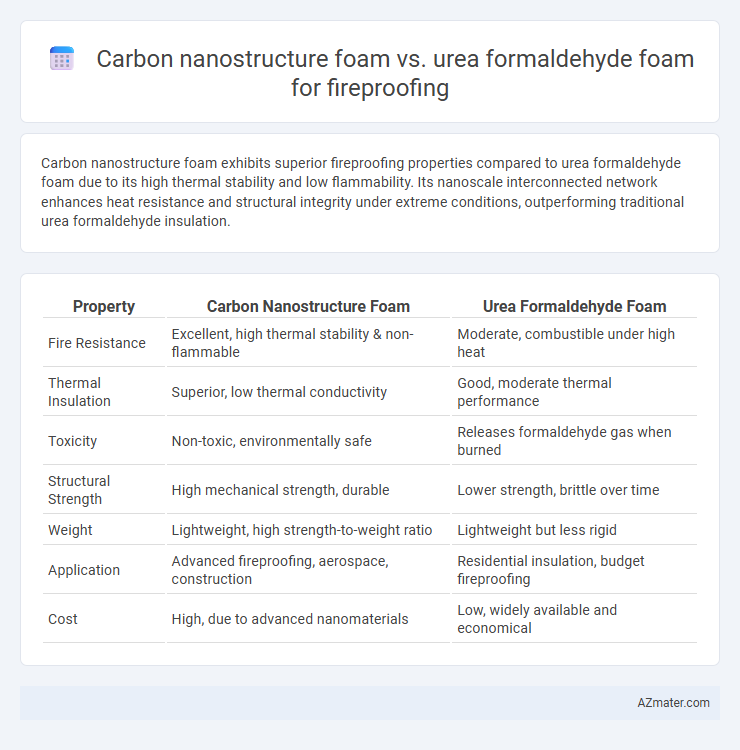
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior fireproofing properties compared to urea formaldehyde foam due to its high thermal stability and low flammability. Its nanoscale interconnected network enhances heat resistance and structural integrity under extreme conditions, outperforming traditional urea formaldehyde insulation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Nanostructure Foam | Urea Formaldehyde Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Excellent, high thermal stability & non-flammable | Moderate, combustible under high heat |
| Thermal Insulation | Superior, low thermal conductivity | Good, moderate thermal performance |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, environmentally safe | Releases formaldehyde gas when burned |
| Structural Strength | High mechanical strength, durable | Lower strength, brittle over time |
| Weight | Lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio | Lightweight but less rigid |
| Application | Advanced fireproofing, aerospace, construction | Residential insulation, budget fireproofing |
| Cost | High, due to advanced nanomaterials | Low, widely available and economical |
Introduction to Fireproofing Materials
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior thermal stability and fire resistance compared to conventional Urea Formaldehyde foam, making it an advanced option in fireproofing materials. Urea Formaldehyde foam, widely used for insulation, tends to release toxic gases upon combustion, highlighting safety concerns in fire scenarios. The development of carbon nanostructure foam addresses these limitations by offering enhanced flame retardancy and reduced smoke generation, critical factors in effective fireproofing solutions.
Overview of Carbon Nanostructure Foam
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits exceptional fireproofing properties due to its high thermal stability, low density, and excellent insulation capabilities, making it an advanced alternative to traditional Urea Formaldehyde foam. This nanostructured material effectively inhibits flame propagation and reduces heat transfer, enhancing safety in construction and industrial applications. Its structural integrity under extreme temperatures surpasses that of Urea Formaldehyde foam, which can degrade and release toxic gases when exposed to fire.
Overview of Urea Formaldehyde Foam
Urea formaldehyde foam is widely used in fireproofing due to its excellent thermal insulation properties and cost-effectiveness. It is a rigid, closed-cell foam that provides moderate fire resistance but tends to release toxic gases when exposed to high temperatures. Compared to carbon nanostructure foam, urea formaldehyde foam offers less durability and lower flame retardancy, limiting its application in high-performance fireproofing scenarios.
Thermal Resistance Capabilities
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to urea formaldehyde foam due to its high thermal stability and low thermal conductivity. Its unique nanostructured composition enables it to withstand temperatures exceeding 1500degC without degradation, making it ideal for extreme fireproofing applications. Urea formaldehyde foam, while cost-effective and providing moderate insulation, typically compromises at temperatures around 100degC to 120degC, limiting its effectiveness in high-temperature fire resistance scenarios.
Fire Retardancy Performance Comparison
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior fire retardancy compared to urea formaldehyde foam due to its high thermal stability and excellent heat dissipation properties, effectively slowing combustion and reducing flame propagation. Urea formaldehyde foam, while commonly used for insulation, tends to release toxic gases and degrade rapidly under high temperatures, compromising fire resistance. The nanostructured carbon foam's ability to maintain structural integrity and resist ignition under extreme heat conditions makes it a more effective fireproofing material.
Structural Integrity Under High Temperatures
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior structural integrity under high temperatures due to its exceptional thermal stability and low thermal conductivity, making it highly effective for fireproofing applications. In contrast, urea formaldehyde foam tends to degrade and lose mechanical strength when exposed to elevated temperatures, compromising its fire resistance and structural performance. The enhanced durability of carbon nanostructure foam ensures long-lasting protection in fire-prone environments, whereas urea formaldehyde foam requires frequent maintenance or replacement.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior fire resistance with minimal smoke and toxic gas emissions, significantly reducing environmental pollution compared to urea formaldehyde foam, which releases harmful formaldehyde and other volatile organic compounds during combustion. The non-toxic, stable nature of carbon nanostructure foam enhances indoor air quality and occupant safety by minimizing exposure to carcinogens and respiratory irritants commonly associated with urea formaldehyde foam. Its eco-friendly production and degradation profile contribute to lower environmental impact throughout the lifecycle, making carbon nanostructure foam a safer and more sustainable choice for fireproofing applications.
Installation and Application Methods
Carbon nanostructure foam offers advanced fireproofing with straightforward installation, typically applied via spray or pour methods allowing seamless integration into complex structures. Urea formaldehyde foam, while also used for fireproofing, requires careful mixing on-site and often needs protective coatings post-application to enhance fire resistance. The nanostructure foam provides superior adhesion and faster curing times, reducing labor costs and improving overall effectiveness in fire mitigation.
Cost Efficiency and Long-Term Value
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior fireproofing performance with enhanced thermal stability and mechanical strength, justifying its higher upfront cost through reduced maintenance and longer lifespan. Urea formaldehyde foam is significantly cheaper initially but tends to degrade faster under fire exposure, leading to increased replacement costs and potential safety risks over time. Investing in carbon nanostructure foam delivers better long-term value by minimizing lifecycle expenses and improving fire resistance efficiency.
Future Prospects: Innovations in Fireproof Foams
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior thermal stability and enhanced flame retardancy compared to traditional urea formaldehyde foam, making it a promising material for next-generation fireproofing applications. Innovations in nanotechnology enable tailored pore structures and improved mechanical strength in carbon nanostructure foams, driving advancements in sustainable and highly effective fire-resistant insulation. Emerging research focuses on hybrid formulations combining carbon nanostructures with bio-based resins to reduce environmental impact while maximizing fireproofing performance.
Infographic: Carbon nanostructure foam vs Urea formaldehyde foam for Fireproofing
 azmater.com
azmater.com