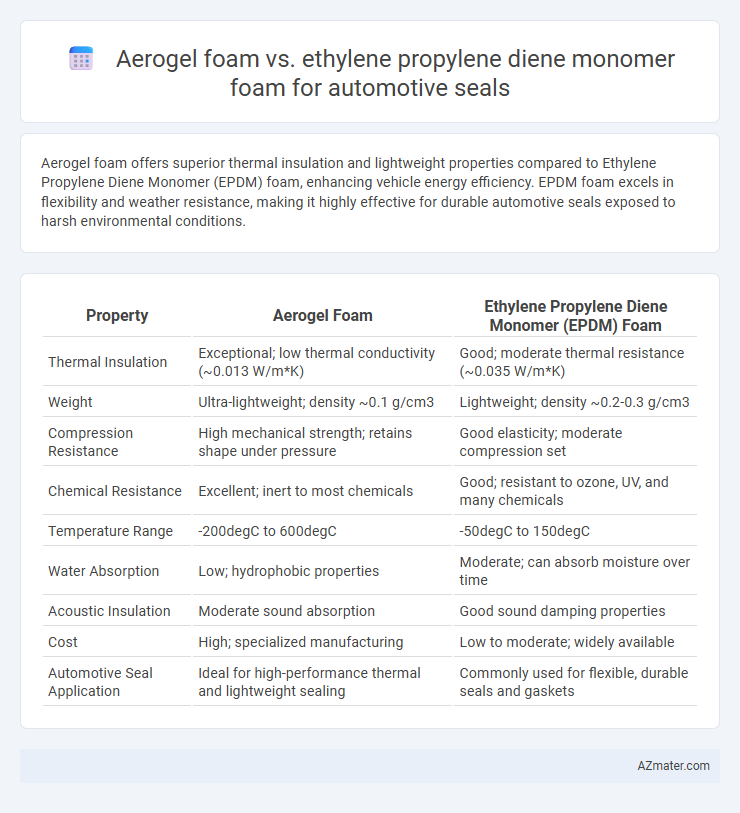
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) foam, enhancing vehicle energy efficiency. EPDM foam excels in flexibility and weather resistance, making it highly effective for durable automotive seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aerogel Foam | Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Exceptional; low thermal conductivity (~0.013 W/m*K) | Good; moderate thermal resistance (~0.035 W/m*K) |
| Weight | Ultra-lightweight; density ~0.1 g/cm3 | Lightweight; density ~0.2-0.3 g/cm3 |
| Compression Resistance | High mechanical strength; retains shape under pressure | Good elasticity; moderate compression set |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent; inert to most chemicals | Good; resistant to ozone, UV, and many chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -200degC to 600degC | -50degC to 150degC |
| Water Absorption | Low; hydrophobic properties | Moderate; can absorb moisture over time |
| Acoustic Insulation | Moderate sound absorption | Good sound damping properties |
| Cost | High; specialized manufacturing | Low to moderate; widely available |
| Automotive Seal Application | Ideal for high-performance thermal and lightweight sealing | Commonly used for flexible, durable seals and gaskets |
Introduction to Automotive Seal Materials
Automotive seal materials play a critical role in ensuring vehicle airtightness, noise reduction, and thermal insulation, with aerogel foam and ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) foam being prominent options. Aerogel foam offers exceptional thermal insulation due to its nanoporous silica structure, making it highly effective for temperature-sensitive automotive applications. EPDM foam provides excellent weather resistance, elasticity, and durability, making it widely used for door seals, window gaskets, and other automotive sealing applications where environmental exposure is significant.
Overview of Aerogel Foam
Aerogel foam offers exceptional thermal insulation and lightweight properties, making it highly effective for automotive seals that require protection against extreme temperatures and noise reduction. Its nanoporous structure provides superior resistance to heat transfer compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) foam, enabling enhanced energy efficiency and durability in automotive applications. Aerogel foam also features excellent compression recovery and chemical stability, ensuring long-lasting sealing performance in harsh under-the-hood environments.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Foam
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) foam is widely used in automotive seals due to its excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and temperature extremes ranging from -50degC to 150degC. Its closed-cell structure provides superior compression set resistance and effective moisture sealing, making it ideal for door seals, window seals, and trunk liners. Compared to aerogel foam, EPDM offers enhanced durability and flexibility, ensuring long-term performance in diverse environmental conditions.
Thermal Insulation Properties Comparison
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation for automotive seals due to its extremely low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.013 W/m*K, significantly outperforming Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) foam, which has thermal conductivity values ranging between 0.034 to 0.055 W/m*K. This difference results in enhanced temperature resistance and better energy efficiency in vehicles utilizing aerogel foam seals. EPDM foam, while flexible and durable, cannot match the thermal barrier performance of aerogel, making the latter ideal for applications requiring advanced heat retention or exclusion.
Acoustic Performance: Aerogel Foam vs EPDM Foam
Aerogel foam demonstrates superior acoustic performance compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) foam in automotive seals due to its ultra-low density and high porosity, which effectively dampens sound waves and reduces noise transmission. EPDM foam provides good sound insulation and weather resistance but cannot match the noise reduction efficiency of aerogel foam, especially in high-frequency acoustic applications. The enhanced sound absorption properties of aerogel foam contribute to quieter vehicle cabins, making it an optimal choice for noise mitigation in automotive sealing solutions.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Aerogel foam offers exceptional durability and superior thermal insulation properties compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) foam, maintaining structural integrity under high-temperature automotive conditions. EPDM foam exhibits strong resistance to ozone, UV rays, and weathering, providing excellent environmental resistance for automotive seals exposed to harsh outdoor elements. Aerogel's lightweight and compressibility enhance durability in dynamic automotive environments, while EPDM's robust chemical resistance ensures long-lasting performance against oils and solvents.
Weight and Flexibility Considerations
Aerogel foam offers significantly lower weight compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) foam, enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing overall vehicle mass. EPDM foam provides superior flexibility and resilience, making it ideal for dynamic sealing applications requiring repeated compression and recovery. Weight-sensitive automotive seals benefit from the lightweight, thermally insulative properties of aerogel foam, while EPDM is preferred for flexible seals subjected to vibration and movement.
Cost and Manufacturing Implications
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties but comes with higher material costs and more complex manufacturing processes compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) foam. EPDM foam provides cost-effective production, easier fabrication, and excellent weather resistance, making it a preferred choice for large-scale automotive seal applications. Manufacturing implications for aerogel involve specialized handling and slow curing times, while EPDM benefits from established, efficient extrusion and molding techniques, reducing overall production expenses.
Applications in Automotive Sealing Systems
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties, making it ideal for automotive sealing applications that require heat resistance and energy efficiency, such as engine compartments and battery enclosures. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) foam excels in durability, weather resistance, and flexibility, providing reliable seals against water, dust, and air in door gaskets, window seals, and HVAC systems. Both materials enhance automotive sealing systems, but Aerogel foam is favored for thermal management while EPDM foam is preferred for exterior sealing and vibration damping.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Foam Material
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties, making it ideal for automotive seals requiring high temperature resistance and energy efficiency. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) foam provides exceptional weatherability, flexibility, and chemical resistance, ensuring durability in harsh environmental conditions. Selecting the optimal foam material depends on prioritizing thermal performance and weight savings with aerogel or favoring long-term weather resistance and flexibility with EPDM for automotive sealing applications.
Infographic: Aerogel foam vs Ethylene propylene diene monomer foam for Automotive seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com