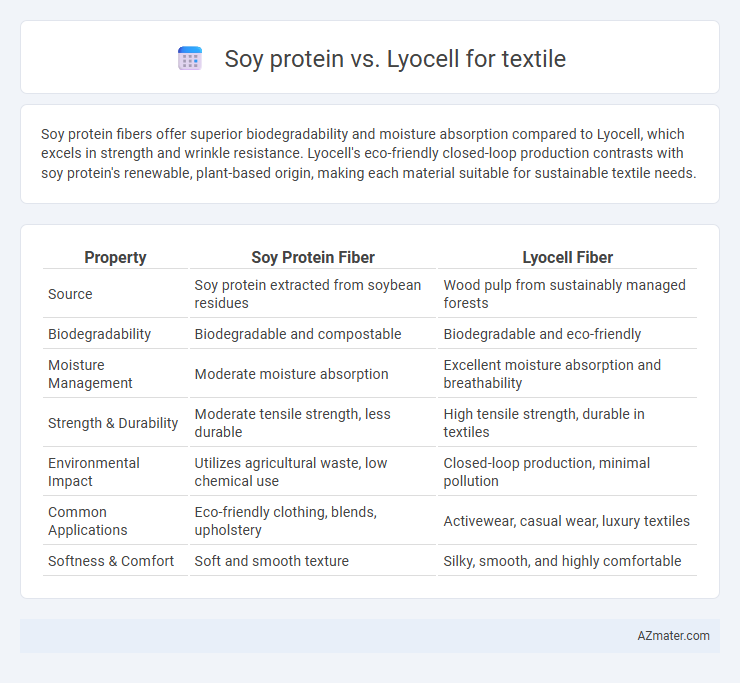
Soy protein fibers offer superior biodegradability and moisture absorption compared to Lyocell, which excels in strength and wrinkle resistance. Lyocell's eco-friendly closed-loop production contrasts with soy protein's renewable, plant-based origin, making each material suitable for sustainable textile needs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Soy Protein Fiber | Lyocell Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Soy protein extracted from soybean residues | Wood pulp from sustainably managed forests |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable and compostable | Biodegradable and eco-friendly |
| Moisture Management | Moderate moisture absorption | Excellent moisture absorption and breathability |
| Strength & Durability | Moderate tensile strength, less durable | High tensile strength, durable in textiles |
| Environmental Impact | Utilizes agricultural waste, low chemical use | Closed-loop production, minimal pollution |
| Common Applications | Eco-friendly clothing, blends, upholstery | Activewear, casual wear, luxury textiles |
| Softness & Comfort | Soft and smooth texture | Silky, smooth, and highly comfortable |
Introduction: Comparing Soy Protein and Lyocell in Textiles
Soy protein fibers, derived from soybean residues, offer biodegradable and moisture-absorbing properties suitable for eco-friendly textiles. Lyocell, produced from sustainably sourced wood pulp via a closed-loop process, is renowned for its strength, softness, and breathability in fabric applications. Both fibers integrate sustainability with performance but differ in source material, texture, and moisture management capabilities.
What is Soy Protein Fiber?
Soy protein fiber is a sustainable textile material derived from soybean protein, known for its softness, breathability, and biodegradability. It offers a natural alternative to synthetic fibers with excellent moisture absorption and antibacterial properties, making it ideal for eco-friendly clothing. Compared to Lyocell, which is made from wood pulp, soy protein fiber emphasizes renewable agricultural resources and a lower environmental footprint.
What is Lyocell Fiber?
Lyocell fiber is a sustainable textile made from cellulose extracted from wood pulp, primarily sourced from eucalyptus, beech, and oak trees. It is produced through a closed-loop process that recycles water and solvents, minimizing environmental impact compared to traditional fibers. Known for its moisture-wicking, breathability, and softness, Lyocell is widely used in apparel and home textiles.
Production Processes: Soy Protein vs Lyocell
Soy protein textiles are produced through a wet spinning process where soy protein isolates are dissolved and extruded into fibers, emphasizing sustainability by utilizing agricultural by-products. Lyocell production involves a more environmentally friendly closed-loop process using wood pulp dissolved in N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO) solvent, which is almost entirely recovered and recycled. The production of Lyocell fibers generally results in higher fiber strength and moisture absorption compared to the soy protein fiber process, which is still emerging in scalability and performance consistency.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Biodegradability
Soy protein fibers, derived from renewable soybeans, offer a biodegradable and sustainable alternative to synthetic textiles due to their low environmental footprint and natural compostability. Lyocell, made from sustainably sourced wood pulp using a closed-loop solvent spinning process, boasts high biodegradability and minimal chemical waste, making it one of the most eco-friendly fibers in the textile industry. Both materials significantly reduce reliance on petroleum-based fibers, but Lyocell's closed-loop production system and superior water efficiency give it a leading edge in sustainability.
Comfort and Wearability: Feel and Performance
Soy protein fibers provide a soft, smooth texture that enhances comfort by mimicking the feel of natural silk, making garments breathable and moisture-wicking for all-day wearability. Lyocell fibers, derived from eucalyptus pulp, offer superior moisture absorption and ventilation, maintaining dryness and reducing irritation during physical activity. Both fibers promote hypoallergenic properties and durability, yet Lyocell excels in tensile strength and wrinkle resistance, contributing to longer-lasting performance and comfort.
Durability and Maintenance
Soy protein fibers offer moderate durability with good moisture absorption but tend to weaken when exposed to prolonged washing and UV light. Lyocell, derived from cellulose pulp, provides superior strength and resilience with excellent resistance to shrinking and pilling during repeated laundering. Textile products made from Lyocell require less maintenance due to their ability to retain shape and color, making them more durable for everyday use compared to soy protein-based fabrics.
Cost and Market Availability
Soy protein fibers generally have higher production costs than Lyocell due to the complexity of extracting and processing soy protein from agricultural byproducts. Lyocell benefits from a more established manufacturing infrastructure, leading to lower costs and greater market availability in the textile industry. Growing consumer demand for sustainable fabrics is expanding Lyocell's market presence, while soy protein fibers remain niche with limited large-scale production and distribution channels.
Applications in Fashion and Textiles
Soy protein fibers offer a sustainable alternative in fashion, prized for their softness, moisture-wicking properties, and biodegradability, making them ideal for activewear, casual garments, and eco-friendly textiles. Lyocell, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, excels in breathability, strength, and wrinkle resistance, widely used in high-end fashion, denim, and functional apparel. Both fibers contribute to reducing environmental impact, with soy protein promoting circular fashion and Lyocell supporting sustainable fiber production.
Conclusion: Which Fiber is Better for the Future?
Soy protein fiber offers sustainability benefits through biodegradability and renewable plant-based sources, making it a strong candidate for eco-friendly textiles. Lyocell excels in moisture-wicking, durability, and environmentally responsible production processes using closed-loop technology, ensuring minimal chemical impact. For the future, Lyocell is generally favored due to its superior performance, scalability, and lower environmental footprint in textile manufacturing.
Infographic: Soy protein vs Lyocell for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com