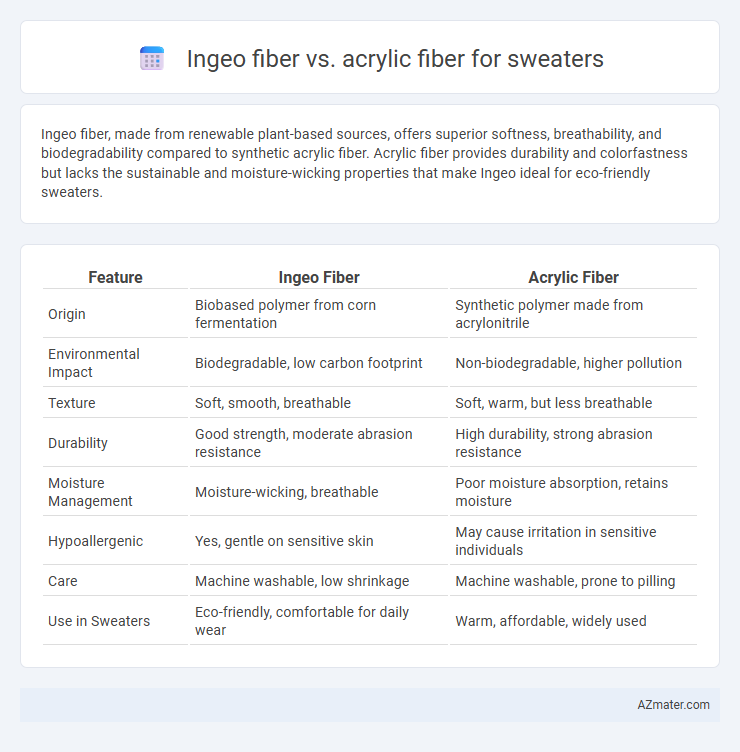
Ingeo fiber, made from renewable plant-based sources, offers superior softness, breathability, and biodegradability compared to synthetic acrylic fiber. Acrylic fiber provides durability and colorfastness but lacks the sustainable and moisture-wicking properties that make Ingeo ideal for eco-friendly sweaters.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ingeo Fiber | Acrylic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Biobased polymer from corn fermentation | Synthetic polymer made from acrylonitrile |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher pollution |
| Texture | Soft, smooth, breathable | Soft, warm, but less breathable |
| Durability | Good strength, moderate abrasion resistance | High durability, strong abrasion resistance |
| Moisture Management | Moisture-wicking, breathable | Poor moisture absorption, retains moisture |
| Hypoallergenic | Yes, gentle on sensitive skin | May cause irritation in sensitive individuals |
| Care | Machine washable, low shrinkage | Machine washable, prone to pilling |
| Use in Sweaters | Eco-friendly, comfortable for daily wear | Warm, affordable, widely used |
Introduction to Ingeo Fiber and Acrylic Fiber
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources such as corn, offers a sustainable and biodegradable alternative for sweater fabrics, promoting eco-friendly fashion. Acrylic fiber, a synthetic polymer made from polyacrylonitrile, provides durability, warmth, and resistance to moths and sunlight, commonly used for affordable and easy-care sweaters. Comparing these fibers highlights Ingeo's environmental benefits versus Acrylic's performance characteristics in sweater production.
Composition and Source of Each Fiber
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources like corn, is composed primarily of polylactic acid (PLA), offering biodegradability and eco-friendly properties. Acrylic fiber, a synthetic fiber made from polymerized acrylonitrile, originates from petroleum-based chemicals and is known for its durability and warmth but lacks biodegradability. Sweaters made from Ingeo fibers emphasize sustainability and reduced environmental impact, while those with acrylic fibers focus on long-lasting wear and resistance to moisture and mildew.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources like corn, offers a significantly lower carbon footprint and biodegradability compared to synthetic acrylic fibers, which are petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. The production of Ingeo fiber consumes less energy and water, contributing to reduced environmental pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Acrylic fibers, while durable and soft, generate microplastic pollution during washing and do not decompose, raising concerns about long-term environmental sustainability in sweater manufacturing.
Comfort and Wearability Comparison
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials, offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to traditional acrylic fiber, enhancing comfort during extended wear. Unlike acrylic, Ingeo fibers are naturally softer and reduce skin irritation, making sweaters more suitable for sensitive skin. The biodegradability and thermal regulation of Ingeo further improve wearability by maintaining consistent warmth without overheating.
Thermal Insulation and Warmth
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials, offers superior thermal insulation compared to acrylic fiber due to its natural moisture-wicking properties and ability to retain heat efficiently. Acrylic fiber provides moderate warmth but lacks the breathability and eco-friendly benefits inherent in Ingeo fiber, often resulting in less effective temperature regulation. Choosing Ingeo fiber for sweaters enhances comfort in cold conditions by maintaining warmth while minimizing moisture buildup, making it a more sustainable and functional option.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Ingeo fiber, made from renewable plant-based materials, offers superior moisture management by wicking sweat away from the skin and allowing faster evaporation compared to acrylic fiber, which tends to retain moisture and dry slower. The natural breathability of Ingeo enhances airflow, maintaining comfort during physical activities, whereas acrylic fibers often trap heat and moisture, leading to reduced ventilation. Choosing sweaters with Ingeo fiber ensures better temperature regulation and dryness, making them ideal for active or humid environments.
Durability and Longevity
Ingeo fiber, made from renewable plant-based materials, offers excellent durability due to its high resistance to pilling and abrasion, making sweaters last longer with minimal wear. Acrylic fiber provides good durability as well, but it tends to pill more over time and can lose shape after repeated washes, reducing the longevity of sweaters. Choosing Ingeo fiber for sweaters ensures extended fabric integrity and sustained appearance, outperforming acrylic in maintaining durability over prolonged use.
Care and Maintenance Requirements
Ingeo fiber sweaters require gentle washing with cold water and mild detergents, as exposure to high heat can cause shrinking or damage, and they should be air-dried to maintain fiber integrity. Acrylic fiber sweaters offer easier care since they are machine washable and more resistant to shrinking, but they may pill over time and benefit from using a fabric softener to reduce static. Both fibers demand careful handling during washing and drying to preserve softness, shape, and longevity.
Cost and Market Availability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, generally costs more than acrylic fiber due to its sustainable production process and limited large-scale manufacturing. Acrylic fiber, a synthetic material, is widely available and budget-friendly, making it a popular choice for mass-market sweaters. Market availability for Ingeo fiber remains niche, with growing demand in eco-conscious segments, whereas acrylic dominates due to established supply chains and lower price points.
Which Fiber is Best for Sweater Knitting?
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant materials, offers superior breathability, softness, and moisture-wicking properties compared to traditional acrylic fiber, making it an eco-friendly and comfortable choice for sweater knitting. Acrylic fiber, a synthetic polymer, provides durability and easy care but often lacks the natural warmth and hypoallergenic benefits found in Ingeo fibers. For sweater knitting, Ingeo fiber is best suited for those seeking sustainable, breathable, and soft garments, while acrylic remains popular for budget-friendly, durable options.
Infographic: Ingeo fiber vs Acrylic fiber for Sweater
 azmater.com
azmater.com