Lyocell fibers offer superior breathability and biodegradability compared to polyester, which is known for its durability and moisture resistance. Textile manufacturers prioritize Lyocell for sustainable fashion, while polyester remains preferred for activewear due to its quick-drying properties.
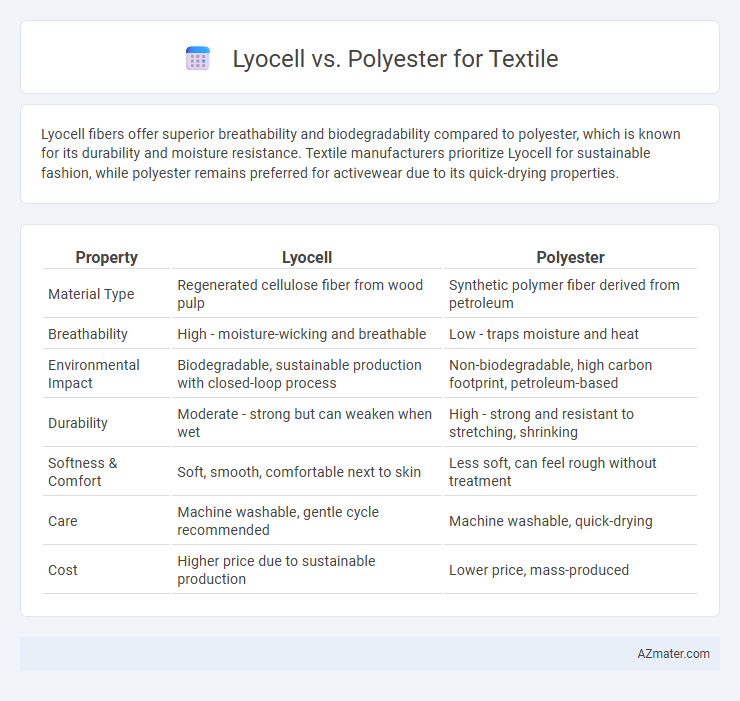
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lyocell | Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Regenerated cellulose fiber from wood pulp | Synthetic polymer fiber derived from petroleum |
| Breathability | High - moisture-wicking and breathable | Low - traps moisture and heat |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, sustainable production with closed-loop process | Non-biodegradable, high carbon footprint, petroleum-based |
| Durability | Moderate - strong but can weaken when wet | High - strong and resistant to stretching, shrinking |
| Softness & Comfort | Soft, smooth, comfortable next to skin | Less soft, can feel rough without treatment |
| Care | Machine washable, gentle cycle recommended | Machine washable, quick-drying |
| Cost | Higher price due to sustainable production | Lower price, mass-produced |
Introduction to Lyocell and Polyester
Lyocell is a sustainable cellulose fiber made from wood pulp, known for its breathability, softness, and biodegradability, making it an eco-friendly alternative in textiles. Polyester, a synthetic fiber derived from petroleum, offers high durability, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking properties commonly used in a wide range of apparel and industrial fabrics. The growing demand for eco-conscious materials has increased interest in Lyocell, while polyester remains favored for its cost-effectiveness and performance characteristics.
Fiber Origins and Production Processes
Lyocell fibers originate from sustainably sourced cellulose, primarily derived from wood pulp of eucalyptus, beech, or spruce trees, processed through a closed-loop system that recycles solvents and minimizes environmental impact. Polyester fibers, synthetic and derived from petroleum-based polymers such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), undergo petrochemical polymerization and melt spinning, involving energy-intensive processes with non-renewable resources. The natural origin and eco-friendly closed-loop production of Lyocell contrast sharply with the fossil fuel dependence and higher carbon footprint associated with traditional polyester manufacturing.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Lyocell is a sustainable textile fiber made from renewable wood pulp using a closed-loop solvent spinning process that recycles water and solvents, significantly reducing environmental pollution and resource consumption. In contrast, polyester is a synthetic fiber derived from petroleum, contributing to microplastic pollution, high carbon emissions, and non-biodegradability, which increases landfill waste and environmental harm. The biodegradable nature and lower carbon footprint of Lyocell make it a more eco-friendly choice compared to the energy-intensive production and persistent environmental impact of polyester.
Durability and Longevity
Lyocell fibers exhibit superior durability and longevity compared to polyester, maintaining strength through repeated washing and resisting pilling. Polyester's synthetic composition contributes to high tensile strength and abrasion resistance but may degrade under prolonged UV exposure and heat. Textile manufacturers often prefer lyocell for sustainable, long-lasting garments due to its biodegradability and resilience, while polyester remains favored for cost-effective, durable performance in activewear and industrial applications.
Comfort and Breathability
Lyocell fibers, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, offer superior moisture-wicking properties and breathability compared to polyester, which is a synthetic fabric known for trapping heat and moisture. Textile products made from lyocell provide enhanced comfort through their soft, breathable structure that regulates temperature and keeps skin dry, making it ideal for sensitive skin and active wear. Polyester, while durable and quick-drying, often lacks the natural airflow and hypoallergenic qualities found in lyocell, resulting in less comfort during prolonged wear.
Moisture Management and Absorbency
Lyocell fibers exhibit superior moisture management and absorbency compared to polyester due to their inherent hydrophilic properties and micro-porous structure, which allow quick moisture absorption and release, enhancing comfort and breathability in textiles. Polyester, being hydrophobic, tends to repel water and traps moisture against the skin, resulting in slower drying times and reduced moisture wicking efficiency. Textile applications prioritize Lyocell for performance apparel and activewear where effective moisture regulation is critical to maintain dryness and prevent bacterial growth.
Texture and Aesthetic Qualities
Lyocell offers a soft, silky texture with excellent breathability and a natural sheen, making it highly desirable for luxurious, eco-friendly textiles. Polyester, known for its smooth, consistent surface, boasts durability and vibrant color retention but often lacks the natural feel and breathability of Lyocell. In terms of aesthetic qualities, Lyocell provides a matte to slightly glossy finish that drapes well, while polyester can appear shinier and less fluid, impacting the overall garment's look and comfort.
Cost and Market Availability
Lyocell typically costs more than polyester due to its sustainable production process and eco-friendly attributes, appealing to premium markets. Polyester is widely available and cheaper, dominating the textile industry with mass production and extensive supply chains. Market availability of polyester remains higher globally, while lyocell is gaining traction in niche and sustainable fashion sectors.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
Lyocell, derived from sustainably harvested wood pulp, is biodegradable and produced through a closed-loop process that recycles water and solvents, minimizing environmental impact. Polyester, primarily made from non-renewable petroleum-based sources, contributes to microplastic pollution and has a significantly higher carbon footprint due to energy-intensive manufacturing. Choosing Lyocell over polyester promotes sustainable textile production by reducing waste, conserving resources, and supporting circular economy principles.
Choosing the Right Fabric for Your Needs
Lyocell offers superior breathability, moisture-wicking, and biodegradability compared to polyester, making it ideal for eco-conscious consumers and those seeking comfort in warm climates. Polyester provides greater durability, wrinkle resistance, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for activewear and long-lasting textiles. Selecting between Lyocell and polyester depends on prioritizing sustainability and comfort versus durability and budget in textile applications.
Infographic: Lyocell vs Polyester for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com