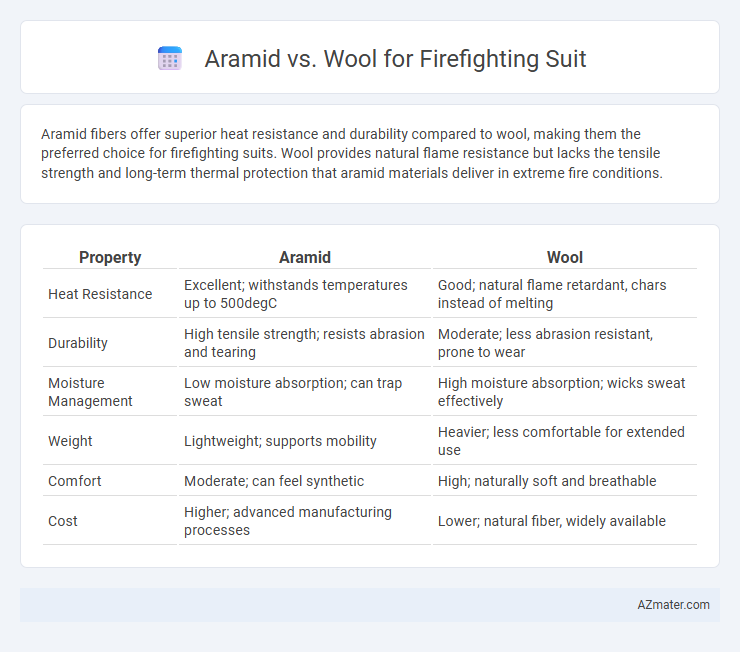
Aramid fibers offer superior heat resistance and durability compared to wool, making them the preferred choice for firefighting suits. Wool provides natural flame resistance but lacks the tensile strength and long-term thermal protection that aramid materials deliver in extreme fire conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid | Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Excellent; withstands temperatures up to 500degC | Good; natural flame retardant, chars instead of melting |
| Durability | High tensile strength; resists abrasion and tearing | Moderate; less abrasion resistant, prone to wear |
| Moisture Management | Low moisture absorption; can trap sweat | High moisture absorption; wicks sweat effectively |
| Weight | Lightweight; supports mobility | Heavier; less comfortable for extended use |
| Comfort | Moderate; can feel synthetic | High; naturally soft and breathable |
| Cost | Higher; advanced manufacturing processes | Lower; natural fiber, widely available |
Introduction to Firefighting Suit Materials
Firefighting suits rely heavily on materials like aramid fibers and wool due to their inherent flame-resistant properties and thermal stability. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, offer exceptional heat resistance, durability, and lightweight comfort, making them ideal for high-risk fire exposure. Wool provides natural flame retardancy and moisture-wicking capabilities, but is often blended with synthetic fibers to enhance overall protection and performance in firefighting gear.
Understanding Aramid Fibers
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, are synthetic materials engineered for exceptional heat resistance and flame retardancy, making them ideal for firefighting suits. Their molecular structure provides high tensile strength and thermal stability, allowing them to maintain integrity under extreme temperatures and resist melting or dripping. Wool, while naturally flame-resistant and moisture-managing, does not match the durability and protective performance of aramid fibers in hazardous firefighting environments.
Properties of Wool in Fire Protection
Wool offers excellent fire resistance due to its high ignition temperature and low heat conductivity, making it effective in preventing burns during firefighting operations. Its natural moisture-wicking ability helps regulate body temperature and reduces steam burns by absorbing sweat without igniting. Wool fibers also exhibit self-extinguishing properties, which minimize flare-ups and enhance overall safety in fire protection gear.
Thermal Resistance: Aramid vs Wool
Aramid fibers, such as Nomex and Kevlar, provide superior thermal resistance compared to wool, withstanding temperatures up to 370degC (700degF) without melting or igniting. Wool offers natural flame-retardant properties but combusts at lower temperatures around 570degC (1058degF) and chars rather than melts, providing moderate thermal protection. In firefighting suits, aramid's high thermal stability and durability make it the preferred choice for enhanced heat and flame resistance.
Comfort and Wearability Comparison
Aramid fibers, such as Nomex, provide superior heat resistance and durability in firefighting suits while maintaining lightweight properties that enhance comfort and reduce fatigue during prolonged use. Wool offers natural insulation and breathability, contributing to moisture management and comfort, but it generally lacks the same level of flame resistance and durability as aramid fibers. Firefighters benefit from aramid suits due to their optimized balance of thermal protection and ergonomic design, whereas wool is often used in combination with synthetic fibers to improve wearability without compromising safety.
Durability and Lifespan of Materials
Aramid fibers, such as Nomex and Kevlar, offer exceptional durability and superior resistance to heat, flames, and abrasion, making them ideal for firefighting suits with a longer lifespan under extreme conditions. Wool provides natural fire resistance and breathability but tends to degrade faster under repeated exposure to intense heat and mechanical stress compared to aramid fabrics. The superior strength and thermal stability of aramid materials significantly enhance the longevity and reliability of protective gear in hazardous firefighting environments.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Aramid fibers used in firefighting suits provide superior moisture management by wicking sweat away and maintaining thermal protection even when wet. Wool offers natural breathability and moisture absorption, helping regulate body temperature but can retain moisture longer, potentially reducing comfort. Aramid's engineered breathability and rapid-drying properties enhance firefighter endurance during intense heat exposure compared to traditional wool fabrics.
Cost Analysis: Aramid vs Wool
Aramid fabrics like Nomex offer higher fire resistance and durability than wool, justifying their higher upfront cost in firefighting suits. Wool is a natural fiber with lower material costs but requires more frequent replacement due to reduced flame resistance and durability. Over time, the total cost of ownership favors aramid suits due to extended service life and enhanced protection despite initial expense.
Environmental Impact of Each Material
Aramid fibers, widely used in firefighting suits for their flame resistance, have a high environmental impact due to energy-intensive production and limited biodegradability. Wool, a natural fiber, offers better sustainability with renewable sourcing, lower carbon footprint, and inherent flame-resistant properties, but it requires extensive water and land resources for sheep farming. Balancing performance with eco-friendly practices involves optimizing material blends and improving lifecycle management for both aramid and wool in protective gear.
Choosing the Best Material for Firefighting Suits
Aramid fibers such as Nomex and Kevlar offer superior heat resistance, flame retardancy, and durability, making them the preferred choice for firefighting suits. Wool, while naturally flame-resistant and breathable, lacks the advanced thermal protection and mechanical strength provided by aramid materials. Selecting aramid-based suits ensures enhanced safety and longevity in extreme fire conditions common in firefighting environments.
Infographic: Aramid vs Wool for Firefighting Suit
 azmater.com
azmater.com