Transparent concrete integrates optical fibers to allow light transmission, enhancing natural illumination for architectural features. High-performance concrete offers superior strength and durability, ideal for structural elements requiring enhanced load-bearing capacity and longevity.
Table of Comparison
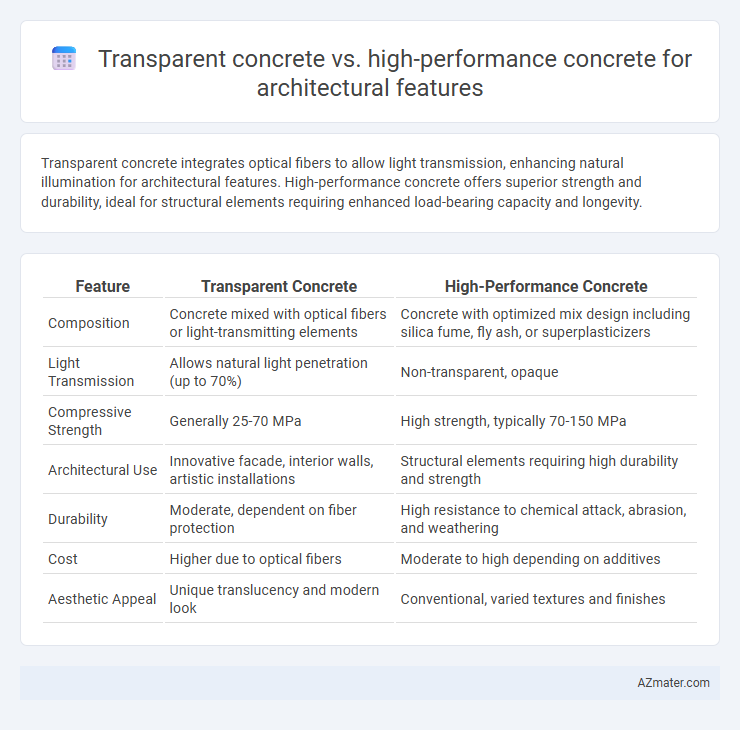
| Feature | Transparent Concrete | High-Performance Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Concrete mixed with optical fibers or light-transmitting elements | Concrete with optimized mix design including silica fume, fly ash, or superplasticizers |
| Light Transmission | Allows natural light penetration (up to 70%) | Non-transparent, opaque |
| Compressive Strength | Generally 25-70 MPa | High strength, typically 70-150 MPa |
| Architectural Use | Innovative facade, interior walls, artistic installations | Structural elements requiring high durability and strength |
| Durability | Moderate, dependent on fiber protection | High resistance to chemical attack, abrasion, and weathering |
| Cost | Higher due to optical fibers | Moderate to high depending on additives |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Unique translucency and modern look | Conventional, varied textures and finishes |
Introduction to Transparent Concrete and High-Performance Concrete
Transparent concrete integrates optical fibers or resin-based light-transmitting elements within a cement matrix, enabling natural light to pass through while maintaining structural integrity. High-performance concrete (HPC) offers superior mechanical properties, including enhanced strength, durability, and reduced permeability, achieved through optimized mix design and advanced materials. Both materials serve unique architectural functions: transparent concrete enhances aesthetic and lighting effects, while HPC ensures longevity and structural reliability in complex designs.
Defining Characteristics of Transparent Concrete
Transparent concrete, also known as light-transmitting concrete, incorporates optical fibers or resin-based materials that allow light to pass through while maintaining structural integrity, creating unique aesthetic effects in architectural features. High-performance concrete, in contrast, emphasizes enhanced strength, durability, and workability through specialized mix designs and additives, but lacks light-transmitting properties. The defining characteristics of transparent concrete include its ability to diffuse natural and artificial light, offering both functional illumination and distinctive visual appeal in facades and interior applications.
Key Features of High-Performance Concrete
High-performance concrete (HPC) offers superior strength, durability, and enhanced workability, making it ideal for architectural features requiring long-lasting structural integrity. Its low permeability and high resistance to environmental stressors allow HPC to maintain aesthetic appeal over time, unlike transparent concrete which emphasizes translucency but may have lower mechanical performance. HPC supports intricate designs and complex forms while ensuring minimal maintenance and resistance to cracks, freeze-thaw cycles, and chemical attacks.
Material Composition and Innovation
Transparent concrete incorporates optical fibers embedded within a cement matrix, allowing light transmission while maintaining structural integrity, making it ideal for innovative architectural features requiring natural illumination. High-performance concrete (HPC) utilizes advanced additives such as silica fume, superplasticizers, and optimized aggregate gradation to achieve superior strength, durability, and workability, enabling intricate and resilient designs. The innovation in transparent concrete lies in its ability to merge aesthetics with functionality by integrating light-conducting elements, whereas HPC emphasizes enhanced mechanical properties through material engineering and precise mix design.
Structural Performance and Durability Comparison
Transparent concrete leverages optical fibers embedded within a cement matrix, enhancing aesthetic appeal while maintaining adequate structural performance for non-load-bearing architectural elements. High-performance concrete (HPC) exhibits superior compressive strength, durability, and resistance to environmental degradation, making it ideal for structural components subjected to heavy loads and harsh conditions. Compared to transparent concrete, HPC offers enhanced long-term durability and load-bearing capacity, ensuring greater structural reliability in demanding architectural applications.
Aesthetic Potential in Architectural Design
Transparent concrete offers unique aesthetic potential through its embedded optical fibers, allowing natural light to penetrate structural elements and create dynamic lighting effects in architectural design. High-performance concrete excels in durability and versatile finishing options, providing architects with a broad palette of textures and colors while maintaining structural integrity. Both materials enhance architectural aesthetics; transparent concrete emphasizes light interaction and visual innovation, whereas high-performance concrete prioritizes strength and customizable surface appearance.
Applications in Modern Architecture
Transparent concrete is increasingly utilized in modern architecture for innovative facade designs and daylighting solutions, offering natural light transmission while maintaining structural integrity. High-performance concrete excels in load-bearing elements and complex shapes due to its enhanced strength and durability, supporting sustainable and long-lasting architectural features. Combining both materials allows architects to balance aesthetics and functionality in cutting-edge building projects.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Transparent concrete incorporates optical fibers or resin to allow light transmission, reducing the need for artificial lighting and enhancing energy efficiency in architectural features. High-performance concrete (HPC) offers superior durability and strength, minimizing maintenance and extending the lifespan of structures, which lowers the overall environmental footprint. Both materials contribute to sustainability by optimizing resource use -- transparent concrete improves indoor natural lighting, while HPC reduces material consumption through enhanced performance.
Cost Implications and Construction Challenges
Transparent concrete, integrating optical fibers or resin, offers unique aesthetics but significantly increases material costs, often doubling expenses compared to conventional high-performance concrete (HPC). HPC, formulated with advanced admixtures and supplementary cementitious materials, delivers superior strength and durability at a relatively lower cost and with established construction techniques. Construction challenges for transparent concrete include complex handling and precise fiber alignment, whereas HPC poses fewer difficulties, benefiting from widespread industry experience and compatibility with standard equipment.
Future Trends in Concrete Technology for Architecture
Transparent concrete integrates optical fibers to transmit light, enabling innovative daylighting and aesthetic effects in architectural features, while high-performance concrete offers superior strength, durability, and workability for complex structural designs. Emerging trends emphasize combining transparency with enhanced mechanical properties through nanomaterial additives and smart sensors embedded in concrete matrices. Future concrete technologies strive to balance sustainability, energy efficiency, and multifunctionality, driving architectural innovation with responsive and adaptive building envelopes.
Infographic: Transparent concrete vs High-performance concrete for Architectural feature
 azmater.com
azmater.com