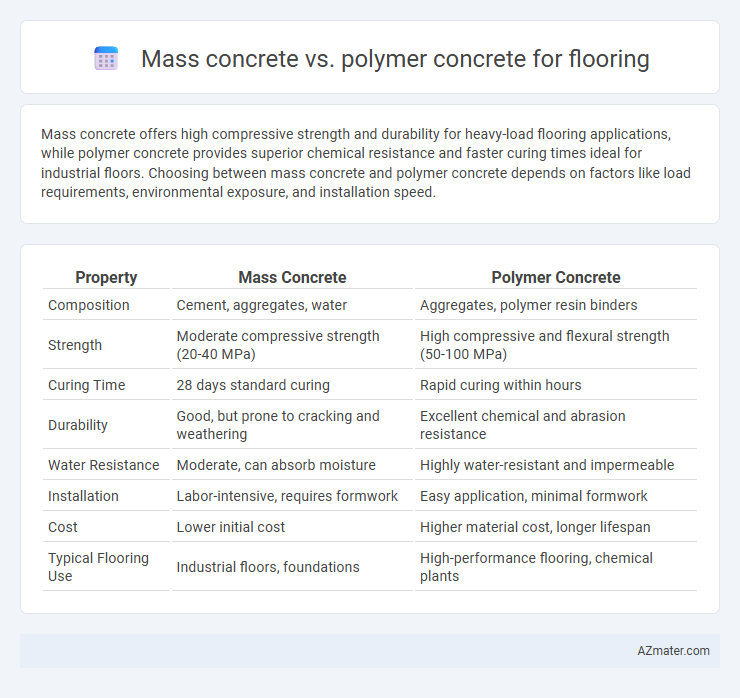
Mass concrete offers high compressive strength and durability for heavy-load flooring applications, while polymer concrete provides superior chemical resistance and faster curing times ideal for industrial floors. Choosing between mass concrete and polymer concrete depends on factors like load requirements, environmental exposure, and installation speed.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Mass Concrete | Polymer Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Cement, aggregates, water | Aggregates, polymer resin binders |
| Strength | Moderate compressive strength (20-40 MPa) | High compressive and flexural strength (50-100 MPa) |
| Curing Time | 28 days standard curing | Rapid curing within hours |
| Durability | Good, but prone to cracking and weathering | Excellent chemical and abrasion resistance |
| Water Resistance | Moderate, can absorb moisture | Highly water-resistant and impermeable |
| Installation | Labor-intensive, requires formwork | Easy application, minimal formwork |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher material cost, longer lifespan |
| Typical Flooring Use | Industrial floors, foundations | High-performance flooring, chemical plants |
Introduction to Mass Concrete and Polymer Concrete Flooring
Mass concrete flooring, composed primarily of cement, coarse aggregates, and water, provides high durability and strength suitable for heavy loads and industrial environments. Polymer concrete flooring incorporates resins such as epoxy or polyester, enhancing adhesion, chemical resistance, and rapid curing times compared to traditional concrete. Both materials offer distinct advantages, with mass concrete excelling in structural stability and polymer concrete delivering superior surface performance for specialized applications.
Key Material Properties: Mass Concrete vs Polymer Concrete
Mass concrete offers high compressive strength and excellent durability, making it suitable for heavy-load flooring applications, while polymer concrete provides superior chemical resistance and faster curing times. Polymer concrete's enhanced adhesion and lower permeability protect against moisture infiltration and corrosive substances better than traditional mass concrete. Both materials have distinct thermal expansion characteristics, with polymer concrete generally exhibiting greater flexibility and reduced cracking risks under temperature variations.
Installation Process Comparison
Mass concrete flooring requires extensive curing time of up to 28 days, involving multiple steps such as subgrade preparation, formwork, mixing, and pouring, which can extend project timelines. Polymer concrete floors offer a rapid installation process thanks to their fast-curing resins, enabling service readiness within 24 to 48 hours and reducing downtime in industrial settings. The polymer mix provides superior adhesion and chemical resistance, simplifying surface preparation and minimizing the need for extensive curing protocols compared to traditional mass concrete.
Performance in High-Traffic Areas
Polymer concrete flooring outperforms mass concrete in high-traffic areas due to its superior tensile strength and resistance to wear and abrasion, reducing maintenance frequency and costs. Its chemical resistance and low permeability improve durability against oils, chemicals, and moisture commonly encountered in industrial or commercial settings. Mass concrete, while cost-effective, tends to exhibit higher susceptibility to cracking and surface degradation under heavy dynamic loads over time.
Durability and Longevity of Each Flooring Type
Mass concrete flooring offers exceptional durability due to its high compressive strength and resistance to heavy loads, making it ideal for industrial environments with constant wear and tear. Polymer concrete flooring enhances longevity through superior chemical resistance and low permeability, preventing damage from corrosive substances and moisture infiltration. While mass concrete excels in structural robustness, polymer concrete provides extended lifespan in chemically aggressive or moisture-prone settings.
Chemical and Moisture Resistance
Polymer concrete exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to mass concrete due to its dense polymer matrix that prevents penetration of aggressive substances like acids and solvents, making it ideal for industrial flooring exposed to harsh chemicals. Mass concrete, composed primarily of cement, aggregates, and water, tends to absorb moisture and chemicals, leading to potential degradation and reduced durability in environments with high chemical exposure. The enhanced moisture resistance of polymer concrete also minimizes water absorption, preventing weakening and extending the floor's lifespan under wet or humid conditions.
Maintenance Requirements and Costs
Mass concrete flooring requires minimal maintenance but is prone to cracking over time, leading to potential repair costs that can increase with the floor's surface area and environmental exposure. Polymer concrete flooring offers superior chemical resistance and durability, significantly reducing maintenance frequency and associated costs, especially in industrial or high-traffic settings. The initial installation cost of polymer concrete is higher than mass concrete, but its long-term savings in maintenance and repair make it a cost-effective choice for demanding flooring applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Mass concrete flooring, composed mainly of cement, sand, and aggregates, has a high carbon footprint due to significant CO2 emissions during cement production. Polymer concrete flooring utilizes synthetic resins, reducing the need for cement and thus lowering greenhouse gas emissions, while offering enhanced durability and chemical resistance. The sustainable advantage of polymer concrete lies in its longevity and reduced maintenance, minimizing resource consumption and waste over the lifecycle of the flooring system.
Suitability for Industrial and Commercial Applications
Mass concrete provides excellent compressive strength and durability, making it suitable for heavy load-bearing industrial floors, while polymer concrete offers superior chemical resistance and faster curing times, ideal for commercial spaces with frequent exposure to corrosive substances. Industrial applications benefit from mass concrete's robustness and long lifespan under extreme mechanical stresses, whereas polymer concrete excels in environments requiring rapid installation and minimal downtime. Both materials support heavy traffic, but polymer concrete's enhanced adhesion and flexibility make it preferable for high-performance commercial flooring solutions.
Choosing the Right Flooring: Factors to Consider
Mass concrete flooring offers high compressive strength and durability, ideal for heavy industrial use and high-load applications. Polymer concrete flooring provides superior chemical resistance, faster curing times, and enhanced adhesion, making it suitable for environments exposed to corrosive substances. Selecting the right flooring depends on assessing load requirements, exposure to chemicals, installation time, and long-term maintenance needs for optimized performance.
Infographic: Mass concrete vs Polymer concrete for Flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com