Sulfate-resistant concrete enhances pavement durability in sulfate-rich soils by minimizing chemical degradation, while pervious concrete improves stormwater management through its high permeability and rapid drainage. Choosing sulfate-resistant concrete prevents sulfate attack damage, whereas pervious concrete reduces runoff and mitigates urban flooding risks.
Table of Comparison
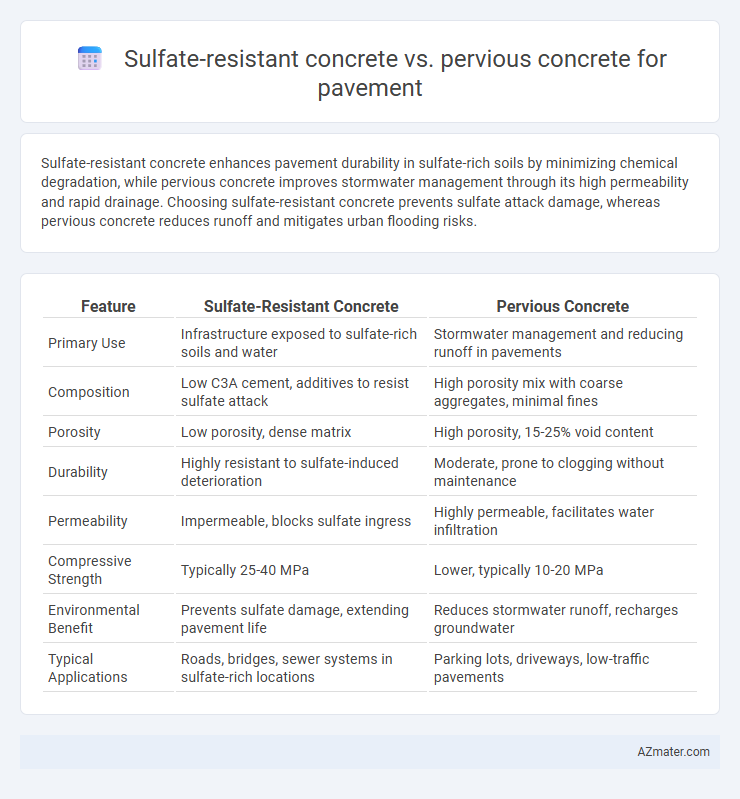
| Feature | Sulfate-Resistant Concrete | Pervious Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Infrastructure exposed to sulfate-rich soils and water | Stormwater management and reducing runoff in pavements |
| Composition | Low C3A cement, additives to resist sulfate attack | High porosity mix with coarse aggregates, minimal fines |
| Porosity | Low porosity, dense matrix | High porosity, 15-25% void content |
| Durability | Highly resistant to sulfate-induced deterioration | Moderate, prone to clogging without maintenance |
| Permeability | Impermeable, blocks sulfate ingress | Highly permeable, facilitates water infiltration |
| Compressive Strength | Typically 25-40 MPa | Lower, typically 10-20 MPa |
| Environmental Benefit | Prevents sulfate damage, extending pavement life | Reduces stormwater runoff, recharges groundwater |
| Typical Applications | Roads, bridges, sewer systems in sulfate-rich locations | Parking lots, driveways, low-traffic pavements |
Understanding Sulfate-Resistant Concrete
Sulfate-resistant concrete is specifically designed to withstand chemical attacks from sulfate-rich soils and groundwater, making it highly durable for pavements in aggressive environments. It achieves this resistance by using low C3A (tricalcium aluminate) cement and supplementary cementitious materials like fly ash or slag, which reduce the permeability and vulnerability to sulfate ions. This durability contrasts with pervious concrete, which prioritizes water permeability and stormwater management but offers less protection against sulfate-induced deterioration.
Exploring Pervious Concrete Technology
Pervious concrete technology enhances pavement sustainability by allowing water infiltration, reducing runoff, and promoting groundwater recharge, which contrasts with sulfate-resistant concrete primarily designed to withstand chemical attack in aggressive soil conditions. While sulfate-resistant concrete offers durability in sulfate-rich environments, pervious concrete's porous structure improves urban drainage and mitigates flooding risks in pavement applications. Exploring pervious concrete technology involves optimizing mix design, aggregate size, and compaction to balance permeability and mechanical strength for effective pavement solutions.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Sulfate-resistant concrete exhibits high durability due to its low tricalcium aluminate content, resisting sulfate attack and chemical corrosion in aggressive environments, making it suitable for pavements exposed to sulfate-rich soils or groundwater. Pervious concrete features high porosity and permeability, enabling rapid water drainage and reducing surface runoff but generally possesses lower compressive strength and reduced resistance to freeze-thaw cycles compared to sulfate-resistant concrete. Key material properties comparison highlights sulfate-resistant concrete's superior chemical stability and compressive strength versus pervious concrete's enhanced permeability and environmental benefits for stormwater management in pavement applications.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Sulfate-resistant concrete exhibits superior durability against sulfate attack in aggressive soil and groundwater environments, making it ideal for pavements exposed to chemical corrosion. Pervious concrete offers excellent water permeability, reducing surface runoff and improving drainage, but it is more susceptible to freeze-thaw damage and chemical ingress. For pavements in sulfate-rich or chemically aggressive environments, sulfate-resistant concrete ensures long-term structural integrity, whereas pervious concrete excels in managing stormwater but requires protective measures to enhance its environmental resistance.
Water Drainage and Permeability
Sulfate-resistant concrete is designed to withstand chemical attacks from sulfate-rich environments, offering durability but limited permeability and water drainage capabilities, which can lead to surface water accumulation in pavement applications. Pervious concrete features high porosity that enables efficient water drainage and rapid permeability, reducing surface runoff and enhancing stormwater management on pavements. Selecting pervious concrete improves water infiltration and reduces hydrostatic pressure, while sulfate-resistant concrete is essential in sulfate-exposed soils but requires supplementary drainage solutions for effective pavement water management.
Durability and Longevity Considerations
Sulfate-resistant concrete offers enhanced durability by resisting chemical attacks from sulfate-rich soils, reducing the risk of expansion and cracking in pavement structures. Pervious concrete improves longevity through effective water drainage, minimizing water retention and freeze-thaw damage but may have lower compressive strength compared to sulfate-resistant mixes. Selecting between the two depends on site-specific conditions, with sulfate-resistant concrete ideal for chemically aggressive environments and pervious concrete suited for managing stormwater and reducing surface runoff.
Typical Applications in Pavement Construction
Sulfate-resistant concrete is primarily used in pavement construction for environments exposed to sulfate-rich soils or groundwater, such as industrial sites and sewage treatment plants, where durability against chemical attack is critical. Pervious concrete is favored in stormwater management applications, including parking lots and low-traffic roads, due to its high permeability that facilitates water infiltration and reduces runoff. Both materials address specific pavement performance needs, with sulfate-resistant concrete enhancing longevity under aggressive chemical conditions and pervious concrete improving environmental sustainability through effective drainage.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Sulfate-resistant concrete requires precise mixing and curing processes to prevent sulfate attack and prolong pavement lifespan, often involving higher material costs and longer installation times. Pervious concrete facilitates rapid water drainage through its porous structure, necessitating careful placement and compaction to maintain void spaces and avoid clogging, with maintenance focused on routine vacuuming or pressure washing to preserve permeability. While sulfate-resistant concrete emphasizes chemical durability against aggressive soils, pervious concrete prioritizes infiltration efficiency, resulting in distinct installation techniques and ongoing maintenance protocols for pavement applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Sulfate-resistant concrete minimizes chemical degradation by effectively resisting sulfate attack, enhancing pavement durability and reducing repair frequency, thus lowering lifecycle environmental impact. Pervious concrete facilitates groundwater recharge by allowing water infiltration, reducing stormwater runoff and mitigating urban heat island effects, promoting sustainable urban drainage systems. Choosing sulfate-resistant concrete extends pavement lifespan, while pervious concrete supports ecosystem health, with both contributing uniquely to sustainable infrastructure development.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Your Pavement Project
Sulfate-resistant concrete is essential for pavement projects exposed to sulfate-rich soils or groundwater, ensuring durability and preventing chemical attack that can degrade standard concrete. Pervious concrete enhances stormwater management by allowing water infiltration, reducing runoff, and minimizing urban flooding, making it ideal for environmentally sensitive areas. Selecting the right concrete depends on environmental conditions and project goals, with sulfate-resistant concrete prioritizing chemical durability and pervious concrete emphasizing permeability and sustainable drainage.
Infographic: Sulfate-resistant concrete vs Pervious concrete for Pavement
 azmater.com
azmater.com