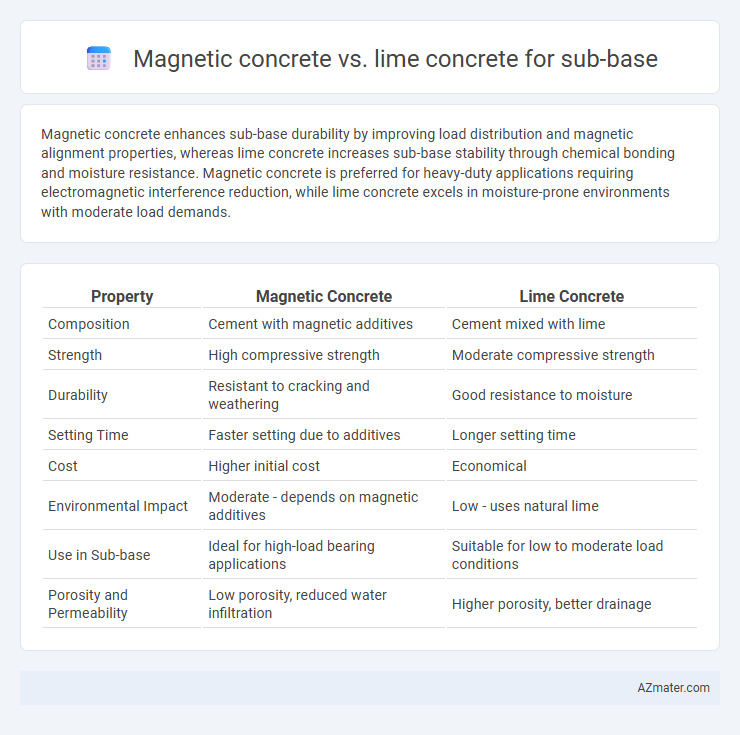
Magnetic concrete enhances sub-base durability by improving load distribution and magnetic alignment properties, whereas lime concrete increases sub-base stability through chemical bonding and moisture resistance. Magnetic concrete is preferred for heavy-duty applications requiring electromagnetic interference reduction, while lime concrete excels in moisture-prone environments with moderate load demands.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Magnetic Concrete | Lime Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Cement with magnetic additives | Cement mixed with lime |
| Strength | High compressive strength | Moderate compressive strength |
| Durability | Resistant to cracking and weathering | Good resistance to moisture |
| Setting Time | Faster setting due to additives | Longer setting time |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Economical |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate - depends on magnetic additives | Low - uses natural lime |
| Use in Sub-base | Ideal for high-load bearing applications | Suitable for low to moderate load conditions |
| Porosity and Permeability | Low porosity, reduced water infiltration | Higher porosity, better drainage |
Introduction to Concrete Types for Sub-base
Magnetic concrete and lime concrete serve as effective sub-base materials, each offering distinct advantages based on composition and performance characteristics. Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic particles, enhancing electromagnetic detection and potentially improving structural integrity in certain geotechnical applications. Lime concrete, traditionally used for its durability and resistance to moisture, provides strong binding properties and excellent workability, making it suitable for foundational layers in road and pavement construction.
What is Magnetic Concrete?
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials like iron filings or magnetite to enhance load distribution and improve electromagnetic interference shielding in sub-base applications. This innovative composite material offers superior durability and resistance to cracking compared to traditional lime concrete, which relies on calcium hydroxide for binding and strength. Utilizing magnetic concrete in sub-base layers can optimize structural stability and reduce maintenance costs in infrastructure projects.
What is Lime Concrete?
Lime concrete is a composite material made from lime, sand, and water, serving as a flexible and breathable sub-base layer in construction. Unlike magnetic concrete, it provides excellent moisture regulation and resistance to sulfate attack, making it ideal for damp environments. Lime concrete's natural hydraulic properties enable sturdy foundations while maintaining environmental sustainability and reducing carbon footprint.
Composition and Material Differences
Magnetic concrete for sub-base construction incorporates magnetic materials such as iron oxide particles, enhancing its electromagnetic properties and improving ground stability through magnetic attraction. Lime concrete, composed primarily of lime, sand, and aggregate, relies on hydraulic and pozzolanic reactions for strength and durability without magnetic components. The key material difference lies in magnetic concrete's inclusion of ferromagnetic additives, which contribute to enhanced load distribution and potential self-sensing capabilities, whereas lime concrete emphasizes traditional binding through lime-based chemical reactions.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Magnetic concrete exhibits higher compressive strength and improved tensile resistance compared to lime concrete, making it more suitable for sub-base applications requiring enhanced load-bearing capacity. The magnetic admixtures in magnetic concrete improve the microstructure, resulting in better durability and reduced porosity, whereas lime concrete typically shows lower mechanical strength and higher susceptibility to cracking under stress. Mechanical testing demonstrates that magnetic concrete sub-bases provide superior stability and longer service life under varying loads and environmental conditions.
Durability and Longevity
Magnetic concrete offers enhanced durability and longevity compared to lime concrete when used as a sub-base, primarily due to its improved resistance to cracking and environmental degradation. The magnetic properties help in better compaction and bonding of materials, resulting in a denser and more resilient sub-base. Lime concrete, while cost-effective, tends to degrade faster under moisture and freeze-thaw cycles, reducing its long-term performance in sub-base applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Magnetic concrete incorporates iron filings and magnetic additives, reducing cement content and lowering CO2 emissions compared to traditional lime concrete used in sub-bases. Lime concrete relies on lime production, which involves significant calcination emissions, whereas magnetic concrete's alternative materials promote resource efficiency and waste reduction. Sustainable sub-base construction benefits from magnetic concrete's enhanced recyclability and potential for magnetic property reuse, improving lifecycle environmental performance.
Cost Analysis of Magnetic vs Lime Concrete
Magnetic concrete typically incurs higher initial costs due to specialized materials and production processes compared to lime concrete, which is more affordable and readily available. However, magnetic concrete offers enhanced durability and reduced maintenance expenses, potentially lowering overall life-cycle costs in sub-base applications. Lime concrete remains cost-effective for projects with strict budget constraints and less demanding performance requirements.
Application Suitability for Sub-base Layers
Magnetic concrete exhibits superior load-bearing capacity and enhanced durability, making it highly suitable for sub-base layers in heavy traffic and industrial pavements. Lime concrete offers excellent soil stabilization properties, reducing plasticity and improving moisture resistance in sub-base applications for flexible pavements. The choice between magnetic and lime concrete depends on site-specific requirements such as load intensity, subgrade conditions, and environmental factors.
Conclusion: Which Concrete is Better for Sub-base?
Magnetic concrete offers enhanced compaction and increased strength due to its iron-based components, making it highly suitable for sub-base applications requiring load-bearing capacity and durability. Lime concrete provides excellent flexibility and resistance to moisture through its natural hydraulic properties, benefiting sub-bases in areas with variable moisture conditions. For sub-base performance, magnetic concrete is generally better for high-strength requirements, while lime concrete excels in environments needing moisture tolerance and flexibility.
Infographic: Magnetic concrete vs Lime concrete for Sub-base
 azmater.com
azmater.com