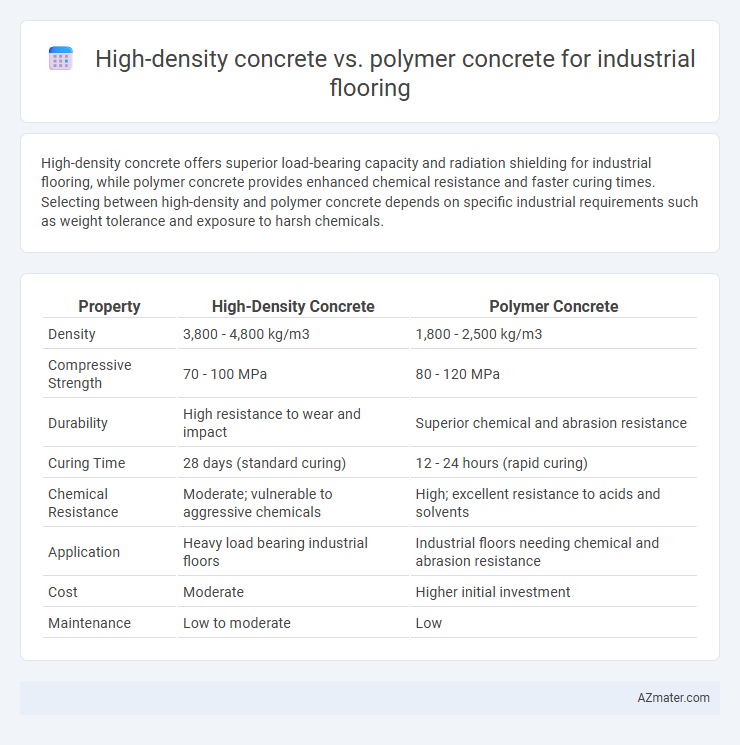
High-density concrete offers superior load-bearing capacity and radiation shielding for industrial flooring, while polymer concrete provides enhanced chemical resistance and faster curing times. Selecting between high-density and polymer concrete depends on specific industrial requirements such as weight tolerance and exposure to harsh chemicals.
Table of Comparison
| Property | High-Density Concrete | Polymer Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 3,800 - 4,800 kg/m3 | 1,800 - 2,500 kg/m3 |
| Compressive Strength | 70 - 100 MPa | 80 - 120 MPa |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and impact | Superior chemical and abrasion resistance |
| Curing Time | 28 days (standard curing) | 12 - 24 hours (rapid curing) |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate; vulnerable to aggressive chemicals | High; excellent resistance to acids and solvents |
| Application | Heavy load bearing industrial floors | Industrial floors needing chemical and abrasion resistance |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher initial investment |
| Maintenance | Low to moderate | Low |
Introduction to Industrial Flooring Materials
High-density concrete offers superior load-bearing capacity and durability for industrial flooring, utilizing heavyweight aggregates like barite or magnetite to enhance strength and radiation shielding properties. Polymer concrete, composed of resin binders and aggregates, provides excellent chemical resistance and rapid curing times, making it ideal for environments with aggressive chemicals or minimal downtime requirements. Selection between these materials depends on specific industrial demands such as mechanical stress, chemical exposure, and maintenance schedules.
High-Density Concrete: Composition and Properties
High-density concrete, primarily composed of heavyweight aggregates such as magnetite, hematite, or barite, offers superior radiation shielding, increased compressive strength, and enhanced durability for industrial flooring applications. Its dense structure provides excellent resistance to abrasion, impact, and chemical exposure, making it ideal for heavy-duty environments requiring robust performance and longevity. Compared to polymer concrete, high-density concrete typically exhibits greater thermal stability and load-bearing capacity, crucial for industrial floors subjected to heavy machinery and continuous traffic.
Polymer Concrete: Composition and Properties
Polymer concrete for industrial flooring is composed primarily of aggregates bonded with polymer resins such as epoxy, polyester, or vinyl esters, offering superior chemical resistance and durability compared to traditional high-density concrete. Its lightweight nature and enhanced tensile strength allow better performance under heavy mechanical stress and dynamic loading conditions. The fast curing time and low permeability of polymer concrete contribute to minimal maintenance and prolonged service life in industrial environments.
Strength and Durability Comparison
High-density concrete offers superior compressive strength, typically reaching 4000 to 6000 psi, making it ideal for heavy industrial flooring subjected to high point loads and impact. Polymer concrete, reinforced with resin binders, provides exceptional chemical resistance and flexibility, enhancing durability against aggressive industrial chemicals and thermal cycling. Combining strength and resilience, polymer concrete often surpasses high-density concrete in long-term performance under corrosive or dynamic industrial conditions.
Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
High-density concrete offers robust chemical resistance due to its dense matrix, making it suitable for industrial flooring exposed to acidic and alkaline substances. Polymer concrete provides superior corrosion resistance, particularly against aggressive chemicals and solvents, due to its resin binder that prevents permeability. Both materials enhance durability, but polymer concrete excels in environments with extreme chemical exposure and corrosive agents.
Installation and Curing Times
High-density concrete typically requires a longer installation process and curing time, often ranging from 7 to 28 days to achieve full strength, making it less ideal for projects needing quick turnaround. Polymer concrete offers significantly faster curing times, sometimes as short as 24 to 48 hours, due to its resin-based composition, allowing for rapid installation and minimal downtime in industrial flooring applications. The accelerated curing and ease of installation with polymer concrete enhance productivity and reduce operational interruptions compared to the traditional high-density concrete option.
Cost-Effectiveness and Lifecycle Analysis
High-density concrete offers superior compressive strength and thermal mass, making it cost-effective for heavy industrial flooring due to its durability and low maintenance needs over long operational cycles. Polymer concrete provides excellent chemical resistance and rapid curing times, reducing downtime and lifecycle costs in environments exposed to corrosive substances. Comparing lifecycle analysis, high-density concrete typically has a lower initial cost but may require more frequent repairs, whereas polymer concrete's higher upfront investment is offset by longer lifespan and reduced maintenance expenses.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
High-density concrete offers exceptional durability and low maintenance requirements due to its dense composition, making it highly resistant to wear, chemical spills, and heavy loads in industrial flooring applications. Polymer concrete provides enhanced chemical resistance and superior bonding strength, reducing the need for frequent repairs and extending the lifespan in harsh environments. Both materials deliver long-term performance, but high-density concrete typically requires less frequent surface treatments, while polymer concrete excels in environments with aggressive chemical exposure.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
High-density concrete for industrial flooring offers excellent durability but often relies on cement production, contributing significantly to CO2 emissions and environmental degradation. Polymer concrete, composed of resins and aggregates, delivers superior chemical resistance and longevity while reducing the carbon footprint through lower cement use and potential for recycled materials incorporation. Choosing polymer concrete can enhance sustainability in industrial flooring by minimizing environmental impact and supporting circular economy practices.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Material
High-density concrete excels in industrial flooring applications requiring superior load-bearing capacity and radiation shielding, making it ideal for heavy machinery zones and nuclear facilities. Polymer concrete offers exceptional chemical resistance and rapid curing, suited for environments exposed to corrosive substances and where minimal downtime is critical. Selecting between high-density and polymer concrete depends on the specific industrial demands such as mechanical stress, chemical exposure, and installation speed.
Infographic: High-density concrete vs Polymer concrete for Industrial flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com