Lightweight concrete offers reduced structural load and improved thermal insulation for road repair, while rapid-setting concrete provides faster curing times essential for minimizing traffic disruption. Selecting between these materials depends on project priorities such as load requirements and repair turnaround speed.
Table of Comparison
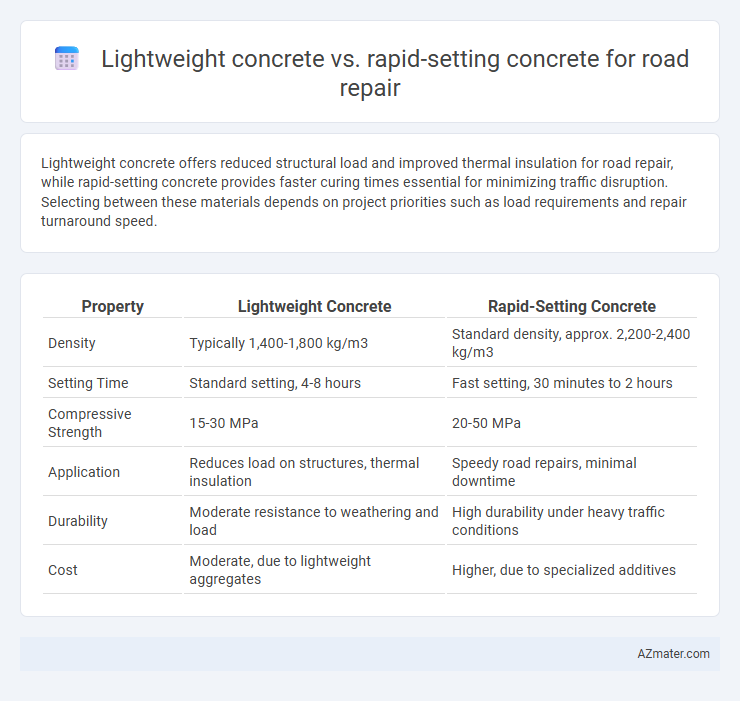
| Property | Lightweight Concrete | Rapid-Setting Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Typically 1,400-1,800 kg/m3 | Standard density, approx. 2,200-2,400 kg/m3 |
| Setting Time | Standard setting, 4-8 hours | Fast setting, 30 minutes to 2 hours |
| Compressive Strength | 15-30 MPa | 20-50 MPa |
| Application | Reduces load on structures, thermal insulation | Speedy road repairs, minimal downtime |
| Durability | Moderate resistance to weathering and load | High durability under heavy traffic conditions |
| Cost | Moderate, due to lightweight aggregates | Higher, due to specialized additives |
Introduction to Concrete Types for Road Repair
Lightweight concrete, characterized by its low density and enhanced insulation properties, offers reduced load on existing road structures and improved durability in repair applications. Rapid-setting concrete, formulated with fast-curing binders, provides accelerated strength gain critical for minimizing traffic disruption during road repairs. Selecting between lightweight and rapid-setting concrete depends on project requirements such as load capacity, curing time, and environmental conditions.
Key Differences Between Lightweight and Rapid-Setting Concrete
Lightweight concrete offers reduced density and enhanced thermal insulation, making it ideal for non-structural road repairs where weight reduction is crucial. Rapid-setting concrete provides accelerated curing times, enabling faster road reopening and minimizing traffic disruption during repairs. The main differences between the two include density, curing time, and typical applications, with lightweight concrete prioritizing ease of handling and insulation, while rapid-setting concrete emphasizes speed and early strength development.
Composition and Material Properties
Lightweight concrete for road repair typically contains low-density aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or perlite, resulting in reduced weight and enhanced thermal insulation, while rapid-setting concrete incorporates specially formulated cementitious materials like calcium sulfoaluminate or high-early-strength Portland cement for accelerated curing. The low density of lightweight concrete reduces load on underlying structures and improves fatigue resistance, whereas rapid-setting concrete achieves high early compressive strength, enabling quick reopening of roads and minimizing traffic disruption. Both materials exhibit distinct porosity and water absorption characteristics, with lightweight concrete offering improved freeze-thaw resistance and rapid-setting concrete providing superior early durability and bonding to existing pavement surfaces.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Lightweight concrete offers a density range of 800-1840 kg/m3, providing moderate strength typically between 17 to 35 MPa, and enhanced durability through reduced thermal conductivity and shrinkage, ideal for less load-bearing road repairs. Rapid-setting concrete achieves compressive strengths above 20 MPa within hours, enabling quick traffic resumption, but may exhibit higher brittleness and reduced long-term durability under freeze-thaw cycles. The choice depends on balancing immediate strength needs and long-term resilience, with lightweight concrete favoring durability and rapid-setting concrete prioritizing speed of repair.
Application Methods for Road Repairs
Lightweight concrete for road repair is applied using conventional mixing and placing techniques, allowing easy handling and reduced load on underlying structures, making it ideal for overlays and patch repairs in areas requiring minimal dead load. Rapid-setting concrete employs expedited curing processes, often through additives or chemical accelerators, enabling quick traffic reopening and reducing downtime on heavily trafficked roadways. Both materials require surface preparation including cleaning and priming, with rapid-setting concrete demanding precise timing and temperature control to optimize strength gain for immediate load-bearing capacity.
Setting Time and Curing Requirements
Lightweight concrete typically has a moderate setting time ranging from 4 to 6 hours and requires standard curing processes of 7 to 28 days to achieve optimal strength, making it suitable for durable, long-lasting road repairs. Rapid-setting concrete offers significantly faster setting times, often within 30 minutes to 2 hours, enabling road repairs to be completed quickly and reopened to traffic soon after application with minimal curing time. The choice between lightweight and rapid-setting concrete depends on project timelines and load-bearing needs, where rapid-setting is preferred for emergency repairs and lightweight concrete for robust, permanent fixes.
Cost Implications and Budget Considerations
Lightweight concrete typically reduces transportation and labor costs due to its easier handling and faster placement, which can be beneficial for budget-sensitive road repair projects. Rapid-setting concrete accelerates work completion and minimizes road closure times, potentially lowering indirect costs such as traffic disruption fees and extended labor expenses. Evaluating the initial material costs alongside long-term savings from reduced downtime is essential for cost-effective budget planning in road repair.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lightweight concrete reduces environmental impact by incorporating recycled materials like fly ash and expanded shale, which lower the overall carbon footprint and improve thermal insulation in road repair. Rapid-setting concrete minimizes construction time and reduces energy consumption on-site, leading to decreased greenhouse gas emissions during road maintenance projects. Both materials contribute to sustainability by enhancing durability and extending road lifespan, reducing the frequency of repairs and resource use.
Suitability for Different Road Repair Scenarios
Lightweight concrete offers excellent thermal insulation and reduced load, making it ideal for bridge decks and overlays where weight reduction is critical. Rapid-setting concrete provides high early strength and fast curing times, suited for emergency repairs and high-traffic areas requiring minimal downtime. Choosing between the two depends on factors like load capacity, environmental conditions, and required repair speed.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Concrete for Road Repairs
Lightweight concrete offers excellent thermal insulation and reduced dead load, making it ideal for bridge decks and overlays requiring durability with minimal weight. Rapid-setting concrete provides fast curing times, allowing for quicker road reopening and minimizing traffic disruptions in urgent repairs. Selecting the right concrete depends on project needs such as load capacity, time constraints, and environmental conditions to optimize repair effectiveness and longevity.
Infographic: Lightweight concrete vs Rapid-setting concrete for Road repair
 azmater.com
azmater.com