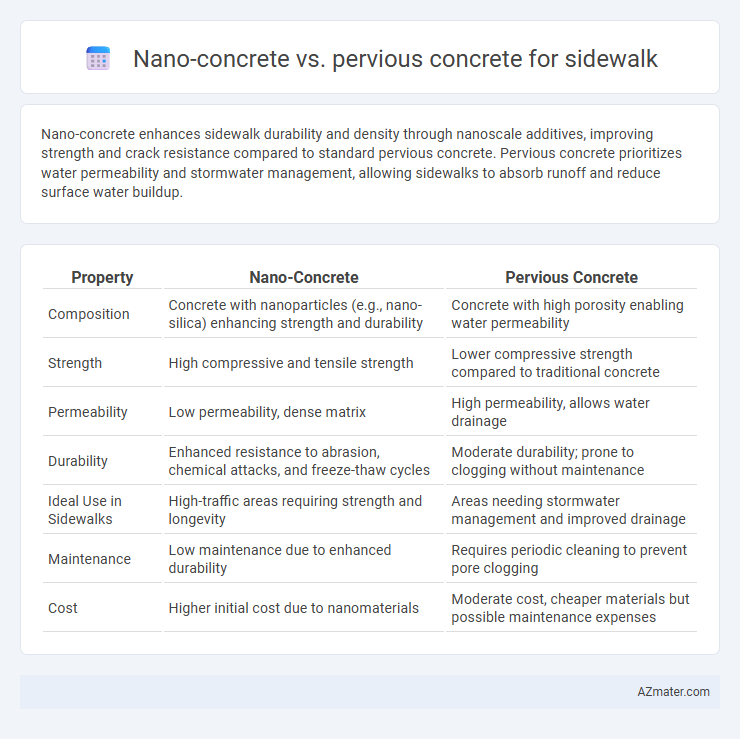
Nano-concrete enhances sidewalk durability and density through nanoscale additives, improving strength and crack resistance compared to standard pervious concrete. Pervious concrete prioritizes water permeability and stormwater management, allowing sidewalks to absorb runoff and reduce surface water buildup.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nano-Concrete | Pervious Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Concrete with nanoparticles (e.g., nano-silica) enhancing strength and durability | Concrete with high porosity enabling water permeability |
| Strength | High compressive and tensile strength | Lower compressive strength compared to traditional concrete |
| Permeability | Low permeability, dense matrix | High permeability, allows water drainage |
| Durability | Enhanced resistance to abrasion, chemical attacks, and freeze-thaw cycles | Moderate durability; prone to clogging without maintenance |
| Ideal Use in Sidewalks | High-traffic areas requiring strength and longevity | Areas needing stormwater management and improved drainage |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to enhanced durability | Requires periodic cleaning to prevent pore clogging |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to nanomaterials | Moderate cost, cheaper materials but possible maintenance expenses |
Introduction to Nano-Concrete and Pervious Concrete
Nano-concrete incorporates nanoparticles like silica fume or carbon nanotubes to enhance strength, durability, and impermeability, making it ideal for high-performance sidewalks requiring longevity and resistance to weathering. Pervious concrete features a porous structure that facilitates efficient water drainage, reducing surface runoff and preventing puddles on sidewalks while promoting groundwater recharge. Both materials offer distinct advantages for sidewalk construction, with nano-concrete maximizing structural integrity and pervious concrete optimizing environmental sustainability.
Composition and Material Properties
Nano-concrete incorporates nanoparticles like silica or titanium dioxide, enhancing its compressive strength, durability, and resistance to micro-cracking, making it ideal for high-stress sidewalk applications. Pervious concrete features a porous matrix composed of coarse aggregates and minimal fine aggregates, enabling superior water permeability and reducing surface runoff. The choice between these materials depends on prioritizing either structural performance with nano-enhanced composites or effective stormwater management through permeable concrete.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Nano-concrete exhibits superior compressive strength and enhanced durability compared to pervious concrete, owing to the incorporation of nanoparticles that improve the microstructure and reduce porosity. Pervious concrete, designed primarily for permeability, generally has lower strength and is more susceptible to wear and freeze-thaw cycles, making it less durable under heavy traffic conditions. For sidewalks requiring optimal load-bearing capacity and longevity, nano-concrete offers a more robust solution while maintaining necessary environmental benefits.
Permeability and Water Drainage Efficiency
Nano-concrete enhances permeability through the incorporation of nanoparticles that fill micro-voids, resulting in improved water drainage and reduced surface runoff on sidewalks. Pervious concrete features a highly porous structure that allows rapid water infiltration, effectively managing stormwater and minimizing puddling. While both materials facilitate drainage, pervious concrete typically offers superior permeability and water drainage efficiency due to its interconnected void network specifically designed for water passage.
Sustainability and Environmental Impacts
Nano-concrete enhances the durability and lifespan of sidewalks by incorporating nanoparticles that improve strength and reduce permeability, leading to less frequent repairs and lower resource consumption. Pervious concrete promotes sustainability by allowing water infiltration, reducing stormwater runoff and recharging groundwater, which mitigates urban flooding and minimizes heat island effects. Both materials contribute to environmental benefits, with nano-concrete reducing maintenance-related emissions and pervious concrete improving urban water management and ecosystem health.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Nano-concrete requires precise mixing and curing processes to ensure the nanoparticles achieve optimal strength and durability, often demanding skilled labor and specialized equipment during installation. Pervious concrete installation involves careful control of aggregate size and compaction to maintain its permeability properties, with routine inspections necessary to prevent clogging from debris and sediment buildup. Maintenance for nano-concrete is minimal due to its enhanced resistance to environmental wear, while pervious concrete necessitates regular vacuuming or pressure washing to sustain effective water drainage.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Nano-concrete offers enhanced durability and strength due to its nanoscale additives, potentially reducing long-term maintenance costs despite higher initial expenses compared to pervious concrete. Pervious concrete, known for its water permeability and environmental benefits, generally has lower upfront costs but may incur increased maintenance due to clogging and reduced structural integrity over time. Economic considerations for sidewalk projects weigh nano-concrete's higher initial investment against its longevity and reduced lifecycle costs, while pervious concrete's affordability and ecological advantages suit budgets prioritizing stormwater management and sustainability.
Performance in Extreme Weather Conditions
Nano-concrete exhibits superior durability and enhanced freeze-thaw resistance compared to pervious concrete, making it highly suitable for sidewalks in extreme weather conditions. Its nano-scale additives improve microstructure density, reducing water permeability and minimizing damage from ice expansion during cold climates. Pervious concrete, while excellent for stormwater management, tends to have lower compressive strength and higher susceptibility to freeze-thaw cycles, which can compromise sidewalk performance in harsh weather.
Suitability for Urban Sidewalk Applications
Nano-concrete offers superior durability and enhanced strength due to its nanoscale additives, making it highly resistant to wear and environmental degradation in urban sidewalk applications. Pervious concrete excels in water permeability, effectively reducing surface runoff and promoting groundwater recharge, which is critical in managing urban stormwater. Selecting between nano-concrete and pervious concrete depends on the specific urban priorities of durability versus permeability for sidewalk performance.
Future Trends and Innovations in Concrete Technology
Nano-concrete and pervious concrete represent cutting-edge advancements in concrete technology, with nano-concrete offering enhanced strength and durability through nanoparticle integration, while pervious concrete promotes sustainable urban drainage by allowing water infiltration. Future trends highlight the integration of self-healing nanomaterials and smart sensors in nano-concrete to extend sidewalk lifespan and reduce maintenance costs. Innovations in pervious concrete focus on improving clog resistance and pollutant filtration, aligning with green infrastructure goals for resilient and eco-friendly urban sidewalks.
Infographic: Nano-concrete vs Pervious concrete for Sidewalk
 azmater.com
azmater.com