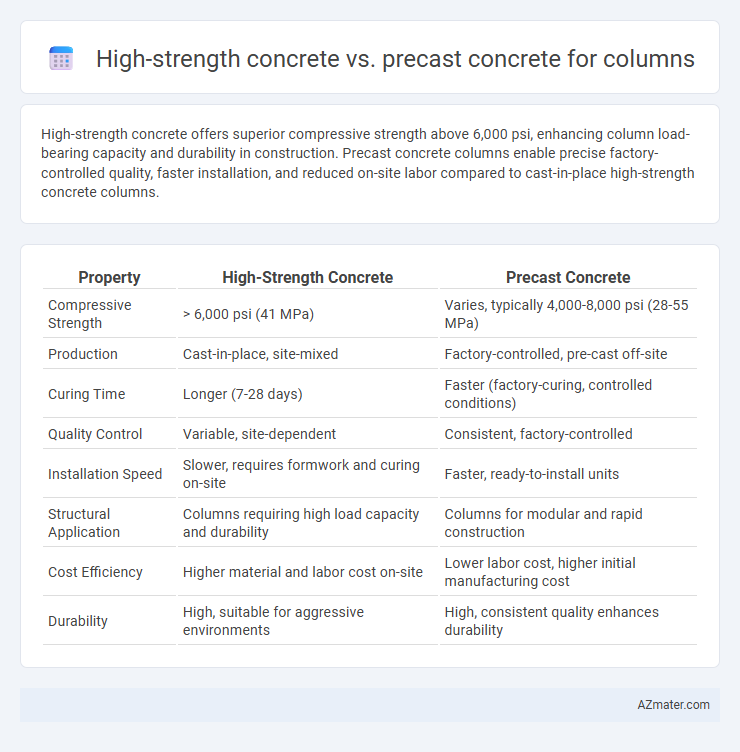
High-strength concrete offers superior compressive strength above 6,000 psi, enhancing column load-bearing capacity and durability in construction. Precast concrete columns enable precise factory-controlled quality, faster installation, and reduced on-site labor compared to cast-in-place high-strength concrete columns.
Table of Comparison
| Property | High-Strength Concrete | Precast Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive Strength | > 6,000 psi (41 MPa) | Varies, typically 4,000-8,000 psi (28-55 MPa) |
| Production | Cast-in-place, site-mixed | Factory-controlled, pre-cast off-site |
| Curing Time | Longer (7-28 days) | Faster (factory-curing, controlled conditions) |
| Quality Control | Variable, site-dependent | Consistent, factory-controlled |
| Installation Speed | Slower, requires formwork and curing on-site | Faster, ready-to-install units |
| Structural Application | Columns requiring high load capacity and durability | Columns for modular and rapid construction |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher material and labor cost on-site | Lower labor cost, higher initial manufacturing cost |
| Durability | High, suitable for aggressive environments | High, consistent quality enhances durability |
Introduction to High-Strength and Precast Concrete Columns
High-strength concrete columns offer enhanced load-bearing capacity due to their elevated compressive strength, typically exceeding 6000 psi, making them ideal for high-rise structures and infrastructure requiring superior durability. Precast concrete columns are manufactured off-site under controlled conditions, ensuring uniform quality, faster installation times, and reduced on-site labor costs while maintaining structural integrity. Both high-strength and precast concrete columns contribute to efficient construction practices but differ primarily in their production methods and application contexts.
Material Composition and Properties
High-strength concrete for columns typically consists of a low water-cement ratio, advanced admixtures like silica fume or fly ash, and optimized grading of aggregates to achieve compressive strengths exceeding 60 MPa. Precast concrete columns are manufactured in controlled factory conditions, incorporating similar high-performance materials but often enhanced with fiber reinforcement or steel inserts to improve durability and load-bearing capacity. The superior material composition of high-strength concrete results in improved density, reduced permeability, and enhanced resistance to environmental stresses, while precast concrete columns benefit from precise curing and quality control to ensure consistency in strength and dimensional accuracy.
Manufacturing and Curing Processes
High-strength concrete used for columns undergoes a precise mixing process with high cement content and low water-cement ratio to achieve compressive strengths often exceeding 6,000 psi, requiring extended curing periods typically employing steam curing to enhance early strength development. Precast concrete columns are manufactured in controlled factory environments where optimized molds and vibration techniques ensure uniform density, followed by accelerated curing processes such as autoclaving or heat curing to reduce production time and improve durability. The controlled conditions in precast manufacturing provide consistent quality, whereas on-site curing for high-strength concrete demands strict monitoring to prevent shrinkage and cracking during hydration.
Structural Performance and Load-Bearing Capacity
High-strength concrete exhibits superior compressive strength exceeding 60 MPa, enhancing column load-bearing capacity and resistance to axial loads compared to standard concrete. Precast concrete columns offer controlled manufacturing conditions, resulting in consistent material quality and improved dimensional accuracy, which optimizes structural performance under dynamic and seismic loads. Both materials contribute to enhanced structural durability, but high-strength concrete is preferred for slender columns requiring higher load capacity, while precast concrete excels in modular construction with rapid assembly demands.
Installation Techniques and Construction Speed
High-strength concrete used for columns requires careful on-site mixing and precise curing times, often extending installation durations compared to precast concrete. Precast concrete columns are manufactured in controlled factory environments, allowing for rapid installation through crane placement, significantly reducing on-site construction time. The streamlined process of precast concrete minimizes weather-related delays and labor intensity, optimizing overall project schedules.
Durability and Longevity
High-strength concrete offers superior durability for columns due to its enhanced compressive strength and resistance to environmental factors like corrosion and freeze-thaw cycles. Precast concrete columns benefit from factory-controlled conditions, ensuring consistent quality and reducing the risk of structural defects, which contributes to longevity. Both materials extend the lifespan of columns, but high-strength concrete is particularly effective in demanding structural applications where longevity under stress is critical.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
High-strength concrete for columns often entails higher material costs due to advanced mix designs featuring supplementary cementitious materials and admixtures, increasing initial expenses by 15-30% compared to standard concrete. Precast concrete columns provide cost savings through factory-controlled production, reducing labor costs by up to 25% and minimizing onsite construction time, leading to earlier project completion and lower financing charges. Economic considerations favor precast concrete in large-scale projects with repetitive designs, while high-strength concrete suits complex, custom-column requirements where transportation and handling costs may offset initial savings from precasting.
Design Flexibility and Architectural Applications
High-strength concrete offers superior compressive strength and durability, enabling slimmer column profiles and greater design flexibility in complex architectural applications. Precast concrete provides precise dimensional control and faster onsite installation, supporting modular construction and repetitive column designs with consistent quality. Combining high-strength concrete in precast elements enhances architectural versatility while optimizing structural performance and construction efficiency.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
High-strength concrete significantly reduces material usage and improves structural efficiency, leading to lower carbon emissions compared to conventional mixes, thus enhancing sustainability in column construction. Precast concrete columns promote environmental benefits by minimizing on-site waste, enabling controlled production environments that reduce energy consumption and enhance quality control. Combining high-strength material with precast methods optimizes lifecycle performance, decreases construction time, and supports sustainable practices by reducing overall resource consumption and carbon footprint.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Concrete Solution for Columns
High-strength concrete offers superior load-bearing capacity and durability, making it ideal for columns requiring enhanced structural performance in high-rise buildings. Precast concrete provides precision manufacturing, faster installation, and quality control benefits, suitable for projects with tight schedules and repetitive column designs. Selecting the right concrete solution depends on balancing structural demands, project timelines, and cost considerations to ensure optimal column performance and longevity.
Infographic: High-strength concrete vs Precast concrete for Column
 azmater.com
azmater.com