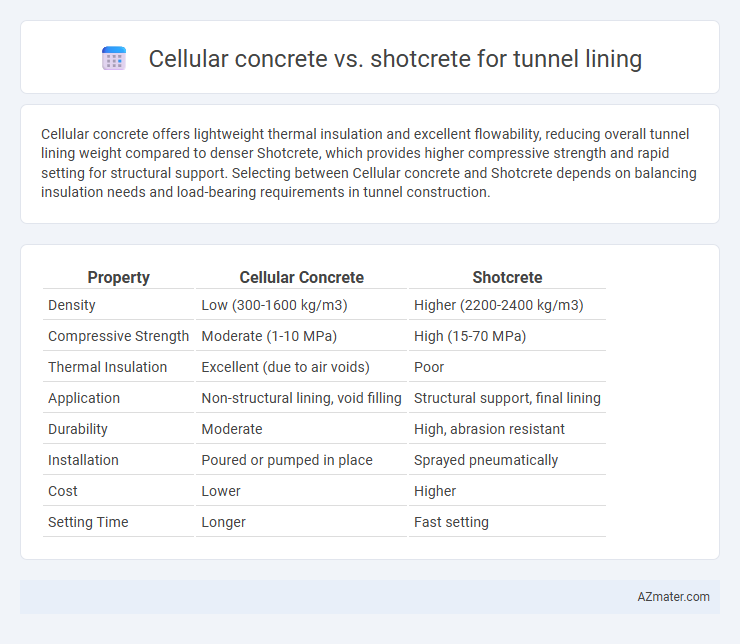
Cellular concrete offers lightweight thermal insulation and excellent flowability, reducing overall tunnel lining weight compared to denser Shotcrete, which provides higher compressive strength and rapid setting for structural support. Selecting between Cellular concrete and Shotcrete depends on balancing insulation needs and load-bearing requirements in tunnel construction.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellular Concrete | Shotcrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low (300-1600 kg/m3) | Higher (2200-2400 kg/m3) |
| Compressive Strength | Moderate (1-10 MPa) | High (15-70 MPa) |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent (due to air voids) | Poor |
| Application | Non-structural lining, void filling | Structural support, final lining |
| Durability | Moderate | High, abrasion resistant |
| Installation | Poured or pumped in place | Sprayed pneumatically |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Setting Time | Longer | Fast setting |
Introduction to Tunnel Lining Methods
Tunnel lining methods play a critical role in ensuring structural stability and safety during tunnel construction. Cellular concrete offers lightweight, high-insulation properties and ease of application, making it suitable for secondary lining in tunnels with complex geometries. Shotcrete provides rapid setting, high strength, and excellent adhesion, favored for primary lining and immediate ground support in underground excavation projects.
Overview of Cellular Concrete
Cellular concrete is a lightweight, aerated material composed of cement, water, and pre-formed foam, offering high flowability and reduced self-weight benefits for tunnel lining applications. Its excellent thermal insulation, fire resistance, and ability to fill irregular voids make it suitable for complex tunnel geometries compared to shotcrete. With lower permeability and good compressive strength, cellular concrete enhances durability and long-term performance in subterranean environments.
Overview of Shotcrete
Shotcrete is a method of applying concrete projected at high velocity onto surfaces, commonly used for tunnel lining due to its excellent adhesion and rapid setting properties. It provides structural support and stability, conforming to complex tunnel geometries and minimizing formwork requirements. Its high early strength and durability make shotcrete ideal for reinforcing tunnels in diverse geological conditions.
Material Properties Comparison
Cellular concrete exhibits lower density and higher thermal insulation compared to shotcrete, making it advantageous for reducing dead load and enhancing energy efficiency in tunnel linings. Shotcrete offers superior compressive strength and abrasion resistance due to its dense matrix and fiber reinforcement, providing robust structural support in high-stress environments. The porosity of cellular concrete contributes to improved drainage and reduced water permeability, whereas shotcrete's dense composition ensures better durability against chemical attack and mechanical wear.
Application Techniques and Equipment
Cellular concrete for tunnel lining is applied using specialized pneumatic or pump equipment designed for low-density, flowable materials, enabling precise placement and rapid curing in complex geometries. Shotcrete involves spraying concrete pneumatically at high velocity through a hose and nozzle using compressed air, which ensures strong adhesion to tunnel surfaces and allows for immediate support in excavation zones. Equipment for shotcrete often includes rotor-stator pumps and robotic arms for automation, while cellular concrete systems prioritize mixers with foaming agents for consistent cellular structure and volume control.
Structural Performance in Tunnel Linings
Cellular concrete offers excellent thermal insulation and lightweight properties but generally exhibits lower compressive strength compared to shotcrete, impacting its load-bearing capacity in tunnel linings. Shotcrete provides superior structural performance with higher compressive strengths and better durability, allowing it to withstand dynamic loads and ground pressures typical in tunnel environments. The choice between the two often depends on balancing structural demands with factors like ease of application and project-specific geological conditions.
Durability and Longevity
Cellular concrete offers enhanced durability in tunnel lining due to its lightweight structure and resistance to freeze-thaw cycles, reducing crack formation and structural degradation over time. Shotcrete, comprised of pneumatically applied concrete, provides superior adhesion and compressive strength, which contributes to its long-lasting performance under heavy load and impacts within tunnel environments. Both materials demonstrate significant longevity, but shotcrete generally excels in high-stress zones, whereas cellular concrete is preferred for insulation and corrosion resistance.
Cost Analysis: Cellular Concrete vs Shotcrete
Cellular concrete offers significant cost advantages over shotcrete for tunnel lining due to lower material expenses and reduced labor requirements, as its lightweight composition simplifies handling and placement. Shotcrete involves higher equipment and operational costs, including specialized spraying machinery and skilled labor, which can increase overall project budgets. Long-term maintenance and durability factors further influence cost-effectiveness, with cellular concrete often providing better thermal insulation and reduced waterproofing expenses.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Cellular concrete offers enhanced environmental benefits over shotcrete due to its lower density, which reduces raw material use and energy consumption during production, leading to a smaller carbon footprint in tunnel lining applications. Safety considerations favor cellular concrete as its lightweight nature minimizes the risk of rebound and creates less dust, improving worker conditions compared to shotcrete, which can generate significant airborne particles and require extensive ventilation. Shotcrete, while providing excellent adhesion and rapid setting, demands rigorous safety protocols to mitigate risks associated with pneumatic spraying, including inhalation hazards and rebound injuries in tunnel construction environments.
Best Practices for Selection and Implementation
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties, making it ideal for tunnel lining where reduced structural load is critical, while shotcrete provides high early strength and excellent adhesion for complex geometries in tunnel excavation. Best practices for selection emphasize evaluating site-specific factors such as load-bearing requirements, moisture conditions, and curing time constraints, ensuring the chosen material aligns with project safety and durability standards. Implementation requires precise mix design control, skilled application techniques, and rigorous quality monitoring to optimize performance and longevity in tunnel environments.
Infographic: Cellular concrete vs Shotcrete for Tunnel lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com