Pervious concrete enhances slope stabilization by improving water drainage and reducing erosion risks, while shotcrete provides immediate structural support through a sprayed concrete layer that adheres to slope surfaces. Choosing between pervious concrete and shotcrete depends on balancing water permeability requirements with the need for rapid slope reinforcement.
Table of Comparison
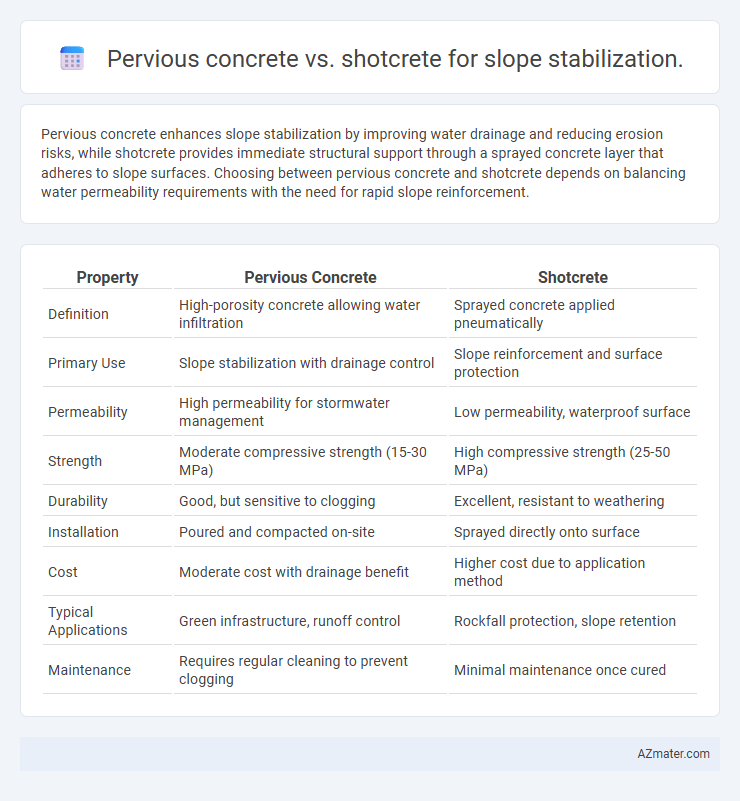
| Property | Pervious Concrete | Shotcrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | High-porosity concrete allowing water infiltration | Sprayed concrete applied pneumatically |
| Primary Use | Slope stabilization with drainage control | Slope reinforcement and surface protection |
| Permeability | High permeability for stormwater management | Low permeability, waterproof surface |
| Strength | Moderate compressive strength (15-30 MPa) | High compressive strength (25-50 MPa) |
| Durability | Good, but sensitive to clogging | Excellent, resistant to weathering |
| Installation | Poured and compacted on-site | Sprayed directly onto surface |
| Cost | Moderate cost with drainage benefit | Higher cost due to application method |
| Typical Applications | Green infrastructure, runoff control | Rockfall protection, slope retention |
| Maintenance | Requires regular cleaning to prevent clogging | Minimal maintenance once cured |
Introduction to Slope Stabilization Methods
Pervious concrete and shotcrete are effective materials for slope stabilization, offering unique benefits based on soil and environmental conditions. Pervious concrete enhances drainage by allowing water to pass through, reducing hydrostatic pressure and erosion on slopes, while shotcrete provides immediate structural reinforcement with a sprayed concrete layer that binds loose soil and rock. Selecting between pervious concrete and shotcrete depends on the slope's stability requirements, drainage needs, and the intended durability of the stabilization method.
What is Pervious Concrete?
Pervious concrete is a porous material designed to allow water to pass through its structure, reducing surface runoff and promoting groundwater recharge, making it ideal for slope stabilization in erosion-prone areas. Its high permeability is achieved by using little to no fine aggregates, creating interconnected voids that facilitate drainage and minimize hydrostatic pressure behind slopes. This characteristic contrasts with shotcrete, which is typically dense and impermeable, highlighting pervious concrete's advantage in slope stabilization applications requiring efficient water management.
Understanding Shotcrete Technology
Shotcrete technology involves the pneumatic application of concrete or mortar onto surfaces at high velocity, ensuring excellent adhesion and compaction for slope stabilization. This method enables rapid placement on steep or irregular terrains, reducing erosion risks and enhancing structural integrity. Its adaptability with fiber reinforcement and additives improves durability and resistance to environmental stress compared to traditional pervious concrete applications.
Material Properties: Pervious Concrete vs Shotcrete
Pervious concrete offers high permeability, allowing water to drain through its interconnected voids, which reduces runoff and enhances slope stability by preventing water buildup. Shotcrete, characterized by its dense, high-strength matrix, provides superior adhesion and resistance to environmental erosion, making it ideal for immediate reinforcement on steep or irregular slopes. While pervious concrete emphasizes drainage and groundwater recharge, shotcrete focuses on structural support and rapid application, with material properties tailored to different slope stabilization needs.
Installation Techniques and Equipment Requirements
Pervious concrete for slope stabilization requires specialized mixing trucks and careful placement using screeds and rollers to maintain its porous structure, allowing efficient water drainage and reducing erosion. Shotcrete installation involves pneumatically spraying concrete onto the slope with high-velocity hoses, requiring skilled nozzle operators and portable compressor equipment to ensure optimal adhesion and structural support. Equipment for shotcrete is more mobile and suitable for uneven terrains, while pervious concrete demands precise batching and controlled compaction for effective slope reinforcement.
Drainage Capabilities and Water Management
Pervious concrete excels in slope stabilization by allowing water to infiltrate through its porous structure, reducing surface runoff and promoting natural groundwater recharge. Shotcrete, while providing strong structural support, is mostly impermeable, directing water away from the slope surface but requiring additional drainage solutions to manage runoff effectively. Proper selection between pervious concrete and shotcrete depends on balancing slope stability needs with efficient water management and erosion control.
Erosion Control and Soil Stabilization Performance
Pervious concrete enhances slope stabilization by allowing water to infiltrate, reducing surface runoff and minimizing erosion while promoting soil moisture retention that supports vegetation growth. Shotcrete provides immediate soil stabilization through its strong adhesion and rapid curing, forming a protective layer that prevents soil displacement and controls erosion effectively on steep or unstable slopes. Combining both materials strategically offers superior erosion control and soil stabilization by balancing permeability and structural reinforcement.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Pervious concrete offers excellent drainage capabilities, reducing water buildup and erosion on slopes, which enhances long-term durability and minimizes maintenance needs. Shotcrete provides superior early strength and adherence on steep or irregular surfaces, but it may require more frequent inspections and repairs due to potential cracking and weathering effects. Maintenance of pervious concrete primarily involves ensuring pore spaces remain unblocked, whereas shotcrete surfaces demand monitoring for structural integrity and surface degradation under harsh environmental conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Pervious concrete significantly reduces runoff by allowing water infiltration, enhancing groundwater recharge and minimizing erosion, which contributes positively to sustainable slope stabilization efforts. Shotcrete, while providing immediate structural support and erosion control, often involves higher cement content and energy-intensive application methods, leading to a larger carbon footprint compared to pervious concrete. Selecting pervious concrete leverages its eco-friendly permeability and reduced environmental impact, making it a more sustainable choice for long-term slope stabilization projects.
Cost Comparison and Economic Viability
Pervious concrete offers cost benefits in slope stabilization through its permeability, reducing the need for extensive drainage systems and lowering long-term maintenance expenses. Shotcrete, while generally more expensive upfront due to specialized application and materials, provides rapid deployment and superior adhesion on irregular surfaces, potentially reducing labor costs in complex terrains. Economic viability depends on project scale and site conditions, with pervious concrete favored for cost-effective drainage and shotcrete preferred where structural reinforcement and quick setting are essential.
Infographic: Pervious concrete vs Shotcrete for Slope stabilization
 azmater.com
azmater.com