Smart concrete incorporates sensors and self-healing properties to enhance pavement durability, while pervious concrete improves water drainage and reduces runoff by allowing water to pass through its porous structure. Both materials offer innovative solutions to extend pavement lifespan and address environmental challenges in urban infrastructure.
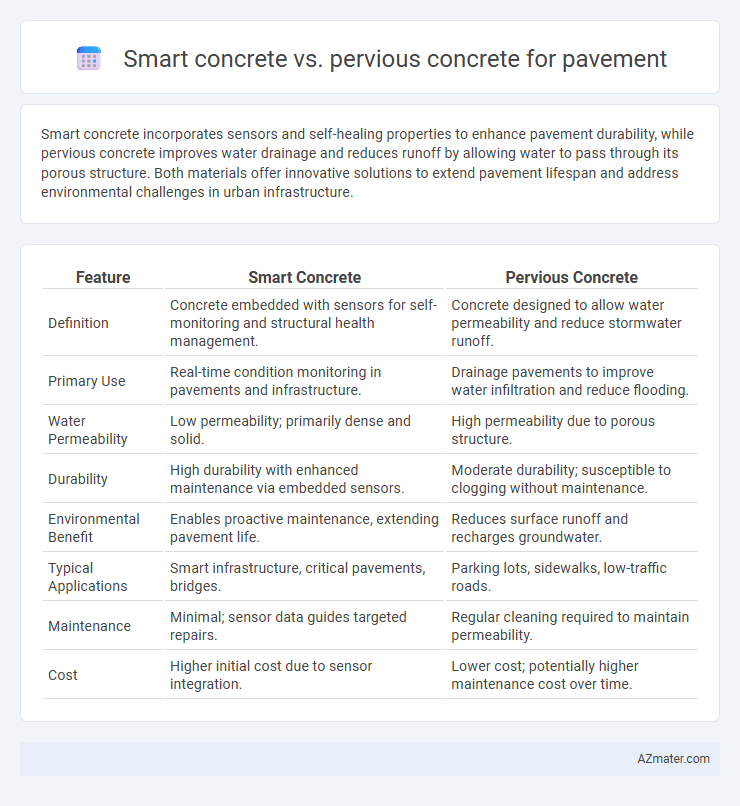
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Concrete | Pervious Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete embedded with sensors for self-monitoring and structural health management. | Concrete designed to allow water permeability and reduce stormwater runoff. |
| Primary Use | Real-time condition monitoring in pavements and infrastructure. | Drainage pavements to improve water infiltration and reduce flooding. |
| Water Permeability | Low permeability; primarily dense and solid. | High permeability due to porous structure. |
| Durability | High durability with enhanced maintenance via embedded sensors. | Moderate durability; susceptible to clogging without maintenance. |
| Environmental Benefit | Enables proactive maintenance, extending pavement life. | Reduces surface runoff and recharges groundwater. |
| Typical Applications | Smart infrastructure, critical pavements, bridges. | Parking lots, sidewalks, low-traffic roads. |
| Maintenance | Minimal; sensor data guides targeted repairs. | Regular cleaning required to maintain permeability. |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to sensor integration. | Lower cost; potentially higher maintenance cost over time. |
Introduction to Smart Concrete and Pervious Concrete
Smart concrete integrates advanced materials like embedded sensors and self-healing agents to enhance durability and monitor structural health in pavement applications. Pervious concrete, characterized by its high porosity, facilitates water infiltration and reduces surface runoff, promoting sustainable urban drainage systems. Both materials offer innovative solutions for pavement design, balancing environmental benefits with functional performance.
Composition and Material Properties
Smart concrete incorporates advanced materials like carbon nanotubes, fiber optics, and phase-change materials, enhancing its self-sensing, thermal regulation, and structural health monitoring capabilities. Pervious concrete consists of coarse aggregates, water, and minimal cement paste, creating a porous matrix that enables water infiltration while maintaining adequate strength and permeability. The high porosity of pervious concrete contrasts with the dense, multifunctional matrix of smart concrete, making each suitable for specific pavement performance requirements.
Key Functional Differences
Smart concrete for pavement integrates embedded sensors and self-healing capabilities to monitor structural health and autonomously repair minor cracks, enhancing durability and safety. Pervious concrete prioritizes permeability, allowing water to infiltrate through the pavement surface to reduce runoff and improve stormwater management. Key functional differences include real-time condition monitoring and self-repair in smart concrete versus water drainage and environmental benefits in pervious concrete.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Smart concrete incorporates self-healing agents and embedded sensors that enhance its strength and durability by automatically repairing micro-cracks and monitoring structural health in real-time. Pervious concrete, designed for water permeability, typically exhibits lower compressive strength ranging from 20 to 30 MPa, which limits its load-bearing capacity compared to smart concrete with strengths exceeding 40 MPa. In terms of durability, smart concrete outperforms pervious concrete due to its ability to prevent crack propagation and resist environmental damage, whereas pervious concrete may experience faster degradation under heavy traffic loads and freeze-thaw cycles.
Water Management Capabilities
Smart concrete incorporates sensors and self-healing properties that monitor and improve pavement durability while actively managing water by reducing surface cracks and preventing water ingress. Pervious concrete, designed with a porous structure, facilitates rapid water infiltration directly through the pavement surface, effectively reducing runoff and replenishing groundwater. While pervious concrete excels in immediate water permeability, smart concrete offers advanced long-term water management through real-time monitoring and maintenance capabilities.
Environmental and Sustainability Benefits
Smart concrete incorporates sensors that monitor structural health, enabling timely maintenance and extending pavement lifespan, which reduces resource consumption and minimizes environmental impact. Pervious concrete enhances stormwater management by allowing water infiltration, reducing runoff, and promoting groundwater recharge, thus mitigating urban flooding and improving water quality. Both materials contribute to sustainable pavement solutions by decreasing lifecycle costs and environmental footprint through innovative performance and eco-friendly features.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Smart concrete for pavement installation requires advanced sensors integration and precise placement techniques to ensure functionality, while pervious concrete relies on conventional methods with emphasis on maintaining porosity during placement. Maintenance of smart concrete involves periodic calibration and monitoring of embedded sensors to maintain data accuracy, whereas pervious concrete demands routine cleaning to prevent clogging and sustain permeability for effective stormwater management. Both materials require specialized approaches tailored to their unique properties, impacting long-term performance and operational costs.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Smart concrete incorporates advanced materials such as self-healing agents and sensors, increasing initial costs by 20-30% compared to traditional mixes, whereas pervious concrete offers lower installation costs due to simpler formulations and reduced drainage infrastructure requirements. Economic considerations favor pervious concrete in projects emphasizing stormwater management and regulatory compliance, with maintenance costs generally lower due to fewer flooding damages. Smart concrete's lifecycle benefits include reduced repair frequency and enhanced durability, potentially offsetting higher upfront expenses through long-term asset management savings.
Suitable Applications and Use Cases
Smart concrete incorporates sensors and self-healing properties, making it ideal for infrastructure requiring real-time monitoring and extended durability, such as bridges and highways with heavy traffic loads. Pervious concrete excels in applications needing effective stormwater management and reduced surface runoff, making it suitable for parking lots, pedestrian walkways, and low-traffic pavements in urban environments. Both materials address sustainability but differ in function: smart concrete enhances structural performance, while pervious concrete focuses on environmental impact and water infiltration.
Future Trends in Pavement Technologies
Smart concrete integrates sensors and self-healing properties to enhance durability and monitor structural health in pavement applications, driving significant advancements in predictive maintenance. Pervious concrete improves stormwater management and reduces runoff by allowing water infiltration, key for sustainable urban development. Future trends emphasize the convergence of these materials with IoT and AI technologies to create adaptive, resilient, and eco-friendly pavement systems.
Infographic: Smart concrete vs Pervious concrete for Pavement
 azmater.com
azmater.com