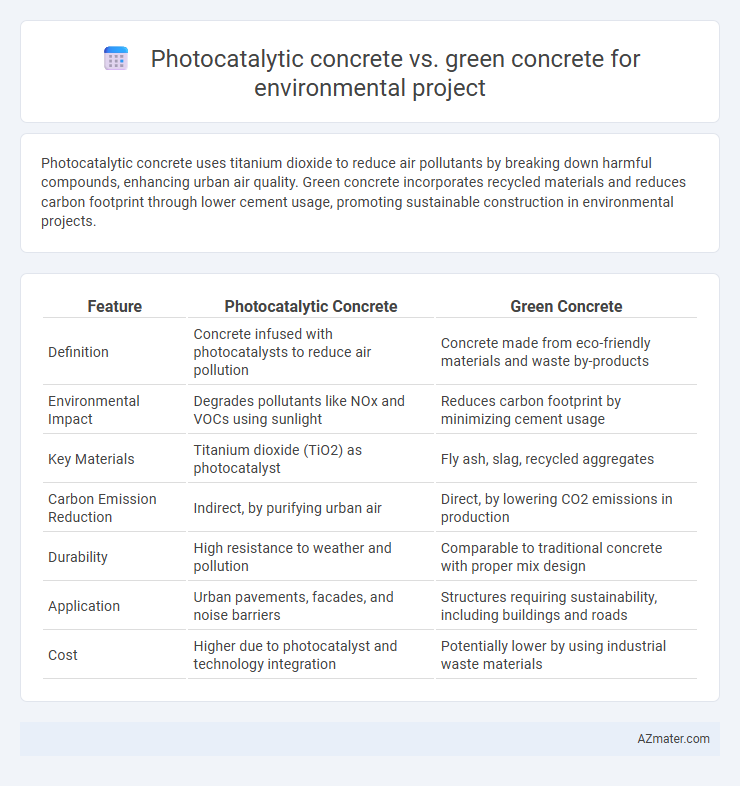
Photocatalytic concrete uses titanium dioxide to reduce air pollutants by breaking down harmful compounds, enhancing urban air quality. Green concrete incorporates recycled materials and reduces carbon footprint through lower cement usage, promoting sustainable construction in environmental projects.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Photocatalytic Concrete | Green Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete infused with photocatalysts to reduce air pollution | Concrete made from eco-friendly materials and waste by-products |
| Environmental Impact | Degrades pollutants like NOx and VOCs using sunlight | Reduces carbon footprint by minimizing cement usage |
| Key Materials | Titanium dioxide (TiO2) as photocatalyst | Fly ash, slag, recycled aggregates |
| Carbon Emission Reduction | Indirect, by purifying urban air | Direct, by lowering CO2 emissions in production |
| Durability | High resistance to weather and pollution | Comparable to traditional concrete with proper mix design |
| Application | Urban pavements, facades, and noise barriers | Structures requiring sustainability, including buildings and roads |
| Cost | Higher due to photocatalyst and technology integration | Potentially lower by using industrial waste materials |
Introduction to Eco-Friendly Concrete Solutions
Photocatalytic concrete incorporates titanium dioxide to break down pollutants and improve air quality through a self-cleaning surface, making it a cutting-edge solution in sustainable construction. Green concrete utilizes recycled materials and industrial byproducts like fly ash or slag to reduce carbon emissions and conserve natural resources during production. Both technologies offer eco-friendly alternatives to traditional concrete, enhancing environmental projects with reduced ecological footprints and improved sustainability performance.
What is Photocatalytic Concrete?
Photocatalytic concrete is a type of concrete embedded with titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles that activate under sunlight to break down air pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). This concrete contributes to improving urban air quality by converting harmful substances into less toxic compounds through photocatalysis. Its environmental project applications focus on reducing smog and airborne contaminants, making it a sustainable alternative in urban infrastructure.
What is Green Concrete?
Green concrete is an eco-friendly building material formulated by incorporating recycled industrial by-products such as fly ash, slag, and silica fume, which reduce the reliance on traditional Portland cement and lower carbon emissions. It improves sustainability through enhanced thermal properties, reduced energy consumption during production, and minimized environmental impact throughout its lifecycle. Compared to photocatalytic concrete, which primarily targets pollution reduction via surface reactions, green concrete emphasizes material efficiency and lower embodied energy for environmental projects.
Raw Materials and Production Processes
Photocatalytic concrete incorporates titanium dioxide particles that activate under UV light to reduce pollutants, requiring additional raw materials and specialized mixing processes compared to conventional concrete. Green concrete emphasizes the use of recycled materials, industrial by-products like fly ash or slag, and reduced cement content to lower carbon emissions during production. Both materials prioritize environmental benefits, but photocatalytic concrete focuses on air purification through its raw materials, while green concrete reduces overall environmental impact via sustainable sourcing and energy-efficient manufacturing.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Photocatalytic concrete significantly reduces air pollutants by breaking down nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds through titanium dioxide activation, contributing to improved urban air quality. Green concrete emphasizes lowering carbon dioxide emissions by substituting Portland cement with industrial byproducts like fly ash or slag, which decreases the carbon footprint during production. Both materials enhance environmental sustainability, but photocatalytic concrete targets air pollution mitigation, while green concrete primarily addresses carbon emissions and resource conservation.
Air Purification Capabilities
Photocatalytic concrete employs titanium dioxide nanoparticles that trigger chemical reactions to break down pollutants such as nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds, effectively reducing urban air pollution. Green concrete emphasizes sustainable materials and reduced carbon emissions but lacks intrinsic photocatalytic properties for active air purification. For environmental projects prioritizing air quality improvement, photocatalytic concrete offers superior air purification capabilities through its ability to neutralize harmful airborne contaminants.
Durability and Longevity
Photocatalytic concrete enhances environmental projects by breaking down pollutants and self-cleaning, significantly improving surface durability against weathering and staining, which extends the lifespan of urban infrastructures. Green concrete incorporates sustainable materials like fly ash and slag, improving resistance to chemical attacks and reducing permeability, thereby increasing structural longevity and reducing maintenance costs. Both materials contribute to longer-lasting, eco-friendly construction with photocatalytic concrete excelling in pollutant degradation and green concrete in sustainable durability.
Cost Efficiency and Scalability
Photocatalytic concrete utilizes titanium dioxide to break down pollutants, offering long-term air purification benefits but involving higher initial costs due to advanced materials and technology, making large-scale deployment more expensive. Green concrete incorporates recycled materials and industrial byproducts, reducing material costs and carbon footprint while allowing easier scalability with existing production processes. Both technologies contribute to sustainable construction, yet green concrete currently provides greater cost efficiency and scalability for widespread environmental projects.
Applications in Environmental Projects
Photocatalytic concrete utilizes titanium dioxide to break down pollutants in urban environments, effectively reducing air contaminants like nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds on roadways and building surfaces. Green concrete emphasizes sustainable materials and carbon footprint reduction by incorporating industrial byproducts such as fly ash or slag, enhancing durability while minimizing environmental impact in construction projects. Both materials contribute to environmental projects, with photocatalytic concrete actively improving air quality and green concrete promoting resource efficiency and lowered greenhouse gas emissions.
Future Trends and Innovations
Photocatalytic concrete leverages titanium dioxide to break down pollutants and improve air quality, positioning it as a cutting-edge solution for urban environments. Green concrete emphasizes sustainable materials, reduced carbon emissions, and energy-efficient production methods, aligning with global climate goals. Future trends indicate increased integration of nanotechnology and bio-based additives in both technologies to enhance durability and environmental performance.
Infographic: Photocatalytic concrete vs Green concrete for Environmental project
 azmater.com
azmater.com