Cellular concrete offers lightweight properties and excellent thermal insulation, reducing dead load on bridge decks. Ultra-high performance concrete provides superior compressive strength and durability, enhancing bridge deck lifespan under heavy traffic and harsh environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellular Concrete | Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low (400-1600 kg/m3) | High (2400-2500 kg/m3) |
| Compressive Strength | 2-15 MPa | 120-250 MPa |
| Flexural Strength | Low (1-3 MPa) | 20-50 MPa |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent | Poor |
| Durability | Moderate | Exceptional, high resistance to corrosion and abrasion |
| Water Absorption | High | Very Low |
| Weight Reduction | Significant weight savings | Minimal weight reduction |
| Application in Bridge Decks | Used for lightweight filler layers, reducing dead load | Used for high-strength, durable wearing surfaces |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Bridge Deck Materials
Cellular concrete offers lightweight properties and excellent thermal insulation, making it suitable for bridge decks requiring reduced dead loads and enhanced durability. Ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) provides exceptional strength, superior durability, and resistance to environmental degradation, ideal for high-traffic bridge decks with extended service life expectations. Selecting between cellular concrete and UHPC depends on balancing load reduction, structural performance, and long-term maintenance costs in bridge deck construction.
Overview of Cellular Concrete
Cellular concrete is a lightweight, aerated material composed of cement, water, and pre-formed foam, offering excellent thermal insulation and reduced dead load for bridge decks. Its low density and high workability make it ideal for applications requiring weight reduction without compromising durability. Compared to ultra-high performance concrete, cellular concrete provides enhanced crack resistance and energy absorption, contributing to improved longevity in bridge deck structures.
Key Properties of Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC)
Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC) exhibits exceptional compressive strength exceeding 150 MPa, superior durability, and enhanced tensile properties due to fiber reinforcement, making it ideal for bridge decks requiring long-term performance and reduced maintenance. Its low porosity and high density offer excellent resistance to environmental factors such as freeze-thaw cycles, chloride penetration, and abrasion, ensuring structural longevity and safety. Compared to cellular concrete, UHPC provides significantly higher load-bearing capacity and resilience, essential for critical infrastructure subjected to heavy traffic and harsh conditions.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) exhibits superior strength, often exceeding 150 MPa compressive strength, compared to cellular concrete which typically ranges between 2 to 20 MPa, making UHPC ideal for high-load bridge decks. In terms of durability, UHPC offers exceptional resistance to chloride penetration, freeze-thaw cycles, and abrasion, ensuring extended service life under harsh environmental conditions. Cellular concrete, while lightweight and providing thermal insulation, generally has lower durability and requires protective coatings to prevent degradation in aggressive bridge deck environments.
Weight and Density Differences
Cellular concrete, characterized by its lightweight nature with densities ranging from 400 to 1600 kg/m3, significantly reduces the overall weight of bridge decks compared to ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC), which has much higher densities typically around 2400 to 2500 kg/m3. This substantial difference in density enhances the structural efficiency and reduces load demands on substructures when using cellular concrete for bridge decks. Despite its lower weight, cellular concrete maintains adequate strength for non-critical load-bearing applications, whereas UHPC offers superior compressive strength and durability but at the cost of increased weight.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Benefits
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation for bridge decks due to its lightweight, porous structure that effectively reduces heat transfer and thermal bridging. Ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) provides excellent strength and durability but has limited insulating properties compared to cellular concrete. For acoustic insulation, cellular concrete's air voids absorb and dampen sound, whereas UHPC's dense matrix reflects noise, making cellular concrete more advantageous for reducing traffic noise on bridge decks.
Construction and Installation Methods
Cellular concrete offers lightweight properties and easy pumpability, allowing rapid placement and reduced formwork loads in bridge deck construction. Ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) requires meticulous mixing, precise casting, and specialized curing conditions to achieve its superior strength and durability on bridge decks. The installation of UHPC often involves the use of prefabricated panels or in-situ casting with advanced vibration techniques to ensure dense, defect-free material.
Cost Analysis: Cellular Concrete vs UHPC
Cellular concrete offers significant cost advantages over ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) for bridge decks due to its lower material price, reduced labor requirements, and faster curing times, leading to shorter project durations and minimized traffic disruption costs. UHPC, while providing superior durability, strength, and enhanced lifespan, entails higher upfront expenses caused by specialized materials like steel fibers, complex mixing processes, and skilled labor demands. Lifecycle cost analysis often reveals that although UHPC has higher initial costs, its reduced maintenance frequency and longer service life can offset expenses over time, making cellular concrete favorable in budgets with tighter capital constraints.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Cellular concrete offers superior sustainability for bridge decks due to its lightweight nature, reduced raw material consumption, and excellent thermal insulation properties that lower energy use over the structure's lifespan. Ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) delivers exceptional durability and strength with a dense microstructure, enhancing longevity and reducing maintenance-related environmental impacts despite higher initial carbon emissions from intensified cement production. Choosing cellular concrete prioritizes environmental impact reduction through lower embodied energy, while UHPC emphasizes lifecycle sustainability by minimizing repair frequency and extending service life in bridge applications.
Best Applications for Bridge Decks
Cellular concrete, known for its lightweight and thermal insulating properties, is best suited for bridge decks requiring reduced dead load and improved thermal performance, particularly in long-span or rehabilitation projects. Ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) excels in bridge decks demanding superior strength, durability, and resistance to environmental degradation, making it ideal for high-traffic or harsh climate conditions. Selecting between cellular concrete and UHPC depends on structural requirements, longevity goals, and maintenance considerations specific to bridge deck applications.
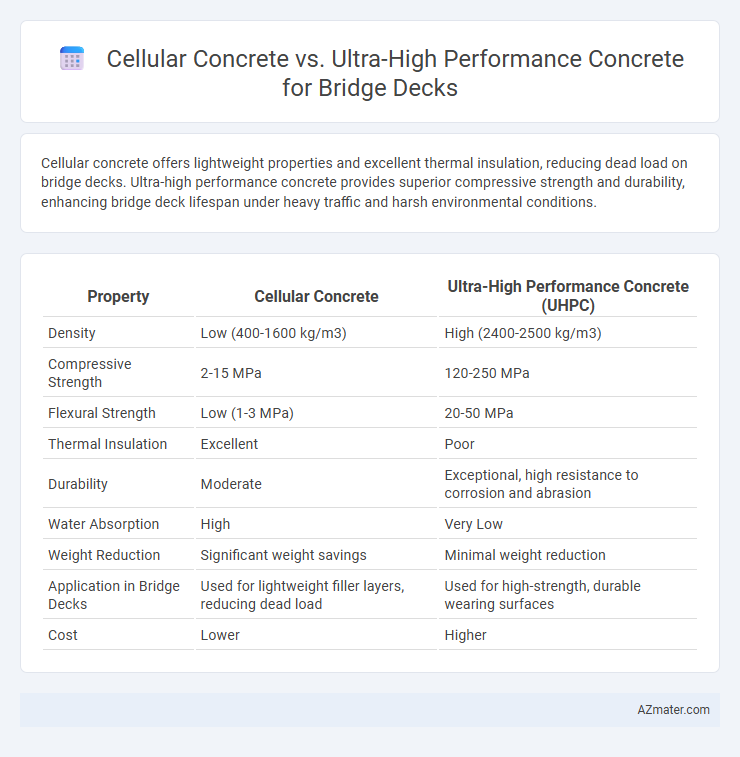
Infographic: Cellular concrete vs Ultra-high performance concrete for Bridge deck
 azmater.com
azmater.com