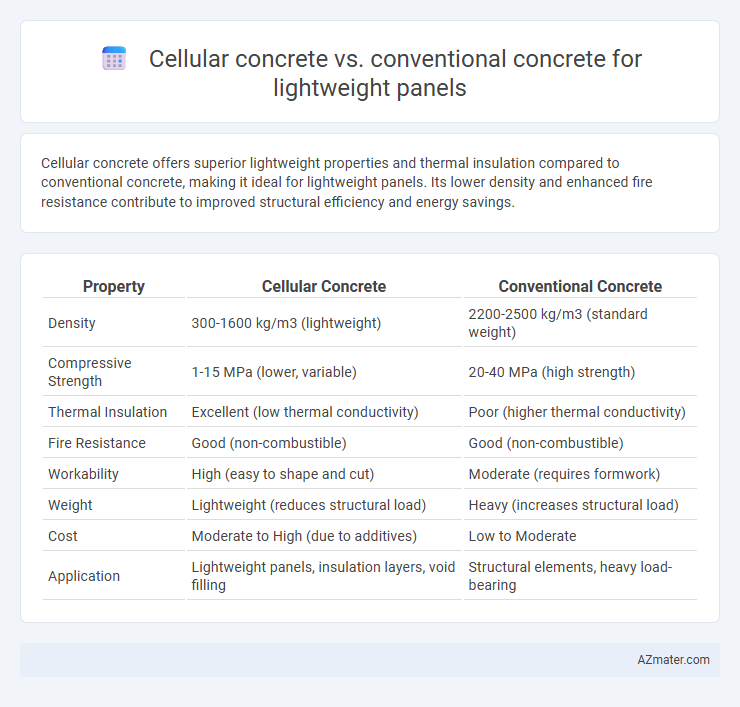
Cellular concrete offers superior lightweight properties and thermal insulation compared to conventional concrete, making it ideal for lightweight panels. Its lower density and enhanced fire resistance contribute to improved structural efficiency and energy savings.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellular Concrete | Conventional Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 300-1600 kg/m3 (lightweight) | 2200-2500 kg/m3 (standard weight) |
| Compressive Strength | 1-15 MPa (lower, variable) | 20-40 MPa (high strength) |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent (low thermal conductivity) | Poor (higher thermal conductivity) |
| Fire Resistance | Good (non-combustible) | Good (non-combustible) |
| Workability | High (easy to shape and cut) | Moderate (requires formwork) |
| Weight | Lightweight (reduces structural load) | Heavy (increases structural load) |
| Cost | Moderate to High (due to additives) | Low to Moderate |
| Application | Lightweight panels, insulation layers, void filling | Structural elements, heavy load-bearing |
Introduction to Lightweight Panels
Lightweight panels utilize cellular concrete and conventional concrete as core materials, with cellular concrete offering significantly lower density due to its porous structure filled with air bubbles. This reduced weight in cellular concrete panels enhances ease of handling, improves thermal insulation, and decreases structural load compared to traditional conventional concrete panels. The choice of concrete type directly influences the panel's performance in construction applications, emphasizing lightweight panels' efficiency and sustainability benefits.
Overview of Cellular Concrete
Cellular concrete, also known as foam concrete, is a lightweight material composed of cement, water, and pre-formed foam, resulting in a low-density and highly insulating product ideal for lightweight panels. Its superior thermal insulation, reduced dead load, and enhanced fire resistance differentiate it from conventional concrete, which is denser and heavier due to aggregates like sand and gravel. The unique cellular structure of cellular concrete improves sound absorption and ease of installation while maintaining adequate compressive strength for non-structural applications.
Overview of Conventional Concrete
Conventional concrete is a composite material composed of cement, water, fine aggregates, and coarse aggregates, offering high compressive strength and durability for structural applications. It is widely used in construction due to its cost-effectiveness and well-established performance under various loading conditions. However, its higher density compared to cellular concrete results in increased weight, which can impact the handling and installation of lightweight panels.
Key Material Composition Differences
Cellular concrete incorporates a mixture of cement, water, and pre-formed foam or gas-forming agents to create air-filled voids, significantly reducing density and enhancing thermal insulation compared to conventional concrete. In contrast, conventional concrete relies on a dense aggregation of cement, water, sand, and coarse aggregates, resulting in higher strength but greater weight and lower insulating properties. The key material composition difference lies in cellular concrete's aerated matrix, which reduces structural weight and improves insulation, making it ideal for lightweight panels.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Cellular concrete exhibits lower compressive strength compared to conventional concrete, typically ranging from 3 to 17 MPa versus conventional concrete's 20 to 40 MPa, making it less suitable for load-bearing lightweight panels. The reduced density of cellular concrete, often between 400 to 1600 kg/m3, directly impacts its mechanical strength but enhances thermal insulation and fire resistance. Conventional concrete panels, with densities of around 2300 kg/m3, deliver superior mechanical strength, making them preferable for structural applications requiring higher load capacity.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation properties compared to conventional concrete due to its high air content and porous structure, which significantly reduce heat conductivity. This enhanced insulation makes cellular concrete an ideal material for lightweight panels in energy-efficient building designs. Conventional concrete, with its dense composition, exhibits higher thermal conductivity, resulting in lower insulating performance for similar panel applications.
Fire Resistance Capabilities
Cellular concrete offers superior fire resistance compared to conventional concrete due to its porous structure, which provides excellent thermal insulation and reduces heat transfer. Lightweight panels made with cellular concrete can withstand high temperatures for extended periods without significant structural damage, making them ideal for fire-rated applications. Conventional concrete, while durable, tends to conduct heat more quickly, increasing vulnerability in fire scenarios where maintaining integrity and insulating properties is critical.
Acoustic Performance
Cellular concrete exhibits superior acoustic performance compared to conventional concrete due to its porous structure, which effectively absorbs and dampens sound waves. The lightweight panels made from cellular concrete significantly reduce noise transmission and enhance sound insulation in building applications. This makes cellular concrete an ideal choice for environments requiring enhanced acoustic comfort without compromising structural integrity.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Cellular concrete significantly reduces environmental impact compared to conventional concrete due to its lower cement content and enhanced thermal insulation properties, which decrease energy consumption in buildings. Its lightweight nature lowers transportation emissions and reduces structural load, enabling the use of less material for supporting frameworks. The improved sustainability profile of cellular concrete supports green building certifications and contributes to carbon footprint reduction in construction projects.
Application Suitability and Cost Considerations
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation and reduced weight, making it highly suitable for lightweight panels in building facades and interior partitions where load reduction is critical. Conventional concrete provides greater compressive strength and durability, fitting applications that demand structural integrity and load-bearing capacity. Cost considerations favor cellular concrete for projects prioritizing energy efficiency and ease of installation, while conventional concrete is more cost-effective for heavy-duty applications requiring robust material performance.
Infographic: Cellular concrete vs Conventional concrete for Lightweight panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com