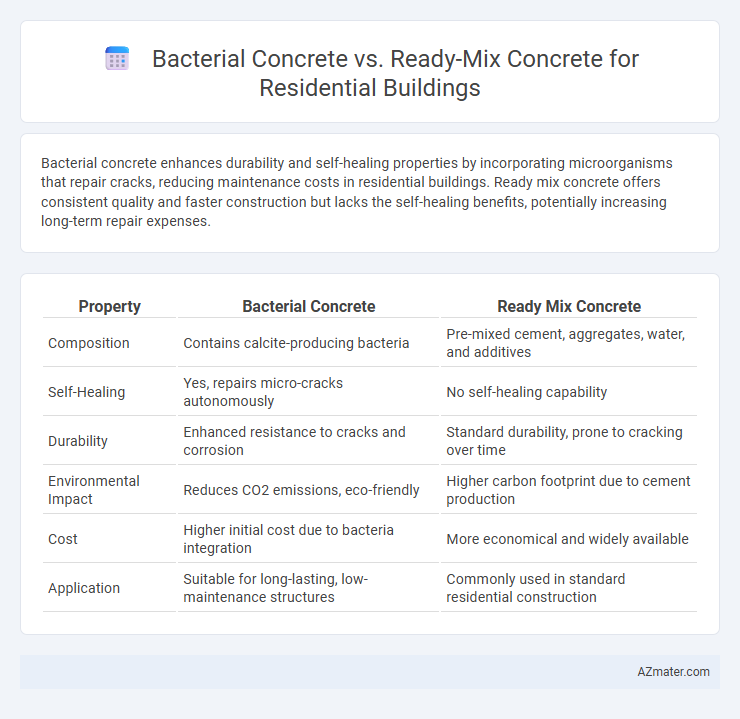
Bacterial concrete enhances durability and self-healing properties by incorporating microorganisms that repair cracks, reducing maintenance costs in residential buildings. Ready mix concrete offers consistent quality and faster construction but lacks the self-healing benefits, potentially increasing long-term repair expenses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bacterial Concrete | Ready Mix Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Contains calcite-producing bacteria | Pre-mixed cement, aggregates, water, and additives |
| Self-Healing | Yes, repairs micro-cracks autonomously | No self-healing capability |
| Durability | Enhanced resistance to cracks and corrosion | Standard durability, prone to cracking over time |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces CO2 emissions, eco-friendly | Higher carbon footprint due to cement production |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to bacteria integration | More economical and widely available |
| Application | Suitable for long-lasting, low-maintenance structures | Commonly used in standard residential construction |
Introduction to Bacterial Concrete and Ready Mix Concrete
Bacterial concrete integrates microbial-induced calcite precipitation to enhance durability and reduce crack formation, leveraging specific bacteria like Bacillus pasteurii to precipitate calcium carbonate within the concrete matrix. Ready mix concrete is a pre-mixed, standardized blend of cement, aggregates, water, and admixtures, produced in batching plants and transported to construction sites for immediate use in residential building projects. Both materials offer unique performance benefits, with bacterial concrete emphasizing self-healing and sustainability, while ready mix concrete ensures consistent quality and rapid application.
Composition and Materials Used
Bacterial concrete incorporates specific strains of bacteria, such as Bacillus pasteurii, mixed with traditional cement, aggregates, and nutrients to enhance self-healing properties and durability, while ready mix concrete consists of cement, water, fine and coarse aggregates, and admixtures standardized for consistent performance. The microbial activity in bacterial concrete induces calcite precipitation, sealing micro-cracks and reducing permeability, whereas ready mix concrete relies solely on physical and chemical hydration processes for strength. Material selection in bacterial concrete includes bio-based additives alongside conventional materials, differentiating it from ready mix concrete's purely mineral and chemical composition tailored for immediate use and uniform quality control.
Mechanism of Strength Development
Bacterial concrete enhances strength through the biomineralization process, where bacteria precipitate calcium carbonate, filling microcracks and pores to improve durability and compressive strength. Ready mix concrete relies on the hydration of cement particles forming calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) gel, which binds aggregates and increases overall structural integrity. The incorporation of bacteria in concrete accelerates self-healing mechanisms that reduce crack propagation, whereas ready mix concrete's strength development depends primarily on controlled curing conditions and mix proportions.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Bacterial concrete incorporates microbial-induced calcite precipitation, significantly enhancing crack healing and increasing resistance to water ingress, which extends the lifespan of residential structures by reducing maintenance needs. Ready mix concrete offers consistent quality and ease of application but lacks the self-healing properties that improve long-term durability. Studies show bacterial concrete can increase the lifespan of residential buildings by up to 25%, making it a superior choice for durability-focused construction.
Cost Analysis for Residential Projects
Bacterial concrete offers long-term cost savings in residential projects by reducing maintenance and repair expenses through self-healing properties, despite higher initial investment compared to ready mix concrete. Ready mix concrete provides lower upfront costs and faster construction times, making it economically viable for budget-sensitive residential developments. Evaluating lifecycle costs favors bacterial concrete when durability and reduced downtime are prioritized over initial expenditure.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bacterial concrete promotes sustainability by reducing carbon emissions through self-healing properties that extend the lifespan of residential buildings, minimizing repair frequency and material consumption. In contrast, ready mix concrete has a higher environmental footprint due to energy-intensive cement production and transportation emissions. Utilizing bacterial concrete can significantly lower the ecological impact in residential construction through enhanced durability and reduced maintenance requirements.
Construction Process and Time Efficiency
Bacterial concrete incorporates microbial-induced calcite precipitation to self-heal cracks, reducing maintenance and extending structural lifespan, while its curing process can be slightly longer due to bacterial activity. Ready mix concrete offers rapid on-site application and consistent quality, significantly accelerating construction timelines with immediate placement after delivery. For residential buildings, ready mix concrete is preferred for time efficiency, whereas bacterial concrete provides long-term durability benefits with a more complex construction process.
Maintenance and Long-Term Performance
Bacterial concrete enhances long-term performance in residential buildings by self-healing microcracks, significantly reducing maintenance frequency and costs compared to ready mix concrete, which may require regular repairs and sealing. The microbes in bacterial concrete help maintain structural integrity and durability under various environmental conditions, leading to extended lifespan and resilience against water ingress and chemical attacks. Ready mix concrete offers convenience and consistent quality but often demands higher maintenance efforts to address wear and deterioration over time.
Suitability for Different Residential Applications
Bacterial concrete enhances durability and self-healing properties, making it ideal for residential foundations and basements prone to cracking and water ingress. Ready mix concrete offers consistent quality and rapid construction, suitable for walls, slabs, and driveways in typical residential projects with standard load requirements. Selecting the appropriate type depends on specific structural demands, with bacterial concrete preferred for longevity and ready mix concrete favored for general construction efficiency.
Future Trends in Concrete Technologies for Homes
Bacterial concrete, enhanced with microbial-induced calcite precipitation, offers self-healing properties that reduce maintenance costs and increase durability in residential buildings, presenting a sustainable alternative to traditional ready mix concrete. Ready mix concrete remains widely used due to its consistency, ease of placement, and established supply chains but lacks the adaptive healing features of microbial concretes. Future trends in concrete technologies for homes emphasize integrating bio-based materials like bacterial concrete to improve structural longevity, reduce carbon footprint, and support eco-friendly construction practices.
Infographic: Bacterial concrete vs Ready mix concrete for Residential building
 azmater.com
azmater.com