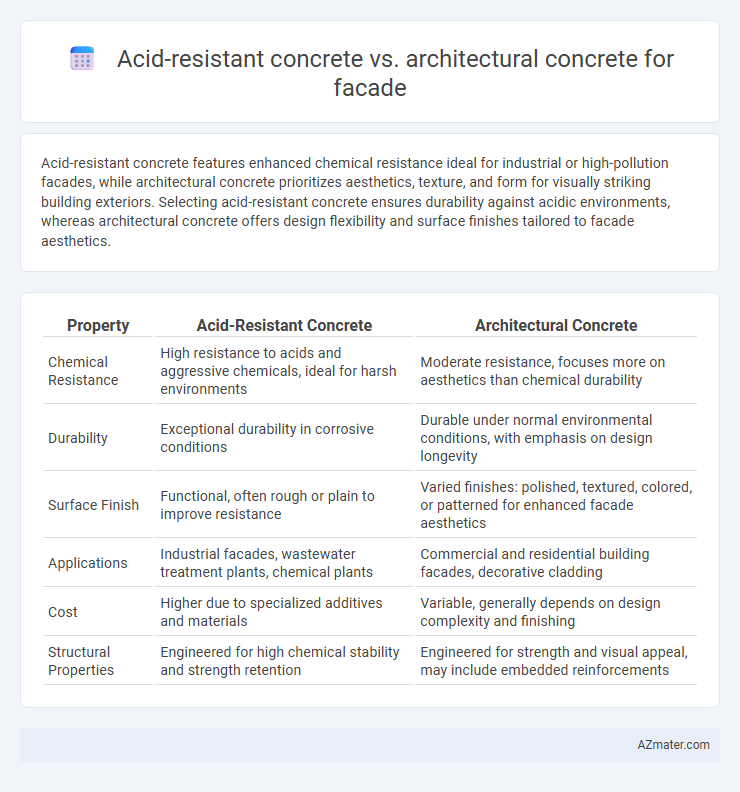
Acid-resistant concrete features enhanced chemical resistance ideal for industrial or high-pollution facades, while architectural concrete prioritizes aesthetics, texture, and form for visually striking building exteriors. Selecting acid-resistant concrete ensures durability against acidic environments, whereas architectural concrete offers design flexibility and surface finishes tailored to facade aesthetics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acid-Resistant Concrete | Architectural Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to acids and aggressive chemicals, ideal for harsh environments | Moderate resistance, focuses more on aesthetics than chemical durability |
| Durability | Exceptional durability in corrosive conditions | Durable under normal environmental conditions, with emphasis on design longevity |
| Surface Finish | Functional, often rough or plain to improve resistance | Varied finishes: polished, textured, colored, or patterned for enhanced facade aesthetics |
| Applications | Industrial facades, wastewater treatment plants, chemical plants | Commercial and residential building facades, decorative cladding |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized additives and materials | Variable, generally depends on design complexity and finishing |
| Structural Properties | Engineered for high chemical stability and strength retention | Engineered for strength and visual appeal, may include embedded reinforcements |
Introduction to Acid-Resistant and Architectural Concrete
Acid-resistant concrete is specially formulated with chemical additives and aggregates that provide enhanced durability against acidic environments, making it ideal for industrial facades exposed to harsh chemicals. Architectural concrete emphasizes aesthetic appeal through surface treatments, texture variations, and color options, focusing on visual design for building exteriors. Selecting between acid-resistant and architectural concrete depends on whether chemical resistance or facade appearance is prioritized in construction projects.
Key Properties of Acid-Resistant Concrete
Acid-resistant concrete for facades is engineered with high chemical durability to withstand corrosive environments, featuring low permeability and enhanced resistance to acids, sulfates, and aggressive chemicals. It often incorporates specialized aggregates, such as quartz or silica sand, and pozzolanic materials like fly ash or silica fume to improve chemical resistance and long-term durability. In contrast to architectural concrete, which prioritizes aesthetics and surface finish, acid-resistant concrete focuses on structural integrity and longevity in harsh chemical exposures.
Distinct Characteristics of Architectural Concrete
Architectural concrete for facades is distinguished by its aesthetic versatility, offering customizable textures, colors, and finishes that enhance building design. Unlike acid-resistant concrete, which prioritizes chemical durability, architectural concrete emphasizes surface detail and visual appeal through techniques like exposed aggregate and form liner patterns. Its ability to combine structural integrity with artistic expression makes it a preferred choice for architects seeking both durability and creative facade solutions.
Performance Requirements for Facade Applications
Acid-resistant concrete for facades offers superior chemical durability, effectively resisting harsh environmental pollutants and acidic rain, which ensures long-term structural integrity in industrial or urban settings. Architectural concrete prioritizes aesthetic appeal and surface finishes, providing customizable textures and colors while meeting essential weather resistance and mechanical strength standards. Performance requirements for facade applications demand acid-resistant concrete where chemical exposure is high, whereas architectural concrete is ideal for visually expressive facades with moderate environmental exposure.
Durability: Acid-Resistant vs Architectural Concrete
Acid-resistant concrete exhibits superior durability compared to architectural concrete due to its enhanced chemical composition that withstands aggressive acidic environments, preventing surface degradation and maintaining structural integrity over time. Architectural concrete prioritizes aesthetic appeal with varied textures and finishes but generally has lower resistance to acid attacks, making it less suitable for chemically aggressive settings. Selecting acid-resistant concrete is essential for facades exposed to industrial pollutants or acidic rain, ensuring long-term performance and reduced maintenance costs.
Aesthetic Considerations in Facade Design
Acid-resistant concrete offers a smooth, consistent surface that maintains its appearance in harsh chemical environments, making it ideal for industrial facades requiring durability without aesthetic compromise. Architectural concrete provides diverse textures, colors, and finishes, allowing designers to create visually striking facades that enhance a building's character and integrate with the surrounding environment. Selecting between these concretes hinges on balancing the need for chemical resistance with the desired artistic expression in facade design.
Cost Comparison: Material and Installation
Acid-resistant concrete typically incurs higher material costs due to specialized additives and coatings designed to withstand chemical exposure, making it more expensive than architectural concrete. Installation of acid-resistant concrete demands skilled labor and precise application techniques, which further increase overall expenses compared to the more straightforward installation process of architectural concrete. While architectural concrete offers cost-efficiency for aesthetic facade purposes, acid-resistant concrete justifies its premium price through durability and longevity in aggressive environmental conditions.
Maintenance and Longevity in Exterior Facades
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability and low maintenance for exterior facades exposed to harsh chemical environments, effectively resisting corrosion and surface degradation. Architectural concrete emphasizes aesthetic appeal with specialized finishes but may require more frequent upkeep to preserve visual quality and prevent weathering effects. Selecting acid-resistant concrete enhances longevity and reduces lifecycle costs in chemically aggressive settings, whereas architectural concrete suits projects prioritizing design with moderate maintenance demands.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Acid-resistant concrete for facades offers superior durability against chemical corrosion, significantly reducing the frequency of repairs and material replacement, which lowers environmental impact through resource conservation and waste minimization. Architectural concrete emphasizes aesthetics and can incorporate recycled materials, enhancing sustainability by reducing the demand for virgin aggregates and minimizing carbon footprint. Selecting acid-resistant concrete in industrial or polluted environments ensures longer facade lifespan, while architectural concrete supports eco-friendly design through customizable use of sustainable additives and finishes.
Best Use Cases: Selecting the Right Concrete for Facades
Acid-resistant concrete is best suited for facades exposed to harsh chemical environments such as industrial plants or areas with acidic rain, ensuring long-term durability and protection against corrosion. Architectural concrete excels in aesthetic applications where design versatility and surface texture are priorities, making it ideal for modern commercial and residential facades. Selecting the right concrete involves balancing functional requirements like chemical resistance with visual appeal to achieve optimal facade performance.
Infographic: Acid-resistant concrete vs Architectural concrete for Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com