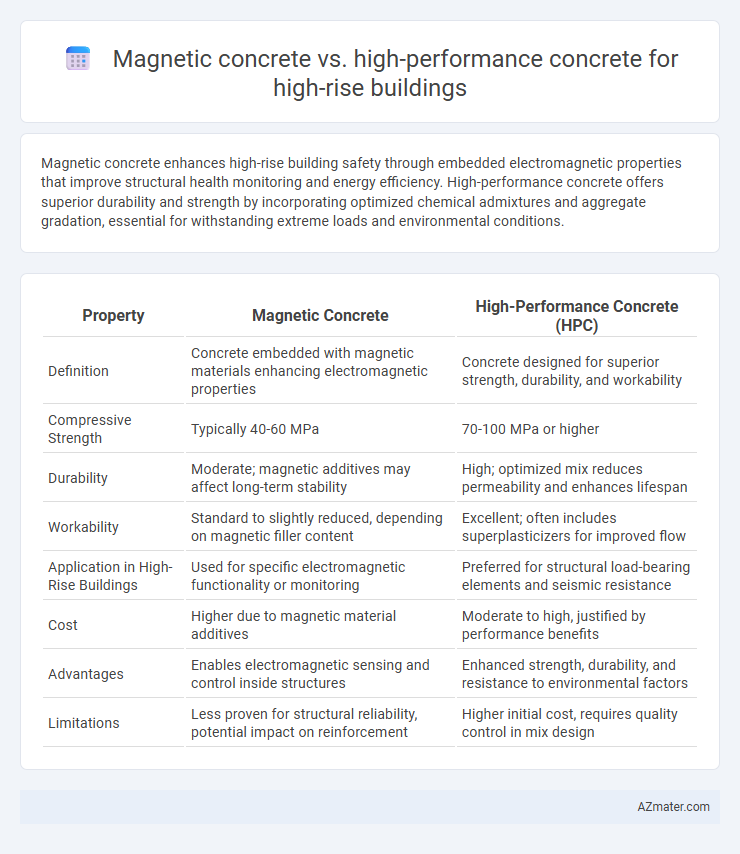
Magnetic concrete enhances high-rise building safety through embedded electromagnetic properties that improve structural health monitoring and energy efficiency. High-performance concrete offers superior durability and strength by incorporating optimized chemical admixtures and aggregate gradation, essential for withstanding extreme loads and environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Magnetic Concrete | High-Performance Concrete (HPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete embedded with magnetic materials enhancing electromagnetic properties | Concrete designed for superior strength, durability, and workability |
| Compressive Strength | Typically 40-60 MPa | 70-100 MPa or higher |
| Durability | Moderate; magnetic additives may affect long-term stability | High; optimized mix reduces permeability and enhances lifespan |
| Workability | Standard to slightly reduced, depending on magnetic filler content | Excellent; often includes superplasticizers for improved flow |
| Application in High-Rise Buildings | Used for specific electromagnetic functionality or monitoring | Preferred for structural load-bearing elements and seismic resistance |
| Cost | Higher due to magnetic material additives | Moderate to high, justified by performance benefits |
| Advantages | Enables electromagnetic sensing and control inside structures | Enhanced strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors |
| Limitations | Less proven for structural reliability, potential impact on reinforcement | Higher initial cost, requires quality control in mix design |
Introduction to Magnetic Concrete and High-Performance Concrete
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials such as magnetite to enhance electromagnetic properties and structural health monitoring capabilities, offering innovative solutions for high-rise buildings. High-performance concrete (HPC) is engineered with optimized mix designs to achieve superior strength, durability, and workability, essential for the demanding loads and environmental conditions of tall structures. Comparing these materials highlights magnetic concrete's potential for smart infrastructure integration versus HPC's proven reliability and enhanced mechanical performance in skyscraper construction.
Key Material Composition Differences
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials such as iron ore and steel fibers to enhance electromagnetic properties, while high-performance concrete primarily uses silica fume, fly ash, and superplasticizers to achieve superior strength and durability. The key material composition difference lies in magnetic concrete's inclusion of magnetic particles that enable electromagnetic shielding, contrasting with high-performance concrete's focus on optimized particle packing and reduced permeability. These variations significantly influence their mechanical and functional performance in high-rise building applications.
Structural Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials that enhance electromagnetic properties but typically offers lower structural strength and load-bearing capacity compared to high-performance concrete (HPC). HPC is engineered with optimized mix designs, including supplementary cementitious materials and chemical admixtures, delivering superior compressive strength often exceeding 100 MPa and enhanced durability critical for high-rise building stability. For high-rise structures, HPC provides reliable load-bearing capacity and structural resilience under dynamic and static loads, making it more suitable than magnetic concrete for core structural elements.
Durability and Lifespan in High-Rise Applications
Magnetic concrete enhances durability in high-rise buildings by improving crack resistance and corrosion protection through embedded magnetic particles, which contribute to self-sensing and early damage detection capabilities. High-performance concrete (HPC) offers superior compressive strength, reduced permeability, and increased resistance to environmental degradation, significantly extending the lifespan of tall structures. Both materials improve durability, but HPC remains the benchmark for longevity in high-rise applications due to its optimized microstructure and mechanically robust properties.
Thermal and Electromagnetic Properties
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials, enhancing electromagnetic shielding useful in high-rise buildings for reducing electromagnetic interference and improving signal integrity. In contrast, high-performance concrete (HPC) offers superior thermal insulation and durability, optimizing energy efficiency and structural longevity under varying environmental conditions. Combining magnetic concrete's electromagnetic attenuation with HPC's thermal stability creates an innovative solution for advanced high-rise construction addressing both electromagnetic compatibility and thermal management.
Construction Efficiency and Workability
Magnetic concrete enhances construction efficiency in high-rise buildings through faster curing times and improved self-sensing capabilities, allowing for real-time structural health monitoring. High-performance concrete offers superior workability with optimized mix designs that facilitate easier placement and compaction, reducing labor efforts. Both materials contribute to structural integrity, but magnetic concrete's integrated monitoring system provides an edge in proactive maintenance and longevity.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
Magnetic concrete, incorporating magnetite and specialized additives, often incurs higher initial material and manufacturing costs compared to high-performance concrete (HPC), which is optimized for strength and durability using admixtures and silica fume. While HPC presents proven long-term economic benefits through reduced maintenance and extended lifespan in high-rise buildings, magnetic concrete's niche functional advantages, such as electromagnetic interference shielding, may justify its premium in specific applications but limit widespread economic feasibility. Cost analysis for high-rise projects favors HPC due to its balanced performance-to-cost ratio and established construction methodologies, making it the more economically viable option for large-scale developments.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Magnetic concrete, embedded with ferromagnetic particles, offers enhanced electromagnetic shielding and potential self-sensing capabilities, contributing to smart infrastructure with reduced maintenance needs in high-rise buildings. High-performance concrete (HPC) emphasizes superior mechanical properties and durability, enabling thinner sections and longer service life, which reduces material consumption and environmental footprint over time. Both materials promote sustainability by enhancing building longevity and resilience, but HPC currently exhibits greater widespread application and established environmental benefits in high-rise construction.
Safety Standards and Regulatory Compliance
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials enhancing structural health monitoring, meeting stringent safety standards for high-rise buildings through real-time stress and damage detection. High-performance concrete (HPC) offers superior strength, durability, and fire resistance, complying with international building codes such as ASTM C 150 and Eurocode 2. Both materials adhere to regulatory compliance, but magnetic concrete provides advanced safety monitoring capabilities that complement HPC's mechanical performance for enhanced high-rise building resilience.
Future Trends and Innovations in High-Rise Concrete Technology
Magnetic concrete integrates ferromagnetic materials to enhance structural health monitoring and electromagnetic shielding, offering innovative solutions for smart high-rise buildings. High-performance concrete (HPC) advances through nano-engineering and admixture optimization, improving strength, durability, and sustainability in skyscraper construction. Future trends emphasize hybrid concretes combining magnetic properties with HPC benefits, enabling adaptive infrastructure with real-time stress detection and energy-efficient design.
Infographic: Magnetic concrete vs High-performance concrete for High-rise building
 azmater.com
azmater.com