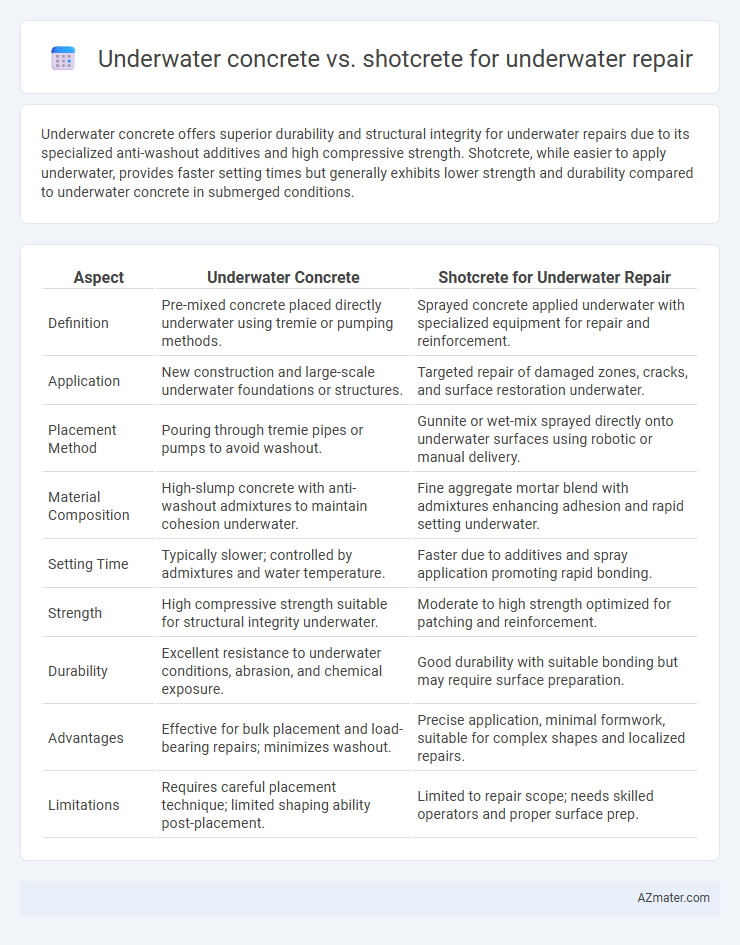
Underwater concrete offers superior durability and structural integrity for underwater repairs due to its specialized anti-washout additives and high compressive strength. Shotcrete, while easier to apply underwater, provides faster setting times but generally exhibits lower strength and durability compared to underwater concrete in submerged conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Underwater Concrete | Shotcrete for Underwater Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-mixed concrete placed directly underwater using tremie or pumping methods. | Sprayed concrete applied underwater with specialized equipment for repair and reinforcement. |
| Application | New construction and large-scale underwater foundations or structures. | Targeted repair of damaged zones, cracks, and surface restoration underwater. |
| Placement Method | Pouring through tremie pipes or pumps to avoid washout. | Gunnite or wet-mix sprayed directly onto underwater surfaces using robotic or manual delivery. |
| Material Composition | High-slump concrete with anti-washout admixtures to maintain cohesion underwater. | Fine aggregate mortar blend with admixtures enhancing adhesion and rapid setting underwater. |
| Setting Time | Typically slower; controlled by admixtures and water temperature. | Faster due to additives and spray application promoting rapid bonding. |
| Strength | High compressive strength suitable for structural integrity underwater. | Moderate to high strength optimized for patching and reinforcement. |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to underwater conditions, abrasion, and chemical exposure. | Good durability with suitable bonding but may require surface preparation. |
| Advantages | Effective for bulk placement and load-bearing repairs; minimizes washout. | Precise application, minimal formwork, suitable for complex shapes and localized repairs. |
| Limitations | Requires careful placement technique; limited shaping ability post-placement. | Limited to repair scope; needs skilled operators and proper surface prep. |
Introduction to Underwater Concrete and Shotcrete
Underwater concrete is specially formulated with anti-washout additives to maintain cement integrity and prevent segregation during subaqueous placement, making it ideal for structural repairs in submerged conditions. Shotcrete, sprayed at high velocity, uses wet- or dry-mix processes to provide rapid setting and strong bonding on underwater surfaces, facilitating efficient repairs in tunnels, dams, and bridge piers. Both materials are engineered to withstand hydrostatic pressure and offer durable solutions for underwater construction and maintenance projects.
Key Differences Between Underwater Concrete and Shotcrete
Underwater concrete is specifically designed for placement in submerged conditions, featuring properties such as anti-washout agents to maintain cohesion and strength during underwater application. Shotcrete, applied pneumatically through a nozzle, is used for repair by spraying concrete onto surfaces and can be adapted for underwater use but typically requires specialized equipment and techniques to ensure proper adhesion and minimize rebound. Key differences include their placement methods, with underwater concrete poured directly into forms or voids, while shotcrete is sprayed, and their mix designs are tailored for respective application challenges like washout resistance and adherence to vertical or overhead surfaces underwater.
Advantages of Underwater Concrete in Submerged Repairs
Underwater concrete offers superior durability and strength for submerged repairs due to its specially formulated mix that resists washout and maintains cohesion in aquatic environments. Its placement techniques ensure precise application and effective bonding on underwater structures, enhancing long-term structural integrity. Compared to shotcrete, underwater concrete minimizes material loss and segregation, delivering a more uniform and reliable repair in submerged conditions.
Benefits of Using Shotcrete for Underwater Applications
Shotcrete offers superior adhesion and rapid setting properties ideal for underwater repair, minimizing washout and ensuring structural integrity. Its adaptability to complex surfaces and ability to be applied in layers improves repair precision and durability in submerged environments. Compared to traditional underwater concrete, shotcrete reduces labor costs and accelerates project timelines due to its efficient placement and curing process.
Material Composition and Application Techniques
Underwater concrete typically consists of a low-slump, anti-washout admixture blend to maintain cohesion and prevent washout during placement, making it ideal for heavy structural repairs. Shotcrete for underwater repair involves pneumatically projecting a cementitious mix enriched with anti-washout agents through a delivery nozzle, allowing precise application on vertical or overhead surfaces. The material composition of underwater shotcrete often includes fine aggregates and polymer modifiers to enhance adhesion and reduce rebound, distinguishing it from conventional underwater concrete mixtures.
Durability and Structural Performance Comparison
Underwater concrete exhibits superior durability due to its low permeability and enhanced chemical resistance, which minimizes chloride ion intrusion and mitigates corrosion of reinforcement in submerged conditions. Shotcrete, while offering excellent adhesion and fast application for repair of complex geometries, can exhibit variable density and potential voids that may compromise long-term structural integrity underwater. Structural performance of underwater concrete typically surpasses shotcrete in load-bearing capacity and resistance to hydraulic pressures, making it more suitable for permanent underwater repair applications requiring robust durability.
Cost Considerations: Underwater Concrete vs Shotcrete
Underwater concrete typically involves higher material and labor costs due to the need for specialized admixtures and pumping equipment to maintain workability and placement underwater. Shotcrete offers cost advantages by enabling faster application and reducing formwork expenses, but may require more skilled labor and additional surface preparation for optimal bonding. Project scale, accessibility, and environmental conditions significantly influence the overall cost-effectiveness of underwater concrete versus shotcrete in repair scenarios.
Common Challenges in Underwater Repair Methods
Underwater concrete and shotcrete both face common challenges such as achieving proper material cohesion and preventing washout in turbulent water conditions. Ensuring sufficient bonding to submerged surfaces and controlling setting time under variable temperatures are critical for successful underwater repairs. Both methods require meticulous handling of admixtures to enhance durability and mechanical properties in corrosive aquatic environments.
Best Practices for Selecting the Appropriate Repair Method
Selecting the appropriate repair method for underwater structures hinges on factors such as water depth, flow conditions, and the structural damage severity. Underwater concrete offers high durability and can be placed using tremie methods for deep or turbulent waters, ensuring proper setting and strength. Shotcrete provides rapid application and excellent adhesion, ideal for surface repairs and areas with restricted access, but requires controlled conditions to prevent washout and ensure bond integrity.
Future Trends in Underwater Repair Technologies
Future trends in underwater repair technologies emphasize the advancement of eco-friendly underwater concrete mixes with enhanced durability and rapid-setting properties for efficient submerged repairs. Shotcrete application methods are increasingly integrating robotic automation and remote-controlled spraying systems to improve precision and safety in challenging underwater environments. Development in admixtures and nanomaterials also targets superior bonding strength and reduced washout resistance, driving innovation in both underwater concrete and shotcrete techniques.
Infographic: Underwater concrete vs Shotcrete for Underwater repair
 azmater.com
azmater.com