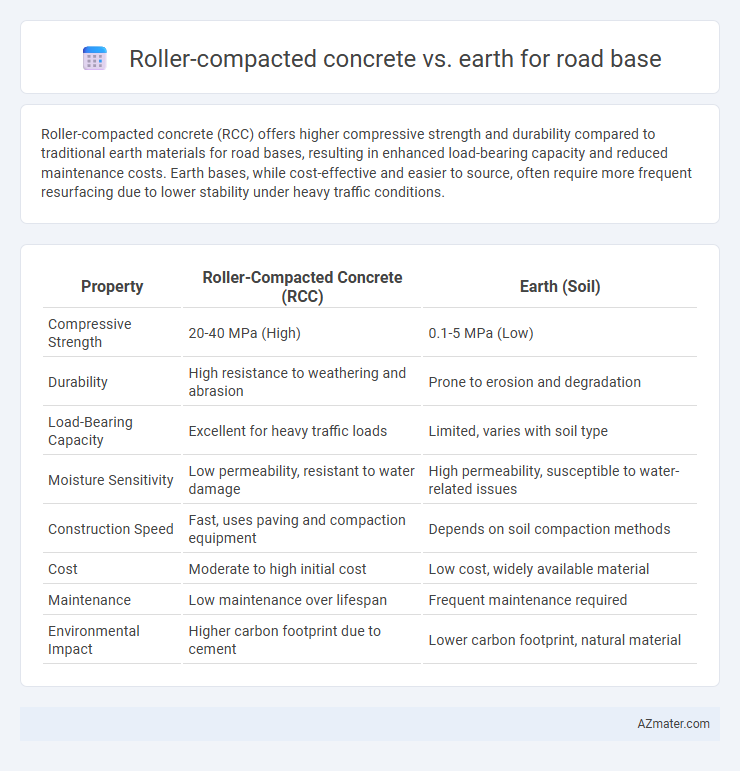
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers higher compressive strength and durability compared to traditional earth materials for road bases, resulting in enhanced load-bearing capacity and reduced maintenance costs. Earth bases, while cost-effective and easier to source, often require more frequent resurfacing due to lower stability under heavy traffic conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) | Earth (Soil) |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive Strength | 20-40 MPa (High) | 0.1-5 MPa (Low) |
| Durability | High resistance to weathering and abrasion | Prone to erosion and degradation |
| Load-Bearing Capacity | Excellent for heavy traffic loads | Limited, varies with soil type |
| Moisture Sensitivity | Low permeability, resistant to water damage | High permeability, susceptible to water-related issues |
| Construction Speed | Fast, uses paving and compaction equipment | Depends on soil compaction methods |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial cost | Low cost, widely available material |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance over lifespan | Frequent maintenance required |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint due to cement | Lower carbon footprint, natural material |
Introduction to Road Base Materials
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers high strength and durability due to its low water content and compacted granular composition, making it ideal for heavy traffic road bases. Earth materials, typically consisting of natural soils and gravels, provide cost-effective and flexible solutions but often require extensive stabilization to achieve adequate load-bearing capacity. Selecting between RCC and earth materials depends on factors like load intensity, environmental conditions, and maintenance requirements for optimal road base performance.
Overview of Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC)
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is a highly durable and low permeability material composed of a zero-slump concrete mix compacted by heavy rollers, providing superior load-bearing capacity for road bases compared to traditional earth materials. RCC offers enhanced structural strength, resistance to erosion, and minimal maintenance requirements, making it ideal for high-traffic and heavy-load applications. Its fast construction process and long service life contribute to cost-effectiveness and sustainability advantages over conventional earth road bases.
Overview of Earth Road Bases
Earth road bases consist primarily of compacted natural soil materials, offering a cost-effective and readily available foundation for road construction. These bases provide adequate structural support when properly graded and compacted but are more susceptible to moisture variation and deformation under heavy traffic compared to roller-compacted concrete. Soil stabilization techniques are often employed to enhance load-bearing capacity and durability, though they generally lack the rigidity and longevity of concrete alternatives.
Material Properties Comparison
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers higher compressive strength and durability compared to traditional earth materials used in road base construction, enabling better load distribution and resistance to deformation. RCC's low permeability and enhanced interlocking aggregate structure provide superior resistance to moisture damage and erosion, whereas earth materials are more susceptible to water-induced weakening and require frequent maintenance. The rigid nature of RCC reduces rutting and settlement issues commonly observed in earth bases, resulting in longer-lasting road performance under heavy traffic conditions.
Construction Techniques: RCC vs Earth
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) for road base construction involves a high-density mix placed and compacted with vibratory rollers, ensuring rapid setting and high load-bearing capacity. Earth road bases rely on mechanical compaction of granular soil or gravel layers, which requires moisture control and multiple passes with heavy rollers to achieve sufficient stability. RCC construction demands precise mixing and placement equipment, while earth base methods depend heavily on soil properties and may require stabilization additives for enhanced performance.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers higher initial costs compared to traditional earth materials for road base construction, driven by material and equipment expenses. However, RCC provides enhanced durability and lower maintenance requirements, reducing long-term operational costs significantly. Economic considerations favor RCC in high-traffic or heavy-load scenarios where lifecycle cost savings outweigh upfront investment.
Performance and Durability Differences
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers superior load-bearing capacity and resistance to deformation compared to earth for road bases, ensuring longer-lasting structural integrity under heavy traffic conditions. RCC's high compressive strength and reduced permeability enhance durability by minimizing water infiltration and subsequent erosion, unlike earth bases which are more susceptible to moisture-related degradation. Maintenance costs are generally lower for RCC bases due to their resilience against rutting and settlement, providing a cost-effective solution for high-performance road construction.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) for road bases offers lower permeability and higher durability, reducing maintenance frequency and associated environmental disturbances compared to traditional earth bases. RCC production involves higher embodied energy and CO2 emissions due to cement use, but its longevity offsets frequent repair emissions typical of earth bases susceptible to erosion and deformation. Earth bases rely on local soil materials, minimizing initial carbon footprint but often require stabilization additives and periodic replenishment, leading to cumulative environmental impacts such as habitat disruption and increased resource extraction.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Expectations
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers superior durability and lower maintenance requirements compared to earth materials for road bases, significantly extending the lifecycle of the pavement structure. RCC's high compressive strength and resistance to erosion reduce frequent repairs caused by weather and heavy traffic loads, resulting in cost savings over time. Earth bases typically require more frequent grading, re-compaction, and stabilization, leading to higher maintenance costs and a shorter overall service life.
Choosing the Right Road Base: Key Factors
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers superior load-bearing capacity and durability compared to traditional earth road bases, making it ideal for high-traffic or heavy-load areas. Soil stability, drainage properties, and project budget are critical factors influencing the choice between RCC and earth materials for road bases. Proper evaluation of site conditions, expected traffic volumes, and maintenance requirements ensures optimal road base performance and longevity.
Infographic: Roller-compacted concrete vs Earth for Road Base
 azmater.com
azmater.com