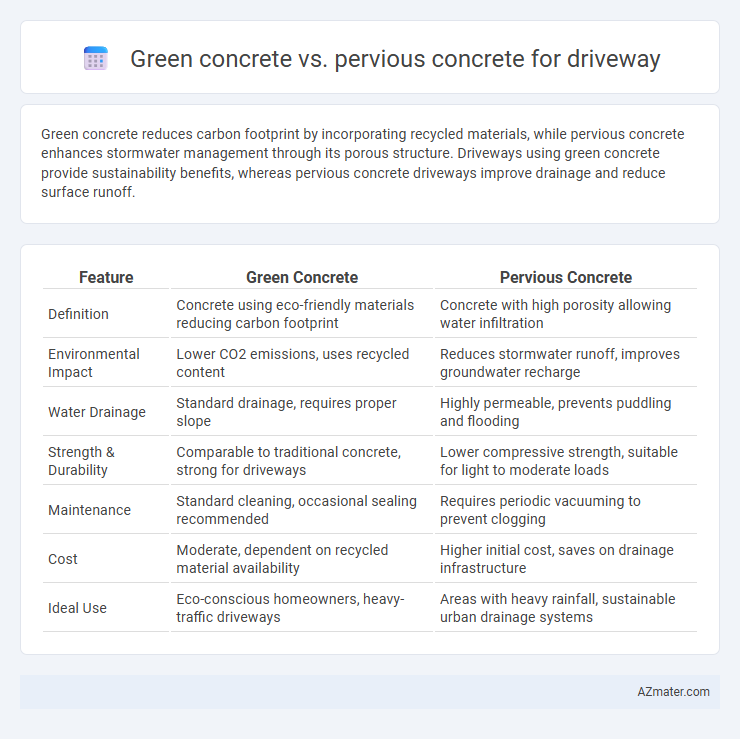
Green concrete reduces carbon footprint by incorporating recycled materials, while pervious concrete enhances stormwater management through its porous structure. Driveways using green concrete provide sustainability benefits, whereas pervious concrete driveways improve drainage and reduce surface runoff.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Green Concrete | Pervious Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete using eco-friendly materials reducing carbon footprint | Concrete with high porosity allowing water infiltration |
| Environmental Impact | Lower CO2 emissions, uses recycled content | Reduces stormwater runoff, improves groundwater recharge |
| Water Drainage | Standard drainage, requires proper slope | Highly permeable, prevents puddling and flooding |
| Strength & Durability | Comparable to traditional concrete, strong for driveways | Lower compressive strength, suitable for light to moderate loads |
| Maintenance | Standard cleaning, occasional sealing recommended | Requires periodic vacuuming to prevent clogging |
| Cost | Moderate, dependent on recycled material availability | Higher initial cost, saves on drainage infrastructure |
| Ideal Use | Eco-conscious homeowners, heavy-traffic driveways | Areas with heavy rainfall, sustainable urban drainage systems |
Introduction to Sustainable Driveway Solutions
Green concrete incorporates recycled materials and industrial byproducts to reduce carbon footprint, offering enhanced durability and environmental benefits for driveways. Pervious concrete improves stormwater management by allowing water to permeate through the surface, reducing runoff and promoting groundwater recharge. Both materials support sustainable driveway solutions by balancing ecological impact with functional performance in urban and residential applications.
What is Green Concrete?
Green concrete is an eco-friendly construction material made by incorporating industrial waste, recycled aggregates, and supplementary cementitious materials to reduce carbon footprint and conserve natural resources. It offers improved durability, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and enhanced insulation properties compared to traditional concrete. When used in driveways, green concrete promotes sustainability while maintaining strength and longevity.
What is Pervious Concrete?
Pervious concrete is a specialized concrete mix designed to allow water to pass through its porous structure, effectively reducing runoff and promoting groundwater recharge. It consists of coarse aggregates, cement, and minimal fine aggregates, creating interconnected voids that facilitate permeability. This makes pervious concrete an ideal choice for driveways in environmentally sensitive areas where stormwater management and sustainable drainage are priorities.
Key Material Differences
Green concrete incorporates recycled materials such as fly ash, slag, and recycled aggregates to reduce its environmental impact, while pervious concrete features a high porosity structure using coarse aggregates and minimal fine aggregates to allow water infiltration. The binder content in green concrete often includes supplementary cementitious materials that enhance durability and reduce carbon footprint, whereas pervious concrete emphasizes void spaces typically between 15% to 25% to facilitate drainage. These material differences influence performance; green concrete prioritizes sustainability and strength, while pervious concrete focuses on permeability and stormwater management for driveways.
Environmental Benefits Compared
Green concrete reduces carbon footprint by incorporating recycled materials and industrial byproducts, significantly lowering CO2 emissions compared to traditional concrete. Pervious concrete enhances groundwater recharge and mitigates stormwater runoff, reducing urban flooding and improving water quality. Both options promote sustainability, but green concrete excels in reducing embodied energy while pervious concrete optimizes water management for environmental benefits.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Green concrete, made with recycled materials and industrial byproducts, offers moderate strength and enhanced environmental sustainability but may have slightly lower load-bearing capacity compared to traditional options. Pervious concrete is designed for high permeability, allowing water to pass through; it generally exhibits lower compressive strength but excellent freeze-thaw durability and resistance to cracking under repeated stress. For driveway applications requiring durability under vehicular traffic, green concrete tends to provide better overall strength, while pervious concrete excels in managing stormwater and reducing surface runoff, though it may require more maintenance to preserve its structural integrity.
Water Management Capabilities
Green concrete incorporates recycled materials and reduces carbon footprint while offering moderate water permeability, making it suitable for sustainable driveway construction where some water runoff control is needed. Pervious concrete excels in water management by allowing rainwater to pass through its porous structure, effectively reducing surface runoff and promoting groundwater recharge. Driveways constructed with pervious concrete significantly mitigate flooding and improve drainage compared to traditional and green concrete options.
Installation and Maintenance
Green concrete installation for driveways requires specialized curing methods to optimize its eco-friendly additives, while pervious concrete demands precise subgrade preparation for effective water infiltration. Routine maintenance of green concrete involves standard sealing and crack monitoring to preserve its durability, whereas pervious concrete necessitates regular vacuuming or pressure washing to prevent clogging and maintain permeability. Both materials offer sustainable benefits, but pervious concrete's maintenance is more intensive due to its porous structure.
Cost and Lifespan Considerations
Green concrete typically incurs higher initial costs due to the use of recycled or eco-friendly materials, but it offers a longer lifespan with enhanced durability and resistance to environmental factors. Pervious concrete involves lower upfront expenses and promotes natural water drainage, yet it may require more frequent maintenance and has a shorter lifespan prone to clogging and wear. When choosing between the two for driveway applications, budget constraints and long-term performance expectations are critical in determining the most cost-effective and sustainable option.
Which Concrete is Best for Your Driveway?
Green concrete offers enhanced environmental benefits by incorporating recycled materials and reducing carbon emissions, making it an eco-friendly choice for driveways. Pervious concrete excels in managing stormwater runoff and preventing flooding by allowing water to infiltrate through its porous structure, ideal for areas with heavy rainfall. Choosing the best concrete depends on your priorities: sustainability and reduced carbon footprint favor green concrete, while superior drainage and water management highlight the advantages of pervious concrete for driveways.
Infographic: Green concrete vs Pervious concrete for Driveway
 azmater.com
azmater.com