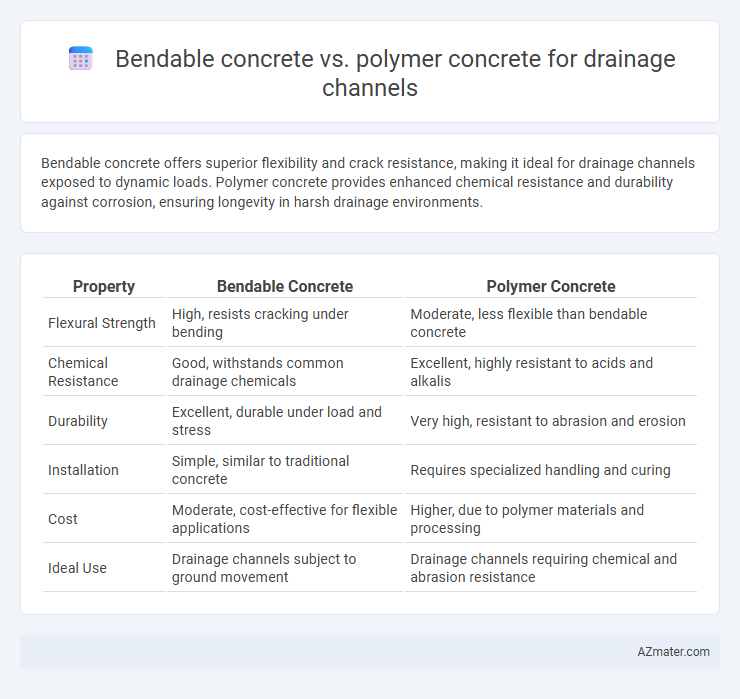
Bendable concrete offers superior flexibility and crack resistance, making it ideal for drainage channels exposed to dynamic loads. Polymer concrete provides enhanced chemical resistance and durability against corrosion, ensuring longevity in harsh drainage environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bendable Concrete | Polymer Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Flexural Strength | High, resists cracking under bending | Moderate, less flexible than bendable concrete |
| Chemical Resistance | Good, withstands common drainage chemicals | Excellent, highly resistant to acids and alkalis |
| Durability | Excellent, durable under load and stress | Very high, resistant to abrasion and erosion |
| Installation | Simple, similar to traditional concrete | Requires specialized handling and curing |
| Cost | Moderate, cost-effective for flexible applications | Higher, due to polymer materials and processing |
| Ideal Use | Drainage channels subject to ground movement | Drainage channels requiring chemical and abrasion resistance |
Introduction to Bendable Concrete and Polymer Concrete
Bendable concrete, also known as engineered cementitious composite (ECC), offers superior tensile strength and flexibility, making it ideal for drainage channels exposed to heavy loads and movements. Polymer concrete integrates polymers with aggregates to enhance chemical resistance and durability, providing long-lasting performance in harsh environments. Both materials improve drainage infrastructure by addressing different challenges: bendable concrete resists cracking due to bending stresses, while polymer concrete withstands corrosive substances and freeze-thaw cycles.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Bendable concrete offers high tensile strength and enhanced crack resistance due to its fiber reinforcement, making it ideal for drainage channels subjected to dynamic loads and ground movement. Polymer concrete exhibits excellent chemical resistance and low permeability, ensuring durability against aggressive water and chemicals commonly encountered in drainage environments. Both materials provide superior performance over traditional concrete, but bendable concrete excels in flexibility while polymer concrete is preferred for its robust chemical and moisture resistance.
Flexural Strength and Durability
Bendable concrete offers higher flexural strength compared to polymer concrete, making it more resistant to cracking under tensile stress in drainage channels. Polymer concrete excels in chemical durability and resistance to aggressive wastewater, but its lower flexural strength may limit performance under heavy load conditions. For drainage systems requiring both mechanical flexibility and long-term durability, bendable concrete provides superior resilience to deformation, while polymer concrete remains preferable in highly corrosive environments.
Installation Techniques and Ease
Bendable concrete offers superior installation flexibility for drainage channels due to its ability to withstand tensile stress and accommodate slight deformations without cracking, facilitating faster and less labor-intensive placement in complex alignments. Polymer concrete, while highly durable and chemically resistant, demands precise mixing and curing conditions, often requiring specialized equipment and skilled labor, which can extend installation time. The ease of bendable concrete installation reduces downtime and adaptation needs on-site, making it preferable for projects with irregular shapes or tight deadlines.
Waterproofing and Chemical Resistance
Bendable concrete offers superior waterproofing capabilities for drainage channels due to its enhanced tensile strength and crack resistance, preventing water infiltration and structural damage. Polymer concrete exhibits exceptional chemical resistance, making it highly effective against aggressive substances and corrosive effluents commonly found in drainage environments. Selecting between the two depends on prioritizing waterproofing performance with bendable concrete or maximizing chemical resistance with polymer concrete for long-term durability.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Bendable concrete offers superior crack resistance and flexibility, significantly reducing maintenance frequency for drainage channels compared to polymer concrete, which is more rigid and prone to brittle failure under stress. Polymer concrete provides excellent chemical resistance and durability in aggressive environments but may require more frequent inspections and repairs due to potential micro-cracking. Long-term performance favors bendable concrete for infrastructure subjected to dynamic loads, whereas polymer concrete suits chemically harsh conditions with moderate mechanical stress.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Lifecycle
Bendable concrete typically involves a higher initial cost due to the inclusion of fibers and specialized mix designs compared to polymer concrete, which uses resin binders and aggregates. Lifecycle costs of bendable concrete are often lower because of its superior crack resistance and reduced maintenance needs, while polymer concrete offers excellent chemical resistance but may require more frequent repairs under heavy load conditions. Evaluating total cost of ownership for drainage channels shows bendable concrete provides better long-term economic benefits through durability and lower maintenance frequency.
Suitability for Various Drainage Channel Applications
Bendable concrete offers enhanced flexibility and crack resistance, making it highly suitable for drainage channels subjected to ground movement or heavy traffic loads. Polymer concrete provides superior chemical resistance and durability, ideal for channels exposed to aggressive chemicals or harsh environmental conditions. Both materials excel in different drainage scenarios: bendable concrete is preferred for applications requiring structural resilience, while polymer concrete dominates settings needing robust chemical and abrasion resistance.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Bendable concrete offers enhanced sustainability for drainage channels due to its high tensile strength, reducing the need for frequent repairs and material replacements, thereby lowering carbon emissions over the product's lifecycle. Polymer concrete, while resistant to chemical corrosion and water infiltration, relies heavily on polymer resins derived from non-renewable petroleum sources, which can increase its environmental footprint. Choosing bendable concrete promotes longer-lasting infrastructure with reduced environmental impact by utilizing mineral-based materials and minimizing plastic content.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material
Bendable concrete offers superior flexibility and crack resistance, making it ideal for drainage channels subject to ground movement or thermal expansion. Polymer concrete provides excellent chemical resistance and rapid curing, which is advantageous in environments exposed to aggressive wastewater or harsh weather conditions. Selecting the right material depends on site-specific factors such as load demands, environmental conditions, and maintenance requirements to ensure long-term durability and performance.
Infographic: Bendable concrete vs Polymer concrete for Drainage channel
 azmater.com
azmater.com