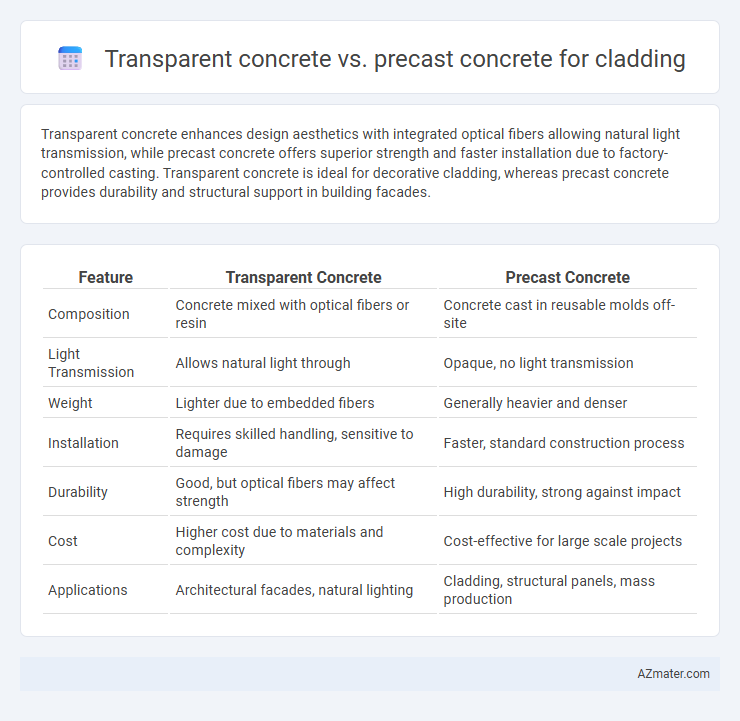
Transparent concrete enhances design aesthetics with integrated optical fibers allowing natural light transmission, while precast concrete offers superior strength and faster installation due to factory-controlled casting. Transparent concrete is ideal for decorative cladding, whereas precast concrete provides durability and structural support in building facades.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Transparent Concrete | Precast Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Concrete mixed with optical fibers or resin | Concrete cast in reusable molds off-site |
| Light Transmission | Allows natural light through | Opaque, no light transmission |
| Weight | Lighter due to embedded fibers | Generally heavier and denser |
| Installation | Requires skilled handling, sensitive to damage | Faster, standard construction process |
| Durability | Good, but optical fibers may affect strength | High durability, strong against impact |
| Cost | Higher cost due to materials and complexity | Cost-effective for large scale projects |
| Applications | Architectural facades, natural lighting | Cladding, structural panels, mass production |
Introduction to Cladding Solutions
Transparent concrete offers innovative cladding solutions by embedding optical fibers to allow light transmission while maintaining structural integrity, enhancing aesthetic appeal and natural lighting in building facades. Precast concrete cladding provides durability, weather resistance, and rapid installation through factory-made panels, ensuring consistent quality and cost-effectiveness. Both materials serve distinct architectural and functional purposes, with transparent concrete promoting light diffusion and precast concrete emphasizing strength and versatility.
What is Transparent Concrete?
Transparent concrete, also known as light-transmitting concrete, incorporates optical fibers or resin-based materials into a cement mixture, allowing light to pass through while maintaining structural strength. This innovative material enhances natural lighting and aesthetic appeal in architectural cladding applications, offering energy efficiency and modern design potential. Compared to traditional precast concrete cladding, transparent concrete provides unique translucency without compromising durability or load-bearing capacity.
What is Precast Concrete?
Precast concrete is a highly durable, factory-manufactured building material molded into specific shapes and sizes before being transported to the construction site for installation, offering consistent quality and faster construction times. Unlike transparent concrete, which incorporates optical fibers to allow light transmission, precast concrete provides robust structural support and versatility in cladding applications without light permeability. Its customization options enable architectural design flexibility, making precast concrete a preferred choice for exterior cladding in commercial and residential buildings.
Material Composition and Structure
Transparent concrete incorporates optical fibers embedded within a fine concrete matrix, enabling light transmission while maintaining structural integrity; its composition often includes a blend of Portland cement, fine aggregates, and translucent fibers arranged in specific patterns. Precast concrete cladding consists of a mixture of cement, coarse and fine aggregates, water, and additives, cast into molds and cured off-site to achieve uniform density and strength; its structure is solid and opaque, designed primarily for durability and load-bearing capacity. The key difference lies in transparent concrete's unique fiber integration for translucency versus precast concrete's conventional composite arrangement for structural robustness.
Aesthetic Potential and Design Flexibility
Transparent concrete offers unique aesthetic potential by integrating light-transmitting optical fibers, enabling innovative facade designs that create dynamic illumination effects and enhance visual appeal. Precast concrete provides extensive design flexibility through modular production, allowing for a variety of textures, colors, and shapes that ensure consistent quality and rapid installation. Both materials serve distinct architectural purposes, with transparent concrete excelling in light manipulation and precast concrete enabling versatile, scalable cladding solutions.
Light Transmission and Daylighting Benefits
Transparent concrete enhances daylighting in cladding applications by allowing up to 5% light transmission through embedded optical fibers, creating illuminated facades without compromising structural integrity. Precast concrete cladding offers durability and design flexibility but significantly limits natural light penetration due to its opaque nature. Optimizing building energy efficiency and interior lighting relies on selecting transparent concrete for improved daylight distribution and reducing artificial lighting dependency.
Structural Performance and Durability
Transparent concrete offers unique structural benefits by incorporating optical fibers that allow light transmission while maintaining comparable compressive strength to traditional concrete, ideal for innovative cladding designs. Precast concrete provides superior durability and uniform quality due to controlled factory conditions, enhancing resistance to weathering, corrosion, and impact, which is critical for long-term facade performance. Both materials deliver robust structural performance, but precast concrete is favored for longevity and maintenance ease, whereas transparent concrete emphasizes aesthetic appeal with moderate durability.
Installation Process and Maintenance
Transparent concrete, incorporating optical fibers, demands precise alignment and careful handling during installation to maintain its light-transmitting properties, often requiring specialized labor compared to traditional methods. Precast concrete cladding benefits from factory-controlled conditions, enabling faster onsite installation with modular panels that reduce construction time and complexity. Maintenance of transparent concrete involves regular cleaning to preserve clarity and occasional fiber inspection, while precast concrete requires routine sealing and checks for cracks or surface damage to ensure long-term durability.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Transparent concrete enhances energy efficiency by incorporating optical fibers, allowing natural light penetration that reduces daytime artificial lighting needs and lowers electricity consumption. Precast concrete offers sustainability benefits through controlled factory production, minimizing waste and enabling the use of recycled materials, which reduces the environmental impact of construction. Both materials contribute uniquely to green building goals, with transparent concrete optimizing daylight use and precast concrete supporting efficient resource management.
Cost Comparison and Practical Applications
Transparent concrete, featuring embedded optical fibers, typically incurs higher costs than precast concrete due to specialized materials and manufacturing processes. Precast concrete offers cost-efficiency benefits with standardized production, quicker installation, and lower labor costs, making it preferable for large-scale cladding projects. Practical applications of transparent concrete include aesthetic facades and innovative lighting solutions, while precast concrete excels in durability and structural versatility for commercial and residential cladding.
Infographic: Transparent concrete vs Precast concrete for Cladding
 azmater.com
azmater.com